初识MyBatis框架
前言:以下内容是我在学习MyBatis框架时候做的笔记总结,学习视频为b站尚硅谷官方MyBatis p1-p66。如有错误请指正,谢谢。
文章目录
- MyBatis
- 快速开始
- 接口式编程
- 全局配置文件
- properties 属性
- settings设置
- typeAliases 类型命名
- typeHandlers 类型处理器
- plugins 插件
- environments 环境
- environment 环境变量
- transactionManager 事务管理器
- dataSource 数据源
- databaseIdProvider 数据库厂商标识
- mappers 映射器
- 映射文件
- 增删改查
- insert获取主键自增值
- Mysql
- Oracle
- 参数处理
- 单个参数处理
- 多个参数处理
- #和$取值区别
- resultmap 自定义结果集映射
- association 联合查询
- 多表查询
- 动态Sql
- if 标签
- trim 标签
- choose 标签
- set 标签
- 内置参数
- bind 标签
- sql 标签
- 缓存机制
- 一级缓存
- 一级缓存失效情况
- 二级缓存
- 工作机制
- 开启二级缓存
- 缓存相关设置/属性
- 缓存原理图示
MyBatis
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生类型、接口和 Java 的 POJO为数据库中的记录。
快速开始
项目总览如下图(log4j.jar包能在控制台中打印出debug步骤)

mybatis-config.xml(全局配置文件)
配置数据库相关信息和将写好的sql映射文件注册到全局配置文件中。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lch" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 将我们写好的sql映射文件(EmployeeMapper.xml)一定要注册到全局配置文件(mybatis-config.xml)中 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
EmployeeMapper.xml
其中namespace为名称空间,id为唯一标识,resultType为返回值类型,#{id}为从传递过来的参数中取出id值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.EmployeeMapper">
<select id="selectEmp" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select id,last_name lastName,email,gender from tbl_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
Test.java
1)根据xml配置文件(全局配置文件)创建一个SqlSessionFactory对象。
2)使用sqlSession工厂,获取到sqlSession对象使用它来执行增删改查,一个sqlSession就是代表和数据库的一次会话,用完关闭。
3)使用sql的唯一标志id来告诉MyBatis执行哪个sql。sql都是保存在sql映射文件中的。
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 2、获取sqlSession实例,能直接执行已经映射的sql语句
// sql的唯一标识:statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
// 执行sql要用的参数:parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
Employee employee = openSession.selectOne(
"com.atguigu.mybatis.EmployeeMapper.selectEmp", 1);
System.out.println(employee);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
接口式编程
项目总览如下图,与快速开始不同的是多了一个dao层的接口。

EmployeeMappe接口
public interface EmployeeMapper {
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
}
EmployeeMapper.xml
该xml文件中与快速开始中不同之处在于namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper"指定为接口的全类名
并且在select标签中的id改成了接口中方法的名称getEmpById。
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
MyBatisTest.java
mapper接口没有实现类,但是mybatis会为这个接口生成一个代理对象(将接口和xml进行绑定)。
public class MyBatisTest {
public SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
return new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取接口的代理对象
try {
EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(mapper.getClass());
System.out.println(employee);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
}
全局配置文件
MyBatis 的配置文件包含了影响 MyBatis 行为甚深的设置(settings)和属性(properties)信息。
在与Spring进行整合后配置文件里的设置由IOC容器进行管理。

但是编写配置文件要遵守结构否则会出错,如下图:
![]()
其中配置文件中的dtd是方便编写XML文件时提示用的:
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
properties 属性
mybatis可以使用properties来引入外部properties配置文件的内容;resource为引入类路径下的资源。在引入资源后在property中的value用${}代替。如下图:
settings设置
MyBatis 中极为重要的调整设置,它们会改变MyBatis 的运行时行为。参数如下图:
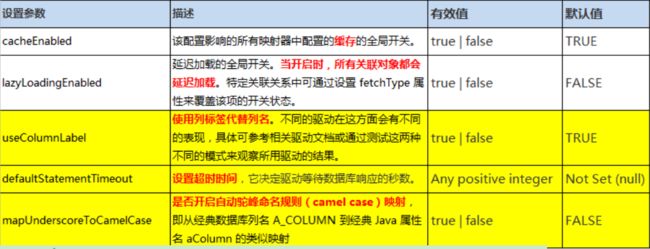
其中mapUnderscoreToCamelCase为驼峰命名规则。根据驼峰命名可以规则JavaBean对象中的lastName属性就是sql语句中搜索的last_name。
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
cacheEnabled缓存全局开关会在后面缓存机制中提到。
typeAliases 类型命名
MyBatis已经为许多常见的 Java 类型内建了相应的类型小写,默认别名就是类名消协。它们都是大小写不敏感的,在起别名的时候千万不要占用已有的别名。
<typeAliases>
<!--
alias:指定新的别名
-->
<typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" alias="emp"/>
<!--
package:为某个包下的所有类批量起别名
name:指定包名(为当前包以及下面所有的后代包的每一个类都起一个默认别名(类名小写))
批量起别名的情况下,使用@Alias注解为某个类型指定新的别名
-->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
typeHandlers 类型处理器
