动手学深度学习PyTorch版-文本情感分类
文本情感分类
读取数据
import collections
import os
import random
import time
from tqdm import tqdm
import torch
from torch import nn
import torchtext.vocab as Vocab
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torch.nn.functional as F
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
def read_imdb(folder='train', data_root="/home/kesci/input/IMDB2578/aclImdb_v1/aclImdb"):
data = []
for label in ['pos', 'neg']:
folder_name = os.path.join(data_root, folder, label)
for file in tqdm(os.listdir(folder_name)):
with open(os.path.join(folder_name, file), 'rb') as f:
review = f.read().decode('utf-8').replace('\n', '').lower()
data.append([review, 1 if label == 'pos' else 0])
random.shuffle(data)
return data
DATA_ROOT = "/home/kesci/input/IMDB2578/aclImdb_v1/"
data_root = os.path.join(DATA_ROOT, "aclImdb")
train_data, test_data = read_imdb('train', data_root), read_imdb('test', data_root)
# 打印训练数据中的前五个sample
for sample in train_data[:5]:
print(sample[1], '\t', sample[0][:50])
数据预处理
def get_tokenized_imdb(data):
'''
@params:
data: 数据的列表,列表中的每个元素为 [文本字符串,0/1标签] 二元组
@return: 切分词后的文本的列表,列表中的每个元素为切分后的词序列
'''
def tokenizer(text):
return [tok.lower() for tok in text.split(' ')]
return [tokenizer(review) for review, _ in data]
def get_vocab_imdb(data):
'''
@params:
data: 同上
@return: 数据集上的词典,Vocab 的实例(freqs, stoi, itos)
'''
tokenized_data = get_tokenized_imdb(data)
counter = collections.Counter([tk for st in tokenized_data for tk in st])
return Vocab.Vocab(counter, min_freq=5)
vocab = get_vocab_imdb(train_data)
print('# words in vocab:', len(vocab))
def preprocess_imdb(data, vocab):
'''
@params:
data: 同上,原始的读入数据
vocab: 训练集上生成的词典
@return:
features: 单词下标序列,形状为 (n, max_l) 的整数张量
labels: 情感标签,形状为 (n,) 的0/1整数张量
'''
max_l = 500 # 将每条评论通过截断或者补0,使得长度变成500
def pad(x):
return x[:max_l] if len(x) > max_l else x + [0] * (max_l - len(x))
tokenized_data = get_tokenized_imdb(data)
features = torch.tensor([pad([vocab.stoi[word] for word in words]) for words in tokenized_data])
labels = torch.tensor([score for _, score in data])
return features, labels
创建数据迭代器
train_set = Data.TensorDataset(*preprocess_imdb(train_data, vocab))
test_set = Data.TensorDataset(*preprocess_imdb(test_data, vocab))
# 上面的代码等价于下面的注释代码
# train_features, train_labels = preprocess_imdb(train_data, vocab)
# test_features, test_labels = preprocess_imdb(test_data, vocab)
# train_set = Data.TensorDataset(train_features, train_labels)
# test_set = Data.TensorDataset(test_features, test_labels)
# len(train_set) = features.shape[0] or labels.shape[0]
# train_set[index] = (features[index], labels[index])
batch_size = 64
train_iter = Data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_iter = Data.DataLoader(test_set, batch_size)
for X, y in train_iter:
print('X', X.shape, 'y', y.shape)
break
print('#batches:', len(train_iter))
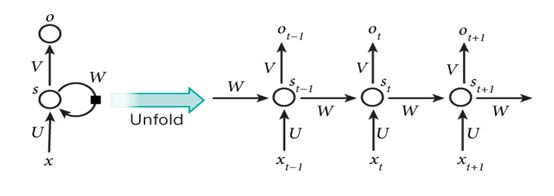
循环神经网络
class BiRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers):
'''
@params:
vocab: 在数据集上创建的词典,用于获取词典大小
embed_size: 嵌入维度大小
num_hiddens: 隐藏状态维度大小
num_layers: 隐藏层个数
'''
super(BiRNN, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(len(vocab), embed_size)
