MyBatis3——初识
1. 写在前头
最近新做的一个项目《人力管道》,Dao层就是用的mybatis,因为是全新的项目,所以从头到尾都要自己写,没有外网,很难受的说,一些内容好久没写了,记忆不是很清晰,没以前写的那么得心应手了,趁着这几天有时间,将mybatis再温故一遍。
1.1 JDBC编程回顾
1.1.1 jdbc编程步骤
1. 加载驱动
2. 创建连接
3. 设置sql语句
4. 创建Statement
5. 设置参数
6. 执行查询,得到resultset
7. 遍历 resultset,输出结果
8. 释放资源
1.1.2 代码实现
public static void testJdbc(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 定义sql语句 ?表示占位符
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// 获取预处理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");
// 向数据库发出sql执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("id") + " " + resultSet.getString("username"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2. myBatis介绍
2.1 前言
MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis 。2013年11月迁移到Github。
Mybatis是面向sql的持久层框架,他封装了jdbc访问数据库的过程,我们开发,只需专注于sql语句本身的拼装,其它复杂的过程全部可以交给mybatis去完成。
mybatis要输出sql语句,但是其本身是不支持sql语句的输出的,那么mybatis是怎么输出sql的了,原来mybatis是借助于log4j来完成的。所以,我们在开发mybatis的时候,需要有log4j,就是这个原因。
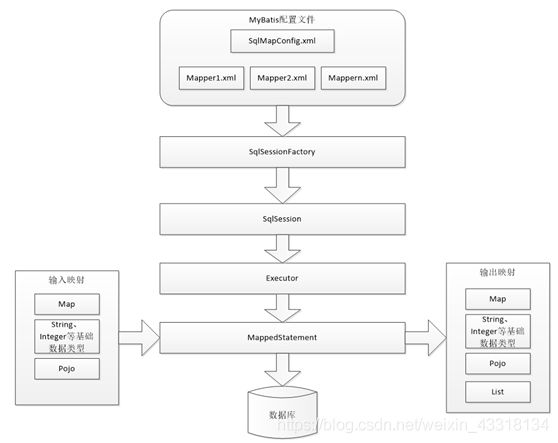
2.2 mybatis的体系架构图
2.3 谈谈你对mybatis的看法
mybatis是目前国内主流的两个持久层框架之一,它是面向sql的持久层框架,他封装了jdbc访问数据库的过程,让我们使用起来更加简单便捷。
mybatis的体系架构也很简单,它要操作数据库,跟所有的框架一样,需要有配置文件,mybatis有两种配置文件,一种是核心配置文件,我们一般命名为sqlMapConfig.xml,另一种是映射配置文件Mapper,其中主要写我们需要的sql语句,程序加载配置文件之后,会得到一个sessionFactory,然后通过该factory得到session会话,打开会话之后,可以有各种各样的api供我们操作,但是,根据源码,可以知道真正执行的不是sqlSession,而是一个接口调用,真正干活的是一个叫做executor的执行器,它会包装一个自己的MappedStatement来做输入输出映射,最后去访问数据库。
3. myBatis的核心配置文件介绍
文件名是任意的,但是我们一般习惯用SqlMapConfig.xml来命名。
3.1 configuration标签
为配置文件的根标签
3.2 environments标签
该标签用于定义环境,其有一个属性default,其属性值为environment标签的id属性值,表示使用哪个环境
3.2.1 environment标签
该标签为environments标签的子标签,表示具体的环境。与环境有关的配置都在该标签中配置,例如:事务管理、数据库连接池配置等。
注意:environment标签可以配置多个,即配置多套环境。通过改变environments的default属性值,来切换不同的开发环境
3.2.2 dataSource标签
该标签表示数据源,用于指定与数据库相关的配置。其属性type表示使用何种数据源,这里用的POOLED连接池。
3.2.3 transactionManager标签
表示事务管理标签,其属性type表示何种事务管理,这里使用的是JDBC事务管理
注意:mybatis与spring整合之后,environments配置将被移除掉
3.3 mappers标签
该标签用于表示映射文件的
3.3.1 mapper标签
该标签用于指定具体的映射文件路径,resource的属性值表示映射文件的路径,是基于classpath来查找的。
4. mybatis映射文件介绍
4.1 mapper标签
为映射文件的根标签,其属性namespace表示名称空间,其作用相当于java中的包,用于隔离sql语句的,属性值任意,最好是有意义的,不重复。
5. Mybatis查询数据库的操作步骤
映射文件:
5.1 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sb = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();5.2 得到session工厂对象
1. 先得到核心配置文件的输入流,通过mybatis提供的工具类获取
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");注意:字符串路径是基于classpath来查找的
2. 通过输入流创建session工厂类
SqlSessionFactory build = sb.build(inputStream);5.3 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession openSession = build.openSession();注意:SqlSession包含了执行sql的所有方法。
