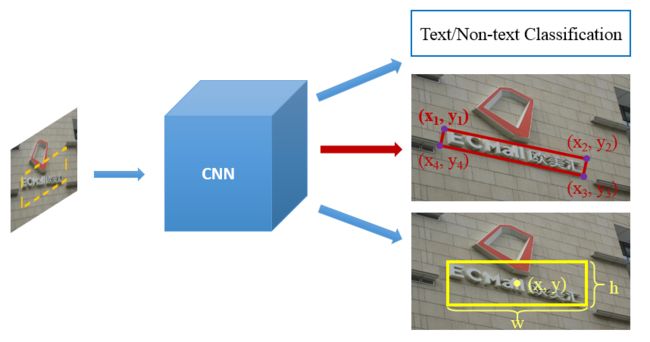
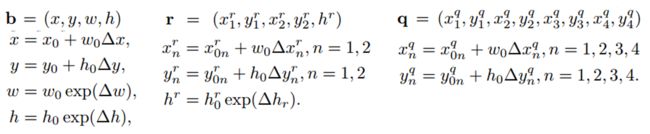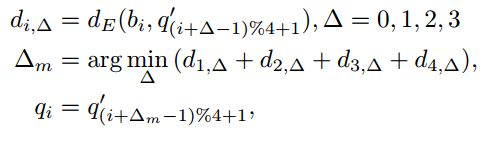XiangBai_TIP2018_TextBoxes++_A Single-Shot Oriented Scene Text Detector
作者和代码
Minghui Liao, Baoguang Shi, Xiang Bai, Senior Member, IEEE
caffe检测torch7识别代码
关键词
文字检测、多方向、SSD、四个点、one-stage、开源
方法亮点
- 把原本只能做水平的TextBoxes改为可以预测任意四边形的多方向文本检测
- 除了常规的分类、回归损失,还增加了四边形的最外接矩形的回归损失(增加监督信息量)
方法概述
本文方法是对TextBoxes(水平文字检测)进行改进,用于多方向文字检测。和SSD一样,该方法是one-stage的端到端模型,测试时只需运行网络+NMS即可得到检测结果(倾斜矩形或者任意四边形)。
方法主要改进点有:
第一,预测的目标从水平框的$(x, y, w, h)$ 变成了任意四边形$(x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3, x_4, y_4)$ 或 倾斜矩形$(x1, y1, x2, y2, h)$;
第二,回归损失除了增加oriented-text的位置regression loss,还增加了包含oriented-text的boundingBox(最小外接正矩形)的regression loss;
方法细节
网络结构
网络结构如下,VGG-16的前13层 + 10个额外卷积层 + 6个Text-box层 = 29层(和TextBoxes类似,FPN结构)
Fig. 2: The architecture of TextBoxes++, a 29-layer fully convolutional network including 13 layers from VGG-16 followed by 10 extra convolutional layers, and 6 Text-box layers connected to 6 intermediate convolutional layers. Each location of a text-box layer predicts an n dimensional vector for each default box consisting of the text presence scores (2 dimensions), horizontal bounding rectangles offsets (4 dimensions), and rotated rectangle bounding box offsets (5 dimensions) or quadrilateral bounding box offsets (8 dimensions). A non-maximum suppression is applied during test phase to merge the results of all 6 text-box layers. Note that “#c” stands for the number of channels.