无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement)中设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时, 都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型。
plugins 插件
插件是MyBatis提供的一个非常强大的机制,可以通过插件来修改MyBatis的一些核心行为,常用的插件有:分页插件、执行分析插件等等。插件通过动态代理机制,可以介入并拦截四大对象的任何一个方法的执行:
• Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback,getTransaction, close, isClosed)
• ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
• ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
• StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
总体概括为:
- 拦截执行器的方法
- 拦截参数的处理
- 拦截结果集的处理
- 拦截Sql语法构建的处理
environments 环境
环境们,mybatis可以配置多种环境,default指定使用某种环境。可以达到快速切换环境(开发或测试)。
environment 环境变量
配置一个具体的环境信息;id代表当前环境的唯一标识。
transactionManager 事务管理器
type为事务管理器的类型:JDBC(JdbcTransactionFactory)|MANAGED(ManagedTransactionFactory);
当然也可以自定义事务管理器,实现TransactionFactory接口,type指定为全类名。
dataSource 数据源
数据源类型:UNPOOLED(UnpooledDataSourceFactory)
|POOLED(PooledDataSourceFactory)
|JNDI(JndiDataSourceFactory),
也可以自定义数据源:实现DataSourceFactory接口,type为全类名。
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
databaseIdProvider 数据库厂商标识
在写好数据库厂商标识后可在Mapper.java文件中的select标签中注入databaseId属性,告知Mybatis其中的数据库是哪个厂商的。
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<!-- 为不同的数据库厂商起别名 -->
<property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/>
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/>
</databaseIdProvider>
mappers 映射器
注册sql映射。
resource为引用类路径下的sql映射文件,如mybatis/mapper/EmployeeMapper.xml;
而url为引用网路路径或者磁盘路径下的sql映射文件,如file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml。
<mappers>
<!-- <mapper resource="mybatis/mapper/EmployeeMapper.xml"/> -->
<!-- <mapper class="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperAnnotation"/> -->
<!-- 批量注册: -->
<package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao"/>
</mappers>
映射文件
增删改查
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapper">
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="employee" >
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="addEmp" parameterType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender)
values(#{lastname},#{email},#{gender})
</insert>
<update id="updateEmp">
update tbl_employee
set last_name=#{lastname},email=#{email},gender=#{gender}
where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteEmpById">
delete from tbl_employee where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
insert获取主键自增值
mysql支持自增主键;而Oracle不支持自增,需要使用序列来模拟自增。
Mysql
useGeneratedKeys=“true”:使用自增主键获取主键策略。
keyProperty=“id”:指定对应的主键属性,也就是mybatis获取到主键值以后,将这个值封装给JavaBean对象的属性。
<insert id="addEmp" parameterType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender)
values(#{lastname},,#{email},#{gender})
</insert>
Oracle
keyProperty:查出的主键值封装给JavaBean的哪个属性。
order=“BEFORE”:当前sql在插入sql之前运行;
order=“AFTER”:当前sql在插入sql之后运行。
resultType:查出的数据的返回值类型。
<insert id="addEmp" databaseId="oracle">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="Integer">
<!-- 编写查询主键的sql语句 -->
<!-- BEFORE-->
select EMPLOYEES_SEQ.nextval from dual
<!-- AFTER
select EMPLOYEES_SEQ.currval from dual -->
</selectKey>
<!-- 插入时的主键是从序列中拿到的 -->
<!-- BEFORE-->
insert into employees(EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,EMAIL)
values(#{id},#{lastName},#{email<!-- ,jdbcType=NULL -->})
<!-- AFTER:sql语句插入成功之后再查询id的值
insert into employees(EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,EMAIL)
values(employees_seq.nextval,#{lastName},#{email}) -->
</insert>
参数处理
对于单个参数而言,mybatis不会做特殊处理。而对于多个参数而言,mybatis会将多个参数封装成一个map,key为param1…paramN,或者参数的索引也可以;而value则是传入的参数值,#{}就是从map中获取指定的key的值。
单个参数处理
#{参数名/任意名}:取出参数值。
多个参数处理
接口
public Employee getEmpByIdAndName(@Param("id")Integer id,@Param("lastname")String lastname);