# encoder-decoder framework
# bidirectional设为True即得到双向循环神经网络
self.encoder = nn.LSTM(input_size=embed_size,
hidden_size=num_hiddens,
num_layers=num_layers,
bidirectional=True)
self.decoder = nn.Linear(4*num_hiddens, 2) # 初始时间步和最终时间步的隐藏状态作为全连接层输入
def forward(self, inputs):
'''
@params:
inputs: 词语下标序列,形状为 (batch_size, seq_len) 的整数张量
@return:
outs: 对文本情感的预测,形状为 (batch_size, 2) 的张量
'''
# 因为LSTM需要将序列长度(seq_len)作为第一维,所以需要将输入转置
embeddings = self.embedding(inputs.permute(1, 0)) # (seq_len, batch_size, d)
# rnn.LSTM 返回输出、隐藏状态和记忆单元,格式如 outputs, (h, c)
outputs, _ = self.encoder(embeddings) # (seq_len, batch_size, 2*h)
encoding = torch.cat((outputs[0], outputs[-1]), -1) # (batch_size, 4*h)
outs = self.decoder(encoding) # (batch_size, 2)
return outs
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers = 100, 100, 2
net = BiRNN(vocab, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers)
加载预训练词向量
cache_dir = "/home/kesci/input/GloVe6B5429"
glove_vocab = Vocab.GloVe(name='6B', dim=100, cache=cache_dir)
def load_pretrained_embedding(words, pretrained_vocab):
'''
@params:
words: 需要加载词向量的词语列表,以 itos (index to string) 的词典形式给出
pretrained_vocab: 预训练词向量
@return:
embed: 加载到的词向量
'''
embed = torch.zeros(len(words), pretrained_vocab.vectors[0].shape[0]) # 初始化为0
oov_count = 0 # out of vocabulary
for i, word in enumerate(words):
try:
idx = pretrained_vocab.stoi[word]
embed[i, :] = pretrained_vocab.vectors[idx]
except KeyError:
oov_count += 1
if oov_count > 0:
print("There are %d oov words." % oov_count)
return embed
net.embedding.weight.data.copy_(load_pretrained_embedding(vocab.itos, glove_vocab))
net.embedding.weight.requires_grad = False # 直接加载预训练好的, 所以不需要更新它
训练模型
def evaluate_accuracy(data_iter, net, device=None):
if device is None and isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
device = list(net.parameters())[0].device
acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval()
acc_sum += (net(X.to(device)).argmax(dim=1) == y.to(device)).float().sum().cpu().item()
net.train()
else:
if('is_training' in net.__code__.co_varnames):
acc_sum += (net(X, is_training=False).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
else:
acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
return acc_sum / n
def train(train_iter, test_iter, net, loss, optimizer, device, num_epochs):
net = net.to(device)
print("training on ", device)
batch_count = 0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n, start = 0.0, 0.0, 0, time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc, time.time() - start))
lr, num_epochs = 0.01, 5
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, net.parameters()), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
train(train_iter, test_iter, net, loss, optimizer, device, num_epochs)
评价模型
def predict_sentiment(net, vocab, sentence):
'''
@params:
net: 训练好的模型
vocab: 在该数据集上创建的词典,用于将给定的单词序转换为单词下标的序列,从而输入模型
sentence: 需要分析情感的文本,以单词序列的形式给出
@return: 预测的结果,positive 为正面情绪文本,negative 为负面情绪文本
'''
device = list(net.parameters())[0].device # 读取模型所在的环境
sentence = torch.tensor([vocab.stoi[word] for word in sentence], device=device)
label = torch.argmax(net(sentence.view((1, -1))), dim=1)
