AbstractMap作为Map接口的骨干实现是一种怎样的存在?
AbstractMap类提供了Map接口的框架实现,以最小化实现此接口所需的工作量。
一、概述
要实现不可修改的map,程序员只需要扩展这个类并为entrySet方法提供一个实现,该方法返回映射的集合视图。通常,返回的集合将依次在AbstractSet之上实现。这个集合不应该支持add或remove方法,它的迭代器不应该支持remove方法。
要实现可修改的map,程序员必须另外重写该类的put方法(否则将抛出UnsupportedOperationException)。而由entrySet().iterator()返回的迭代器,必须另外实现其remove方法。
程序员通常应该按照Map接口规范中的建议,提供一个void(无参数)和map构造函数。
该类中每个非抽象方法的文档详细描述了其实现。如果正在实现的map允许更有效的实现,则可以覆盖这些方法。
二、结构
AbstractMap作为Map接口的骨干实现,设计上尽量降低实现具体Map的工作量。因此,一些通用的Map具体实现将由AbstractMap抽象类提供。
public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
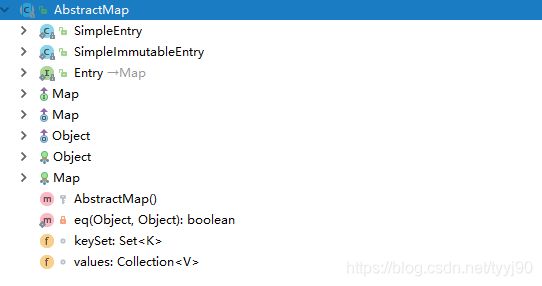
从结构图中不难看出,AbstractMap抽象类实现了Map接口。SimpleEntry和SimpleImmutableEntry实体类实现了Entry
public static class SimpleEntry<K,V>
implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable
public static class SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>
implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable
既然实现了Map接口,以下方法是其具体实现。另外则使用了Map接口的默认实现。
三、详细设计
3.1 SimpleEntry
该类是维护键和值的条目。可以使用setValue方法更改该值。该类简化了构建自定义map实现的过程。例如,可以方便地在方法Map.entrySet().toArray中返回SimpleEntry实例的数组。
该类同时实现了java.io.Serializable接口,可被序列化。它包含了两个private修饰的Field,可以看到key被final修饰,而value却没有。意味着key只要被初始化以后就不能更改,而value却可以。它的构造函数其一是通过形参传入key和value实现,其二是形参传入实现Entry接口的对象。
接着通过getKey()和getValue()获取相应的key和value值,既然value值是可以更改的,所以也提供了setValue方法。最后实现了方法equals、hashCode和toString。
/**
* An Entry maintaining a key and a value. The value may be
* changed using the setValue method. This class
* facilitates the process of building custom map
* implementations. For example, it may be convenient to return
* arrays of SimpleEntry instances in method
* Map.entrySet().toArray.
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static class SimpleEntry<K,V>
implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8499721149061103585L;
private final K key;
private V value;
/**
* Creates an entry representing a mapping from the specified
* key to the specified value.
*
* @param key the key represented by this entry
* @param value the value represented by this entry
*/
public SimpleEntry(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
/**
* Creates an entry representing the same mapping as the
* specified entry.
*
* @param entry the entry to copy
*/
public SimpleEntry(Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> entry) {
this.key = entry.getKey();
this.value = entry.getValue();
}
/**
* Returns the key corresponding to this entry.
*
* @return the key corresponding to this entry
*/
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
/**
* Returns the value corresponding to this entry.
*
* @return the value corresponding to this entry
*/
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
/**
* Replaces the value corresponding to this entry with the specified
* value.
*
* @param value new value to be stored in this entry
* @return the old value corresponding to the entry
*/
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Compares the specified object with this entry for equality.
* Returns {@code true} if the given object is also a map entry and
* the two entries represent the same mapping. More formally, two
* entries {@code e1} and {@code e2} represent the same mapping
* if
* (e1.getKey()==null ?
* e2.getKey()==null :
* e1.getKey().equals(e2.getKey()))
* &&
* (e1.getValue()==null ?
