C# winForm自定义弹出页面
在C#的windows窗体应用程序中,添加弹出框效果.最后就是这样的效果.
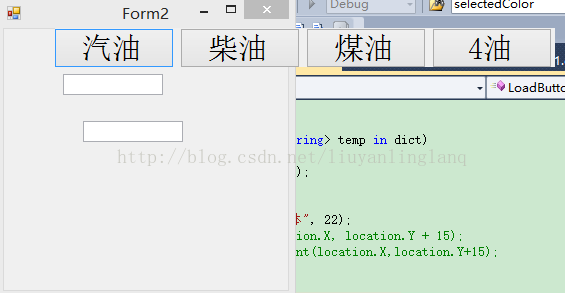
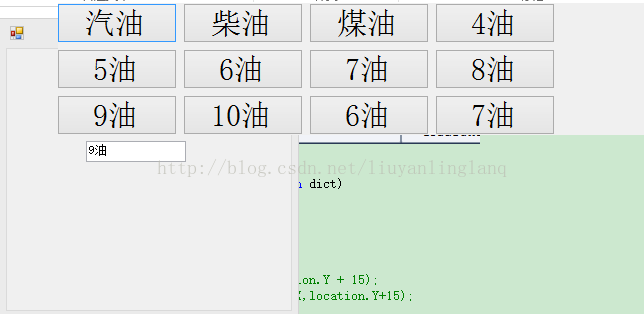
页面Form2上有2个文本框,textBox1和textBox2.点击任意一个文本框,根据准备好的数据,弹出Form1.其中Form1中的button个数是根据准备好的数据生成的.并且Form1的弹出位置,应该是文本框上面.最后,点击任意一个按钮,会将按钮上的值,显示到对应的文本框中,然后弹出页面关闭.
两个文本框显示的数据效果就是如下,这是textBox2.
这个是textBox1的效果.
主要做法就是,自定义了一个用户控件.由于此代码是在颜料板的基础上改过来的,所以起名不大对.这个用户控件的作用就是根据数据生成button数,并且给button绑定click事件,并且接收参数textBox.在click事件中,获取button的text,然后给之前的textBox的Text赋值button的text,然后textBox初始化.这样就可以在textBox上显示button按钮上的值.而生成的button是放在flowLayoutPanel1控件中,这样他就会自动的一个一个排列.
首先单独新建一个windows窗体应用程序,叫ColorHelper.然后在里面加自定义用户控件ColorSelector.整个项目完成之后的截图是这样的.
然后再ColorSelector中,拖一个flowLayoutpanel控件就是flowLayoutPanel1。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
using System.Data;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ColorHelper
{
///
/// 自定义颜色控件
///
public partial class ColorSelector : UserControl
{
//接收传递的参数,文本框和键值对的数据。
public Control textBox = new Control();
public Dictionary dict = new Dictionary();
public Dictionary Dict
{
get { return dict; }
set
{
dict = value;
}
}
//构造函数
public ColorSelector()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//选中的Text值
private string selectText;
public string SelectedText
{
get { return selectText; }
set
{
selectText = value;
}
}
//选中的Key值
private string selectKey;
public string SelectedKey
{
get { return selectKey; }
set
{
selectKey = value;
}
}
///
/// 生成Button
///
public void LoadButton()
{
//情况panel中原来的所有控件
flowLayoutPanel1.Controls.Clear();
//根据传递的dict键值对生成Button,并设置button的大小,Text,Tag值,以及绑定鼠标点击事件。
foreach (KeyValuePair temp in dict)
{
Button button1 = new Button();
button1.Text = temp.Value;
button1.Tag = temp.Key;
button1.Font = new Font("宋体", 22);
button1.AutoSize = true;
button1.Width = 120;
button1.MouseClick += new MouseEventHandler(button_MouseClick);
flowLayoutPanel1.Controls.Add(button1);
}
}
///
/// 绑定到button上的事件
///
///
///
private void button_MouseClick(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
//声明一个button,获取到button上的Text和Tag上的值,分别是value和key。
Button cb = (Button)sender;
selectText = cb.Text;
selectKey = cb.Tag.ToString();
//将value和key分别给textBox的Text和Tag。
textBox.Text = selectText;
textBox.Tag = selectKey;
//重绘textBox
textBox.Invalidate();
textBox.Enabled = true;
//隐藏控件,并将控件所在的Form关闭
this.Visible = false;
this.FindForm().Close();
}
}
} 然后自定义用户控件建立好了。可以再建立一个项目ColorTest,然后建立2个Form。其中Form1放这个控件,Form2放文本框,弹出Form1.