xml文件
<select id="getEmpByIdAndName" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} and last_name = #{lastname}
</select>
#和$取值区别
#{}:是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到sql语句中,类似PreparedStatement防止sql注入。
${}:取出的值直接拼装在sql语句中;会有安全问题。
resultmap 自定义结果集映射
Mapper.xml
type:自定义规则的Java类型;id:唯一id方便引用。
id用来定义主键,底层会有优化。
column:指定哪一列;property:指定对应的javaBean属性。
<resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MySimpleEmp">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!-- 定义普通列封装规则 -->
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<!-- 其他不指定的列会自动封装:我们只要写resultMap就把全部的映射规则都写上。 -->
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- resultMap:自定义结果集映射规则; -->
<!-- public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); -->
<select id="getEmpById" resultMap="MySimpleEmp">
select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id}
</select>
association 联合查询
association可以指定联合的JavaBean对象。
property=“dept”:指定哪个属性是联合的对象,javaType:指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略]。
场景:查询Employee的同时查询员工对应的部门。
<resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastname"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
多表查询
场景:查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来。
Mapper.xml
<resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDept">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
<!--
collection定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则
properyu:为该对象在另一个对象中的属性名
ofType:指定集合里面元素的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<!-- 定义这个集合中元素的封装规则 -->
<id column="eid" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id); -->
<select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="MyDept">
SELECT d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name,
e.id eid,e.last_name last_name,e.email email,e.gender gender
FROM tbl_dept d
LEFT JOIN tbl_employee e
ON d.id=e.d_id
WHERE d.id=#{id}
</select>
动态Sql
MyBatis最强大的特性之一一直是它的动态SQL功能。MyBatis使用强大的基于OGNL的表达式来消除大部分其他表达式元素。
if 标签
当编写Mapper.xml文件时如果传递过来的其中一个参数为null值或者为空值的时候sql语句就会报错,为了避免这种情况发生就需要if标签。
<!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionIf(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="lastname!=null and lastname!=''">
and last_name like #{lastname}
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email !=''">
and email =#{email}
</if>
<if test="gender == 0 or gender == 1">
and gender=#{gender}
</if>
</where>
</select>
trim 标签
当sql语句中约束条件中多个and或者or之中有一个无法满足的时候,sql语句中就会多出来一个and或者or,where不能解决的时候就可以使用trim标签。
<select id="getEmpsByConditionTrim" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<!-- 后面多出的and或者or where标签不能解决
prefix="":前缀:trim标签体中是整个字符串拼串 后的结果。
prefix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个前缀
prefixOverrides="":
前缀覆盖: 去掉整个字符串前面多余的字符
suffix="":后缀
suffix给拼串后的整个字符串加一个后缀
suffixOverrides=""
后缀覆盖:去掉整个字符串后面多余的字符
-->
<!-- 自定义字符串的截取规则 -->
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id} and
</if>
<if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">
last_name like #{lastName} and
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=""">
email=#{email} and
</if>
<!-- ognl会进行字符串与数字的转换判断 "0"==0 -->
<if test="gender==0 or gender==1">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
choose 标签
在如下Mapper.xml文件中choose标签的用法:如果带了id就用id查,如果带了lastName就用lastName查,只会进入其中一个。
<!-- public List<Employee> getEmpsByConditionChoose(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsByConditionChoose" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select * from tbl_employee
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</when>
<when test="lastname!=null">
last_name like #{lastname}
</when>
<otherwise>
gender=0