* e2.getValue()==null :
* e1.getValue().equals(e2.getValue()))
* This ensures that the {@code equals} method works properly across
* different implementations of the {@code Map.Entry} interface.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this map entry
* @return {@code true} if the specified object is equal to this map
* entry
* @see #hashCode
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
return eq(key, e.getKey()) && eq(value, e.getValue());
}
/**
* Returns the hash code value for this map entry. The hash code
* of a map entry {@code e} is defined to be:
* (e.getKey()==null ? 0 : e.getKey().hashCode()) ^
* (e.getValue()==null ? 0 : e.getValue().hashCode())
* This ensures that {@code e1.equals(e2)} implies that
* {@code e1.hashCode()==e2.hashCode()} for any two Entries
* {@code e1} and {@code e2}, as required by the general
* contract of {@link Object#hashCode}.
*
* @return the hash code value for this map entry
* @see #equals
*/
public int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
/**
* Returns a String representation of this map entry. This
* implementation returns the string representation of this
* entry's key followed by the equals character ("=")
* followed by the string representation of this entry's value.
*
* @return a String representation of this map entry
*/
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
3.2 SimpleImmutableEntry
该类维护不可变键和值的条目。这个类不支持方法setValue。这个类在返回键值映射的线程安全快照的方法中可能很方便。
仔细和SimpleEntry对比不难发现,Field中value也被final修饰,当在构造函数中初始化以后,就不能再修改了。当然调用setValue方法会抛出UnsupportedOperationException。
public static class SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>
implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7138329143949025153L;
private final K key;
private final V value;
/**
* Creates an entry representing a mapping from the specified
* key to the specified value.
*
* @param key the key represented by this entry
* @param value the value represented by this entry
*/
public SimpleImmutableEntry(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
/**
* Creates an entry representing the same mapping as the
* specified entry.
*
* @param entry the entry to copy
*/
public SimpleImmutableEntry(Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> entry) {
this.key = entry.getKey();
this.value = entry.getValue();
}
/**
* Returns the key corresponding to this entry.
*
* @return the key corresponding to this entry
*/
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
/**
* Returns the value corresponding to this entry.
*
* @return the value corresponding to this entry
*/
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
/**
* Replaces the value corresponding to this entry with the specified
* value (optional operation). This implementation simply throws
* UnsupportedOperationException, as this class implements
* an immutable map entry.
*
* @param value new value to be stored in this entry
* @return (Does not return)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException always
*/
public V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* Compares the specified object with this entry for equality.
* Returns {@code true} if the given object is also a map entry and
* the two entries represent the same mapping. More formally, two
* entries {@code e1} and {@code e2} represent the same mapping
* if
* (e1.getKey()==null ?
* e2.getKey()==null :
* e1.getKey().equals(e2.getKey()))
* &&
* (e1.getValue()==null ?
* e2.getValue()==null :
* e1.getValue().equals(e2.getValue()))
* This ensures that the {@code equals} method works properly across
* different implementations of the {@code Map.Entry} interface.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this map entry
* @return {@code true} if the specified object is equal to this map
* entry
* @see #hashCode
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
return eq(key, e.getKey()) && eq(value, e.getValue());
}
/**
* Returns the hash code value for this map entry. The hash code
* of a map entry {@code e} is defined to be:
* (e.getKey()==null ? 0 : e.getKey().hashCode()) ^
* (e.getValue()==null ? 0 : e.getValue().hashCode())
* This ensures that {@code e1.equals(e2)} implies that
* {@code e1.hashCode()==e2.hashCode()} for any two Entries
* {@code e1} and {@code e2}, as required by the general
* contract of {@link Object#hashCode}.
*
* @return the hash code value for this map entry
* @see #equals
*/
public int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
/**
* Returns a String representation of this map entry. This
* implementation returns the string representation of this
* entry's key followed by the equals character ("=")
* followed by the string representation of this entry's value.
