SpringBoot参数校验
即使在前端对数据进行校验的情况下,我们还是要对传入后端的数据再进行一遍校验,避免用户绕过浏览器直接通过一些 HTTP 工具直接向后端请求一些违法数据。
一、环境搭建
1、依赖
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.6.RELEASE
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
2、实体类
import lombok.*;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private Integer id;
@NotNull(message = "classId不能为空")
private String classId;
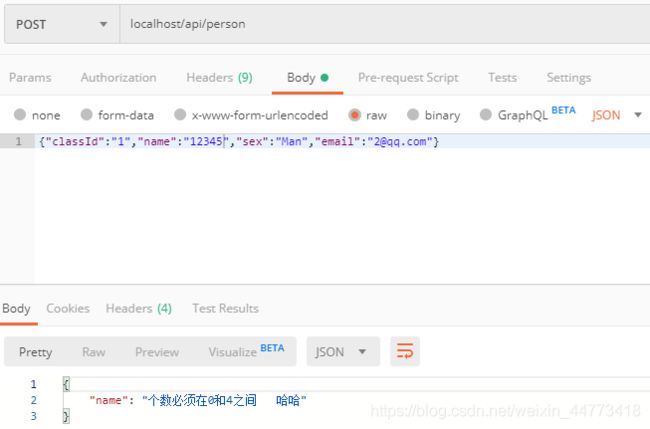
@Size(max = 4)
@NotNull(message = "name不能为空")
private String name;
/**
* 正则表达式说明:
* - ^string : 匹配以 string 开头的字符串
* - string$ :匹配以 string 结尾的字符串
* - ^string$ :精确匹配 string 字符串
* - ((^Man$|^Woman$|^UGM$)) : 值只能在 Man,Woman,UGM 这三个值中选择
*/
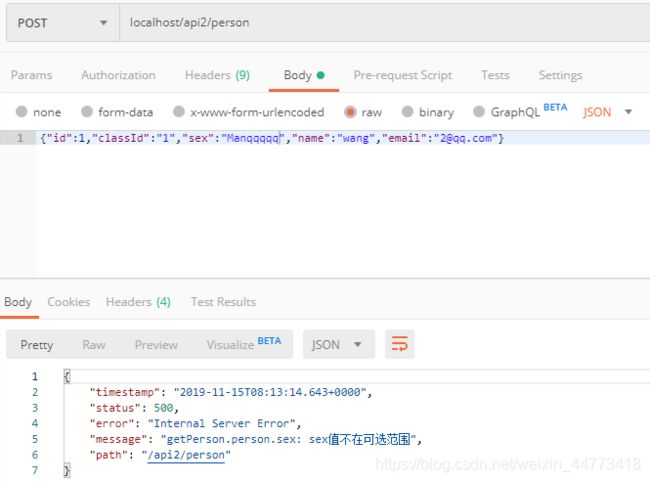
@Pattern(regexp = "((^Man$|^Woman$|^UGM$))",message = "sex值不在可选范围")
@NotNull(message = "sex不能为空")
private String sex;
@Email(message = "email格式不正确")
@NotNull(message = "email不能为空")
private String email;
}
2.1 JSR提供的校验注解:
@Null被注释的元素必须为 null@NotNull被注释的元素必须不为 null@AssertTrue被注释的元素必须为 true@AssertFalse被注释的元素必须为 false@Min(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值@Max(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值@DecimalMin(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值@DecimalMax(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值@Size(max=, min=)被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内@Digits (integer, fraction)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内@Past被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期@Future被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期@Pattern(regex=,flag=)被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
2.2 Hibernate Validator提供的校验注解:
@NotBlank(message =)验证字符串非null,且长度必须大于0@Email被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址@Length(min=,max=)被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内@NotEmpty被注释的字符串的必须非空@Range(min=,max=,message=)被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内
二、验证Controller的输入
1、验证请求体(RequestBody)
Controller:
我们在需要验证的参数上加上了@Valid注解,如果验证失败,它将抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException。默认情况下,Spring会将此异常转换为HTTP Status 400(错误请求)。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PersonController {
