Java socket编程,模拟modbus协议收发温湿度数据
任务:socket编程,服务端模拟温湿度采集器,实现与客户端的通信。
知识点:
- socket编程(网络有实例,模仿实现)
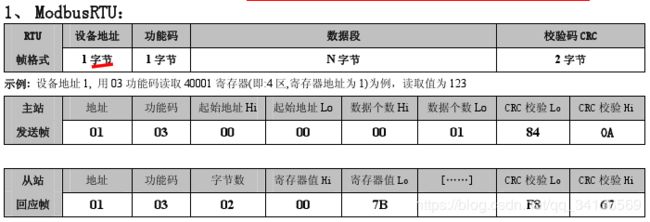
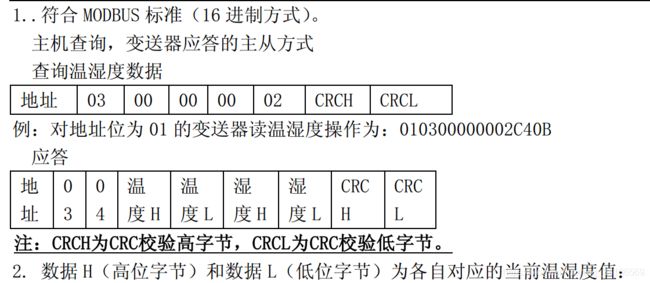
- modbus协议(仅用到ModbusRTU)
温湿度采集器
思路:
- 客户端写死数据,合并crc校验,发送到服务端。服务端截取校验位之前的数据通过crc校验与客户端发来的数据比较,如果相同,返回温湿度数据。
- 同样,写死数据,合并crc校验,发送到客户端。客户端截取校验位之前的数据通过crc校验与客户端发来的数据比较,如果相同,则计算并打印温湿度。
服务端
package hellosocket;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 服务端
*/
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CRC crc= new CRC();
// 监听指定的端口
int port = 55533;
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port);
// server将一直等待连接的到来
System.out.println("server开启...");
Socket socket = server.accept();
System.out.println("客户端:"+socket.getInetAddress().getLocalHost()+"已连接到服务器");
// 建立好连接后,从socket中获取输入流,并建立缓冲区进行读取
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.print(bytes[i]);
}
System.out.println();
//截取校验位之前的数据
byte[] a = new byte[12];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = bytes[i];
}
//截取校验位
byte[] check1 = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < check1.length; i++) {
check1[i]=bytes[12+i];
}
byte[] check2 = crc.getCRC(a).getBytes();
//如果客户端传过来的校验位和计算得到的校验位相等,则返回数据
if(Arrays.equals(check2, check1)){
byte[] rt = new byte[] {0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x03, 0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x13, 0x00, 0x05,0x00, 0x04, 0x00, 0x08 };
byte[] check_digit = crc.getCRC(rt).getBytes(); //校验数据
byte[] bb = new byte[18]; //组合校验位后的数组
//把原始数据和校验位组合到bb数组中
System.arraycopy(rt, 0, bb, 0, rt.length);
for (int i = 0; i < check_digit.length; i++) {
bb[14+i]=check_digit[i];
}
socket.getOutputStream().write(bb);
}
//inputStream.close();
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
CRC校验(此处来源,十分感谢https://www.cnblogs.com/lujiannt/p/9246256.html)
package hellosocket;
public class CRC {
/**
* CRC校验
* @param bytes 输入的字节数组
* @return
*/
public static String getCRC(byte[] bytes) {
// ModBus 通信协议的 CRC ( 冗余循环校验码含2个字节, 即 16 位二进制数。
// CRC 码由发送设备计算, 放置于所发送信息帧的尾部。
// 接收信息设备再重新计算所接收信息 (除 CRC 之外的部分)的 CRC,
// 比较计算得到的 CRC 是否与接收到CRC相符, 如果两者不相符, 则认为数据出错。
//
// 1) 预置 1 个 16 位的寄存器为十六进制FFFF(即全为 1) , 称此寄存器为 CRC寄存器。
// 2) 把第一个 8 位二进制数据 (通信信息帧的第一个字节) 与 16 位的 CRC寄存器的低 8 位相异或, 把结果放于 CRC寄存器。
// 3) 把 CRC 寄存器的内容右移一位( 朝低位)用 0 填补最高位, 并检查右移后的移出位。
// 4) 如果移出位为 0, 重复第 3 步 ( 再次右移一位); 如果移出位为 1, CRC 寄存器与多项式A001 ( 1010 0000 0000 0001) 进行异或。
// 5) 重复步骤 3 和步骤 4, 直到右移 8 次,这样整个8位数据全部进行了处理。
// 6) 重复步骤 2 到步骤 5, 进行通信信息帧下一个字节的处理。
// 7) 将该通信信息帧所有字节按上述步骤计算完成后,得到的16位CRC寄存器的高、低字节进行交换。
// 8) 最后得到的 CRC寄存器内容即为 CRC码。
int CRC = 0x0000ffff;
int POLYNOMIAL = 0x0000a001;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