*
* @return a String representation of this map entry
*/
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
3.3 实现Map接口的方法
3.3.1 size
此方法实现非常简单,调用entrySet()(待继承了AbstractMap的实现类实现)返回entry集合视图,然后返回其size。
public int size() {
return entrySet().size();
}
public abstract Set<Entry<K,V>> entrySet();
3.3.2 isEmpty
实际为判断size()是否为0,返回对应的布尔值。
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
3.3.3 containsValue
代码非常简单,通过value是否为null,分别通过两个分支while循环迭代,和value相等后直接返回true,如果不存在相等的value返回false。
不难看出这个方法平均查找花费的时间和键值对的个数成正比。
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (value==null) {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (e.getValue()==null)
return true;
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (value.equals(e.getValue()))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
3.3.4 containsKey
此方法实现和containsValue类似。
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (key==null) {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null)
return true;
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
3.3.5 get
这个方法通过key获取对应的value,同样分两种情况,一种key为null,另一种key非空。然后逐个迭代元素,查找到对应的key,返回其value。否则找不到返回null。
public V get(Object key) {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (key==null) {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null)
return e.getValue();
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
return e.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
3.3.6 put
这个实现总是抛出一个UnsupportedOperationException。所以实现类需要重写此方法。
public V put(K key, V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
3.3.7 remove
先遍历获取对应key的条目(correctEntry),如果correctEntry为null,就返回null。否者调用迭代器的remove方法删除对应条目,删除之前先获取其值,最后返回被删除的键值对对应的值。
public V remove(Object key) {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
Entry<K,V> correctEntry = null;
if (key==null) {
while (correctEntry==null && i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null)
correctEntry = e;
}
} else {
while (correctEntry==null && i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
correctEntry = e;
}
}
V oldValue = null;
if (correctEntry !=null) {
oldValue = correctEntry.getValue();
i.remove();
}
return oldValue;
}
3.3.8 putAll
通过for循环遍历Map,对每个Entry调用put方法实现。
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
3.3.9 clear
调用entrySet()获取集合视图,然后对集合进行clear。
public void clear() {
entrySet().clear();
}
3.3.10 keySet
这个方法返回key的集合,如果Field keySet为null没有初始化,先进行初始化。
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks = keySet;
if (ks == null) {
ks = new AbstractSet<K>() {
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new Iterator<K>() {
private Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
return i.hasNext();
}
public K next() {
return i.next().getKey();
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
}
};
}
public int size() {
return AbstractMap.this.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return AbstractMap.this.isEmpty();
}
public void clear() {
AbstractMap.this.clear();
}
public boolean contains(Object k) {
return AbstractMap.this.containsKey(k);
}
};
keySet = ks;
}
return ks;
}
3.3.11 values
这个方法返回value的集合,如果Field values为null没有初始化,先进行初始化。
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vals = values;
if (vals == null) {
vals = new AbstractCollection<V>() {
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return new Iterator<V>() {
private Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
return i.hasNext();
}
public V next() {
return i.next().getValue();
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
}
};
}
public int size() {
return AbstractMap.this.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return AbstractMap.this.isEmpty();
}
public void clear() {
AbstractMap.this.clear();
}
public boolean contains(Object v) {
return AbstractMap.this.containsValue(v);
}
};
values = vals;
}
return vals;
}
3.4 重写Object方法equals和hashCode
最后来看重写Object方法equals和hashCode。
3.4.1 equals
两个Map是否相等:
(1) 如果形参送入的对象Object o就是本对象,直接返回true;
(2) 如果Object o不是Map的子类,返回false;
(3) 不满足(1)和(2),则强制将Object o转化为Map,判断是否和本对象size相等,如果不相等直接返回false;
(4) 然后逐个对象去比较,只要发现存在不相等的元素,直接返回false。所有元素均相等,跳出while循环后,返回true。
不难看出,先从简单判断入手,如果满足条件则直接返回,如此可高效的实现返回。两个Map相等则是最苛刻的要求(所有元素均相等),所有条件都满足,不会return false,最后return true。
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o;
if (m.size() != size())
return false;
try {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
3.4.2 hashCode
作为Map骨干实现,哈希码为集合中每个元素哈希码的累加值。
public int hashCode() {
int h = 0;
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
h += i.next().hashCode();
return h;
}