基于Skip-Thought的Sentence2Vec神经网络实现
一、前言
1、Skip-Thought-Vector论文
2、本文假设读者已了解Skip-Gram-Vector和RNN相关基础,以下文章可做参考:
(1)RNN古诗词生成
(2)Skip-Gram-Vector
(3)LSTM/GRU门控机制
二、实战
1、数据处理
(1)网络小说《神墓》,基于版权原因,请自行寻找数据源
(2)先对特殊符号进行处理,将整本小说按行分割成一个列表
def _process_words(file_list):
words = ''.join(file_list)
vocab = sorted(set(words))
mask = vocab[:110]+vocab[-57:]
mark = ['!', ',', ':', ';', '?', '~', '…', '、', '。', '.', '?', ';', ':', '.', ',', '!']
for m in mask:
words = words.replace(m, '\\') if m in mark else words.replace(m, '')
return words其中f(w)代表该句子出现的概率,t为一个阈值。
def _process_sentence_list(sentence_list, t=1e-5, threshold=0.5):
sentence_count = Counter(sentence_list)
total_count = len(sentence_list)
# 计算句子频率
sentence_freqs = {w: c / total_count for w, c in sentence_count.items()}
# 计算被删除的概率
prob_drop = {w: 1 - np.sqrt(t / sentence_freqs[w]) for w in sentence_count}
# 剔除出现频率太高的句子
sentence_list = [w for w in sentence_list if prob_drop[w] < threshold]
return sentence_list(4)生成包含所有字的字典,添加特殊字符‘
def _get_vocab(self):
# 生成词字典
special_words = ['', '', '', '']
words = ''.join(self.sentence_list)
vocab = sorted(set(words))+special_words
word_to_int = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(vocab)}
int_to_word = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(vocab)}
return vocab, word_to_int, int_to_word (5)Skip-Thought-Vector借鉴了Skip-Gram-Vector的思想,这里选取窗口的大小都规定为1,所以其实是取句子的上一句及下一句
def _get_target(sentences, index, window_size=1):
# 获取句子相邻句子
start = index - window_size if (index - window_size) > 0 else 0
end = index + 2*window_size
targets = set(sentences[start:index] + sentences[index+1:end])
return list(targets)2、Skip-Thought-Vector
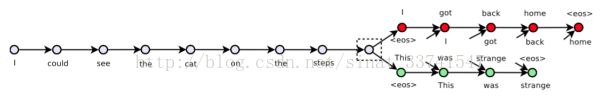
首先看Skip-Thought-Vector的示意图,
模型分为两个部分,encoder对句子进行encode,将final state传递到decoder,deocoder分别对当前句子的上一句及下一句进行decode。这是一个经典的encode-decode框架,原论文每个encoder、decoder使用了GRU-RNN,这里我们使用简单的LSTM来实现,两者的不同可参考前言提供链接。
3、模型输入定义
def build_inputs():
with tf.variable_scope('inputs'):
# 句子
encode = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name='encode')
encode_length = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, ], name='encode_length')
# 句子的前一句
decode_pre_x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name='decode_pre_x')
decode_pre_y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name='decode_pre_y')
decode_pre_length = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, ], name='decode_pre_length')
# 句子的后一句
decode_post_x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name='decode_post_x')
decode_post_y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name='decode_post_y')
decode_post_length = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, ], name='decode_post_length')
return encode, decode_pre_x, decode_pre_y, decode_post_x, decode_post_y, encode_length, decode_pre_length, decode_post_length4、对输入句子进行embedding
def build_word_embedding(self, encode, decode_pre_x, decode_post_x):
# embedding
with tf.variable_scope('embedding'):
embedding = tf.get_variable(name='embedding', shape=[len(self.vocab), self.embedding_dim],
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1))
encode_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, encode, name='encode_emb')
decode_pre_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, decode_pre_x, name='decode_pre_emb')
decode_post_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, decode_post_x, name='decode_post_emb')
return encode_emb, decode_pre_emb, decode_post_emb5、构建encoder
encoder对句子进行encode,得到最终的hidden state,这里采用了单层的LSTM网络,传递sequence_length作为掩码,去除padding的干扰,提高训练速度
def build_encoder(self, encode_emb, length, train=True):
batch_size = self.batch_size if train else 1
with tf.variable_scope('encoder'):
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=self.num_units)
initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32)
_, final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, encode_emb, initial_state=initial_state, sequence_length=length)
return initial_state, final_state需要分别建立两个decoder,代码是一样的,也采用了单层的LSTM网络,然后对输出进行一次全连接,得到logits,再进行softmax分类。需要注意这里w,b两个deocoder是共享的,得到预测输出
def build_decoder(self, decode_emb, length, state, scope='decoder', reuse=False):
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=self.num_units)
outputs, final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, decode_emb, initial_state=state, sequence_length=length)
x = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, self.num_units])
w, b = self.soft_max_variable(self.num_units, len(self.vocab), reuse=reuse)
logits = tf.matmul(x, w) + b
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits, name='predictions')
return logits, prediction, final_state这里用soft_max_entropy_with_logits进行交叉熵计算并进行softmax操作
def build_loss(self, logits, targets, scope='loss'):
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
y_one_hot = tf.one_hot(targets, len(self.vocab))
y_reshaped = tf.reshape(y_one_hot, [-1, len(self.vocab)])
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y_reshaped))
return loss加上梯度剪切防止梯度爆炸,进行最小化损失优化
def build_optimizer(self, loss, scope='optimizer'):
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
grad_clip = 5
# 使用clipping gradients
tvars = tf.trainable_variables()
grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(loss, tvars), grad_clip)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.learning_rate)
optimizer = train_op.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars))
return optimizerencoder-decoder模型中,encoder的initial state应该为上一个docoder的final state,这里用post deocoder的final state作为输入,进行训练,具体代码可以github上看到,这里就不贴了
10.生成结果
辰南与无尽星光闪耀
他的身体在刹那间变大
在刹那间他们感觉到了一股强大的窒息感
一声大喝
在这片区域后
他们似乎已经不是他的一个世界
这是一片奇异的世界
这里是葬天之所
他们知道这些人都知道
但是却没有人敢与我一战这里训练了25个循环,耗时5个小时,效果并不是特别好,增加训练循环次数或者将decoder的网络层数适量增加或许会有更好的效果
三、其他
具体代码可以在我的github上找到:https://github.com/lpty/tensorflow_tutorial