CRC ^= (int) bytes[i];
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if ((CRC & 0x00000001) == 1) {
CRC >>= 1;
CRC ^= POLYNOMIAL;
} else {
CRC >>= 1;
}
}
}
//高低位转换,看情况使用(譬如本人这次对led彩屏的通讯开发就规定校验码高位在前低位在后,也就不需要转换高低位)
CRC = ( (CRC & 0x0000FF00) >> 8) | ( (CRC & 0x000000FF ) << 8);
return Integer.toHexString(CRC);
}
}
客户端
package hellosocket;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 客户端
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
CRC c = new CRC();
// 要连接的服务端IP地址和端口
String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 55533;
// 与服务端建立连接
Socket socket = new Socket(host, port);
// 建立连接后获得输出流
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[] { 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02 };
byte[] bb = new byte[16]; //组合校验位后的数组
byte[] check_digit = c.getCRC(b).getBytes();
//把原始数据和校验位组合到bb数组中
System.arraycopy(b, 0, bb, 0, b.length);
for (int i = 0; i < check_digit.length; i++) {
bb[12+i]=check_digit[i];
}
//写入请求数据
socket.getOutputStream().write(bb);
//获取服务端返回数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.print(bytes[i]);
}
System.out.println();
//截取校验位之前的数据
byte[] a = new byte[14]; //截取校验位之前的
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = bytes[i];
}
//截取校验位
byte[] check1 = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < check1.length; i++) {
check1[i]=bytes[14+i];
}
//计算校验码
byte[] check2 = c.getCRC(a).getBytes();
//如果传过来的校验位和计算得到的校验位相等,则计算并显示数据
if(Arrays.equals(check2, check1)){
int temperature = a[7]*10+a[9];
double humidity = (a[11]*10+a[13]);
System.out.println("温度:"+temperature+"度"+"\n湿度:"+humidity+"%");
}
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
socket.close();
}
/**
* byte数组转hex
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
public static String byteToHex(byte bytes){
String strHex = "";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
strHex = Integer.toHexString(bytes & 0xFF);
/*for (int n = 0; n < bytes.length; n++) {
strHex = Integer.toHexString(bytes[n] & 0xFF);
sb.append((strHex.length() == 1) ? "0" + strHex : strHex); // 每个字节由两个字符表示,位数不够,高位补0
}*/
sb.append((strHex.length() == 1) ? "0" + strHex : strHex);
return sb.toString().trim();
}
}
存在的问题:
- Java IO 不熟练
- crc校验返回的是十六进制的String,通过getBytes()函数转为byte[],byte[]中存的就是asc码,所以比较的就是asc码。解决的话会回来更新。
- 解决了,其实根本就是错的,本来的编码要求是modbusrtu,实际我写的组码是modbusasc
- 另外,百度了一下,getBytes函数返回的byte[]存的是asc码,有一个2018年的新人总结博文(https://blog.csdn.net/qian15116170940/article/details/80611335)
- 进制转换,位操作不熟练。
学习到的东西:
1.byte[] 数组比较
==,比较的是两个字节数组是否为同一个字节数组,不是比较两个字节数组的内容是否相同
equals,比较是两个字节数组是否为同一个字节数组
Arrays.equals(a,b)
2.数组拷贝 arrayCopy( arr1, 2, arr2, 5, 10);
意思是;将arr1数组里从索引为2的元素开始, 复制到数组arr2里的索引为5的位置, 复制的元素个数为10个