5.4 执行sql
User selectOne = openSession.selectOne("user.getUserById",1);注意:
1. 第一个参数表示sql id(名称空间.sqlId)
2. 第二个参数表示传入参数的参数,其数据类型对应映射文件中的parameterType
6. mybatis的两个参数指令
6.1 占位符#{}
6.2 字符串拼接指令${}
注意:
1. 如果parameterType为普通类型的话,那么字符串拼接指令必须用value表示。
2. 如果parameterType为pojo,那么字符串拼接指令写pojo的属性名即可
3. 因为是字符串拼接指令,所以,${}要用单引号括起来
7. mybatis的增删改查
7.1 查询
查询通常通过select标签来完成
7.2 添加
通常用insert标签
INSERT INTO USER
(`username`,
`birthday`,
`sex`,
`address`)
VALUES (#{username},
#{birthday},
#{sex},
#{address});
注意:保存操作需要提交事务
1. 自动提交事务
在openSession的时候,传入true
SqlSession openSession = build.openSession(true);2. 手动提交事务
openSession.commit();7.3 主键返回
7.3.1 插入的主键返回方式一:配置selectKey标签的形式
mysql方式:
select last_insert_id();
insert into user ... ...
注意:selectKey标签详解
1. keyProperty:组件属性
2. resultType:组件数据类型
3. order:指定selectKey何时执行
4. select last_insert_id(),查询,当insert执行成功之后,调用函数select last_insert_id(),将函数查询的值,交给resultType的pojo
7.3.2 插入的主键返回方式二:使用useGeneratedKeys与keyProperty
注意:
1. 在insert标签中,还有一个属性useGeneratedKeys,表示使用自增,默认为false
2. 在insert标签中,还有一个属性keyProperty,与useGeneratedKeys配套,表示接收组件的属性
7.4 返回UUID
配置:
select UUID()
INSERT INTO mybatis.user
(
username,
birthday,
sex,
address,
uuid2
)
VALUES
(
#{username},
#{birthday},
#{sex},
#{address},
#{uuid2}
);
测试代码:
public void testGetUserById() throws Exception{
// 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sb = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 得到核心配置文件的输入流 通过mybatis的工具类获取
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml"); // 字符串路径是基于classpath来查找的
// 通过输入流创建session工厂类
SqlSessionFactory build = sb.build(inputStream);
// 得到SqlSession对象,SqlSession对象包含了操作sql的所有方法
SqlSession openSession = build.openSession(true);
// 执行sql:第一个参数表示sql id(名称空间.sqlId),传入参数
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("mary1");
user.setSex("女");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setAddress("武汉");
openSession.insert("user.saveUser1",user); // user表示名称空间
System.out.println(user);
openSession.commit();
// 释放资源
openSession.close();
}我们发现,输出的user对象id为null了,这是为什么呢?是因为在mybatis中使用了selectKey的时候,主键返回useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" 配置将失效。
注意:
主键返回,useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"与selectKey都可以作为主键返回,配置一种即可。
7.5 修改
update user
set
username=#{username},
address=#{address}
where id=#{id}
7.6 删除
delete from user where id=#{id}
注意:
1. 在mybatis中,select、update、delete、insert标签都可以互用,但是为了规范,还是各司其职的好
2. 通过openSession操作数据库的时候,insert,update,select,delete,也可以互用。