return 'positive' if label.item() == 1 else 'negative'
predict_sentiment(net, vocab, ['this', 'movie', 'is', 'so', 'great'])
卷积神经网络
def corr1d(X, K):
'''
@params:
X: 输入,形状为 (seq_len,) 的张量
K: 卷积核,形状为 (w,) 的张量
@return:
Y: 输出,形状为 (seq_len - w + 1,) 的张量
'''
w = K.shape[0] # 卷积窗口宽度
Y = torch.zeros((X.shape[0] - w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]): # 滑动窗口
Y[i] = (X[i: i + w] * K).sum()
return Y
X, K = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]), torch.tensor([1, 2])
print(corr1d(X, K))
def corr1d_multi_in(X, K):
# 首先沿着X和K的通道维遍历并计算一维互相关结果。然后将所有结果堆叠起来沿第0维累加
return torch.stack([corr1d(x, k) for x, k in zip(X, K)]).sum(dim=0)
# [corr1d(X[i], K[i]) for i in range(X.shape[0])]
X = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
K = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [-1, -3]])
print(corr1d_multi_in(X, K))
时序最大池化层
class GlobalMaxPool1d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GlobalMaxPool1d, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
'''
@params:
x: 输入,形状为 (batch_size, n_channels, seq_len) 的张量
@return: 时序最大池化后的结果,形状为 (batch_size, n_channels, 1) 的张量
'''
return F.max_pool1d(x, kernel_size=x.shape[2]) # kenerl_size=seq_len
TextCNN
class TextCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab, embed_size, kernel_sizes, num_channels):
'''
@params:
vocab: 在数据集上创建的词典,用于获取词典大小
embed_size: 嵌入维度大小
kernel_sizes: 卷积核大小列表
num_channels: 卷积通道数列表
'''
super(TextCNN, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(len(vocab), embed_size) # 参与训练的嵌入层
self.constant_embedding = nn.Embedding(len(vocab), embed_size) # 不参与训练的嵌入层
self.pool = GlobalMaxPool1d() # 时序最大池化层没有权重,所以可以共用一个实例
self.convs = nn.ModuleList() # 创建多个一维卷积层
for c, k in zip(num_channels, kernel_sizes):
self.convs.append(nn.Conv1d(in_channels = 2*embed_size,
out_channels = c,
kernel_size = k))
self.decoder = nn.Linear(sum(num_channels), 2)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5) # 丢弃层用于防止过拟合
def forward(self, inputs):
'''
@params:
inputs: 词语下标序列,形状为 (batch_size, seq_len) 的整数张量
@return:
outputs: 对文本情感的预测,形状为 (batch_size, 2) 的张量
'''
embeddings = torch.cat((
self.embedding(inputs),
self.constant_embedding(inputs)), dim=2) # (batch_size, seq_len, 2*embed_size)
# 根据一维卷积层要求的输入格式,需要将张量进行转置
embeddings = embeddings.permute(0, 2, 1) # (batch_size, 2*embed_size, seq_len)
encoding = torch.cat([
self.pool(F.relu(conv(embeddings))).squeeze(-1) for conv in self.convs], dim=1)
# encoding = []
# for conv in self.convs:
# out = conv(embeddings) # (batch_size, out_channels, seq_len-kernel_size+1)
# out = self.pool(F.relu(out)) # (batch_size, out_channels, 1)
# encoding.append(out.squeeze(-1)) # (batch_size, out_channels)
# encoding = torch.cat(encoding) # (batch_size, out_channels_sum)
# 应用丢弃法后使用全连接层得到输出
outputs = self.decoder(self.dropout(encoding))
return outputs
embed_size, kernel_sizes, nums_channels = 100, [3, 4, 5], [100, 100, 100]
net = TextCNN(vocab, embed_size, kernel_sizes, nums_channels)
训练并评价模型
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, net.parameters()), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
train(train_iter, test_iter, net, loss, optimizer, device, num_epochs)