然后再ColorTest中添加引用,把colorHelper引用过来。
而添加到工具箱中,需要在工具箱中右击,选择选择项,然后浏览找到dll或者exe,就可以了。效果就是这样。
然后就能把这个Colorselector的自定义控件拖到Form1上。然后Form1的边框风格FormBorderStyle改为None,并且Form的AutoSize一定要是false。还有Form1的startPosition属性要改为Manual,自定义。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace colorTest
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
//接收textBox和dict数据
public TextBox textBox;
public Dictionary dict;
//有参构造函数,接收Form1传递的值
public Form1(TextBox textBox, Dictionary dict)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.textBox = textBox;
this.dict = dict;
}
//加载时将textBox和Dict给自定义控件,并生成button按钮,最后显示button框
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//设置重画控件
colorSelector1.textBox = textBox;
//返回到自定义用户控件上
colorSelector1.Dict = dict;
colorSelector1.LoadButton();
//设置弹出事件
colorSelector1.Visible = true;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace colorTest
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void textBox2_MouseClick(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
//先去查询数据,获取到返回值为实体数组,转成Dictionary
Dictionary dict = new Dictionary();
dict.Add("1", "汽油");
dict.Add("2", "柴油");
dict.Add("3", "煤油");
dict.Add("4", "4油");
Form1 form = new Form1(this.textBox2, dict);
form.Size = new Size(10, 10);
//MessageBox.Show(textBox2.Location.X + " " + textBox2.Height + " " + textBox2.Location.Y + " " + textBox2.Width + " ");
//form.Location = new Point(textBox2.Location.X + this.Location.X, this.Location.Y + textBox2.Location.Y - textBox2.Height);
//MessageBox.Show(textBox2.Location.X + " " + textBox2.Height+" "+ textBox2.Location.Y+" " +textBox2.Width+ " " );
//form.Location = new Point(textBox2.Location.X - textBox2.Height, textBox2.Location.Y - textBox2.Width);
//MessageBox.Show(this.Location.X + " " + this.Location.Y );
//每行显示5个button按钮
if (dict.Count >= 5)
{
//并且设置5个时,form的size,直接为626,这个是多次测试过得到的结果。
form.Size = new Size(626, 33 * (dict.Count / 5 + 1));
}
else
{
form.Size = new Size(125 * dict.Count, 33);
}
//form的弹出位置,必须要设置Form2的startposition为自定义,否则不管用。
//在窗体的x的基础上,加上textBox的x坐标,就能控制弹出框的x坐标,而窗体的y坐标加上窗体的y坐标,还要考虑form的height
form.Location = new Point(textBox2.Location.X + this.Location.X, this.Location.Y + textBox2.Location.Y - 15 * (dict.Count / 5 + 1));
//弹出form
form.ShowDialog();
}
///
/// textBox1的鼠标点击事件
///
///
///
private void textBox1_MouseClick(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
//先去查询数据,获取到返回值为实体数组,转成Dictionary
Dictionary dict = new Dictionary();
dict.Add("1", "汽油");
dict.Add("2", "柴油");
dict.Add("3", "煤油");
dict.Add("4", "4油");
dict.Add("5", "5油");
dict.Add("7", "6油");
dict.Add("8", "7油");
dict.Add("9", "8油");
dict.Add("10", "9油");
dict.Add("11", "10油");
dict.Add("12", "6油");
dict.Add("13", "7油");
dict.Add("14", "8油");
dict.Add("15", "9油");
dict.Add("16", "10油");
Form1 form = new Form1(this.textBox1, dict);
if (dict.Count >= 5)
{
form.Size = new Size(626, 33 * (dict.Count/5+1));
}
else
{
form.Size = new Size(125 * dict.Count, 33);
}
form.Location = new Point(textBox2.Location.X + this.Location.X, this.Location.Y + textBox2.Location.Y -15*(dict.Count/5+1));
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
}
以上就是弹出框的全部代码了。花了我不少时间,并且,学会了算x,y的值。发现所有的显示的location的值,都是相对值,相对于包含他们的容器。textBox是在form2中,他的location是相对于form2,而form2的location的相对于屏幕。
知道了改不来FlowLayoutpanel,每5个换一行,可以控制他的容器Form1,控制他的大小。所以里面的FlowLayoutpanel也不能设置autosize为true,不能自适应,否则他就一行显示了。