@PostMapping("/person")
public Person getPerson(@RequestBody @Valid Person person) {
return person;
}
}
ExceptionHandler:
自定义异常处理器可以帮助我们捕获异常,并进行一些简单的处理。
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity> handleValidationExceptions(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
HashMap errors = new HashMap<>();
ex.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().forEach((error) -> {
//字段名
String fieldName = ((FieldError) error).getField();
//错误信息
String errorMessage = error.getDefaultMessage();
errors.put(fieldName, errorMessage+" 哈哈");
});
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).body(errors);
}
}
使用postman测试
2、验证请求参数(Path Variables 和 Request Parameters)
Controller:
一定一定不要忘记在类上加上 @Validated 注解了,这个参数可以告诉 Spring 去校验方法参数。(验证请求体(RequestBody)不用在类上加@Validated)
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api1")
@Validated
public class PersonController1 {
@PostMapping("/person/{id}")
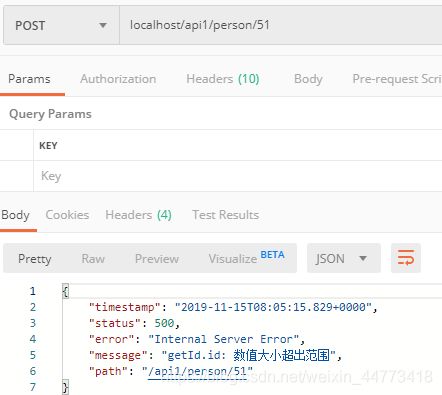
public String getId(@PathVariable @Valid @Max(value = 5, message = ("数值大小超出范围")) Integer id) {
return "id : " + id;
}
@PostMapping("/person/name")
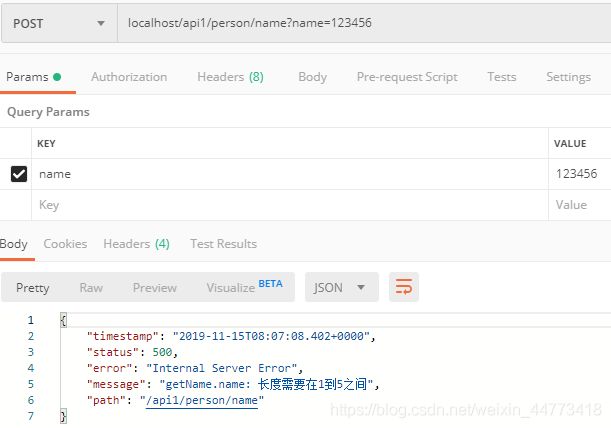
public String getName(@RequestParam @Valid @Size(min = 1, max = 5, message = ("长度需要在1到5之间")) String name) {
return "name : " + name;
}
}
2.1 id参数前加注解 @Max(value = 5, message = (“数值大小超出范围”)) 表示限制参数id的最大值为5
2.2 name参数前加注解 @Size(min = 1, max = 5, message = (“长度需要在1到5之间”)) 表示限制参数name的长度最小为1,最大为5
实体类Person中字段name上的 @Size(max = 4) 表示限制字段name的长度最大为4
实体类字段和方法参数中同时存在限制时,方法参数的优先级更高
三、验证 Service 中的方法
我们还可以验证任何Spring组件的输入,而不是验证控制器级别的输入,我们可以使用@Validated和@Valid注释的组合来实现这一需求。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api2")
public class PersonController2 {
@Autowired
private PersonService personService;
@PostMapping("/person")
public Person getPerson(@RequestBody Person person) {
return personService.getPerson(person);
}
}
@Service
@Validated
public class PersonService {
public Person getPerson(@Valid Person person){
return person;
}
}