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
set 标签
常规sql语句update中每个条件后都有一个逗号来隔开,set标签可以帮助无视逗号,否则sql语句会编译报错,用trim标签也可以达到相同效果。
<!--public void updateEmp(Employee employee); -->
<update id="updateEmp">
<!-- Set标签的使用 -->
update tbl_employee
<set>
<if test="lastName!=null">
last_name=#{lastName},
</if>
<if test="email!=null">
email=#{email},
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
<!-
Trim:更新拼串
update tbl_employee
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="lastName!=null">
last_name=#{lastName},
</if>
<if test="email!=null">
email=#{email},
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</trim>
where id=#{id} -->
</update>
内置参数
mybatis默认还有两个内置参数:
- _parameter:如果是单个参数则_parameter就是这个参数;如果是多个参数,_parameter就代表封装这些参数的map。
- _databaseId:如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签即代表当前数据库别名。
<!--public List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
select * from tbl_employee
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
select * from employees
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{_parameter.lastName}
</if>
</if>
</select>
bind 标签
可以将OGNL表达式的值绑定到一个变量中,方便后来引用这个变量的值。
模糊查询的Mapper.xml(其中用了内置参数来处理)
<!--public List<Employee> getEmpsTestInnerParameter(Employee employee); -->
<select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee">
<bind name="_lastName" value="'%'+lastName+'%'"/>
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
select * from tbl_employee
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
select * from employees
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{_parameter.lastName}
</if>
</if>
</select>
sql 标签
抽取可重用的sql片段,方便后面引用 。
<sql id="insertColumn">
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
employee_id,last_name,email
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
last_name,email,gender,d_id
</if>
</sql>
<include refid="insertColumn"></include>
缓存机制
MyBatis 包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。缓存可以极大的提升查询效率。默认定义了两级缓存。
- 默认情况下,只有一级缓存(SqlSession级别的缓存,也称为本地缓存)开启。
- 二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,它是基于namespace级别的缓存。
- 为了提高扩展性MyBatis定义了缓存接口Cache,也可以通过实现Cache接口来自定义二级缓存。
一级缓存
一级缓存是一直开启的;SqlSession级别的一个Map(查询到的数据先放在map之中,有的话就拿)。与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中,以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中拿,没必要再去查询数据库。
Test.java
@Test
public void testFirstLevelCache() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee emp01 = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(emp01);
Employee emp02 = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(emp02);
System.out.println(emp01==emp02);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
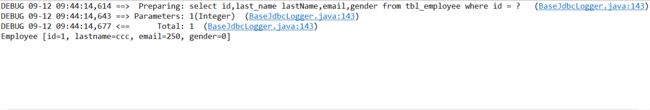
控制台输出:sql语句查询只出现了一次,并且两次get到的对象是相等的,说明对象在缓存之中。
一级缓存失效情况
- sqlSession不同。
- sqlSession相同,查询条件不同(当前一级缓存中还没有这个数据)。
- sqlSession相同,两次查询之间执行了增删改操作(这次增删改可能对当前数据有影响)。
- sqlSession相同,手动清除了一级缓存(缓存清空)即openSssion.clearCache()。
二级缓存
(全局缓存):基于namespace级别的缓存,一个namespace对应一个二级缓存。
工作机制
- 一个会话,查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中。
- 如果会话关闭,一级缓存中的数据会被保存到二级缓存中;新的会话查询信息,就可以参照二级缓存中的内容。
开启二级缓存
mybatis-config.xml
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
Mappe.xml
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache>
缓存相关设置/属性
- cacheEnabled=true:false:关闭缓存(二级缓存关闭)(一级缓存一直可用的)。
- 每个select标签都有useCache=“true”;false:不使用缓存(一级缓存依然使用,二级缓存不使用)。
- 每个增删改标签的:flushCache=“true”:(一级二级都会清除),增删改执行完成后就会清除缓存;缓存是没有被使用的。
- sqlSession.clearCache();只是清楚当前session的一级缓存。
- localCacheScope:本地缓存作用域(一级缓存SESSION);当前会话的所有数据保存在会话缓存中;属性:STATEMENT,可以禁用一级缓存。
缓存原理图示

结束语:其实关于MyBatis还是有很多尚未学完,如逆向工程,源码解析,单/多插件运行机制,四大对象工作原理,自定义TypeHandler、MyBatis存储过程&游标处理等。长路漫漫。