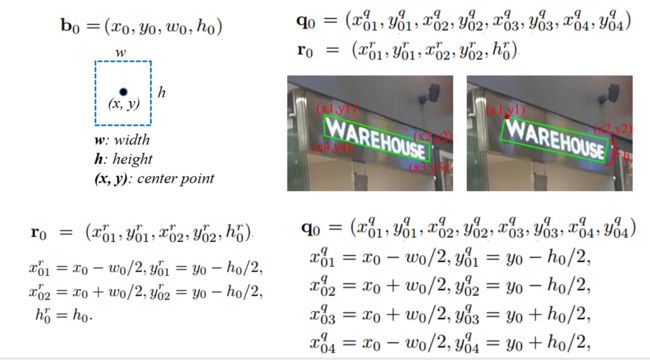
Default box
(实际是水平的default box,以下为方便可视化后面预测的 ${q}$ or ${r}$ 故配图使用倾斜框)
预测四边形和倾斜矩形
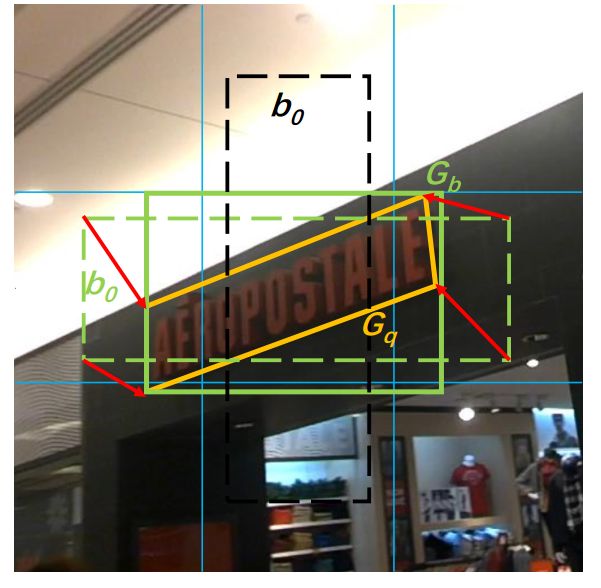
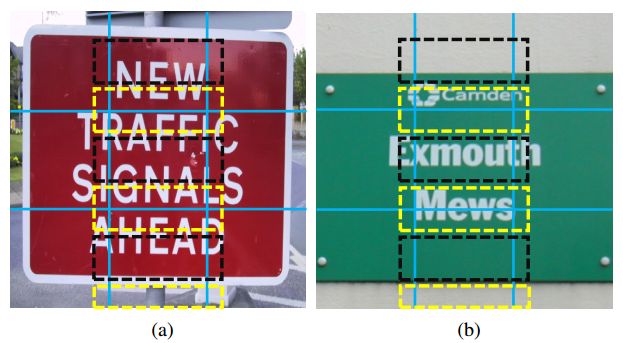
下图Fig.3中,黄色实线框为oriented bounding boxes ${q}$ or ${r}$ ,绿色实线框为minimum horizontal bounding rectangles ${b}$,绿色虚线框为对应match的default box。
Fig. 3: Illustration of the regression (red arrows) from a matched default box (green dashed) to a ground truth target quadrilateral (yellow) on a 3 × 3 grid. Note that the black dashed default box is not matched to the ground truth. The regression from the matched default box to the minimum horizontal rectangle (green solid) containing the ground truth quadrilateral is not shown for a better visualization.
predict的${b} $,{q}$ , ${r}$ 与default box的regression shift计算公式如下(下标为0表示是default box的相应值)
其他细节点
default box的aspect ratio从1,2,3,5,7 换成1,2,3,5,$\frac{1}{2}$,$\frac{1}{3}$,$\frac{1}{5}$
vertical offset和textBoxes一样(竖直的step更小,更dense一些而已)
Fig. 4: Vertical offsets of default boxes on a 3×3 grid. Black (resp. yellow) dashed bounding boxes are normal default boxes (resp. default boxes with vertical offsets). Note that only the default boxes of appropriate aspect ratio are shown for better visualization.
text-box layer的convolutional filter从$15$变成$35$
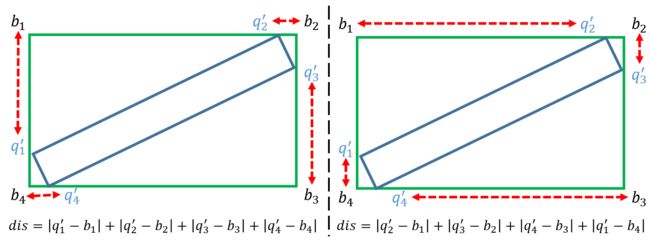
如何统一四边形的四个点的顺序?
简单说,首先算出四个点的最外接正矩形$G_b = (b_1, b_2, b_3, b_4)$, 正矩形有top-left点的概念(最左上角点)。然后依次算出$G_q = (q_1, q_2, q_3, q_4)$的四个点和$G_b$的四个点的欧氏距离(都按顺时针或者逆时针方式连接点),求出使得欧氏距离和最小的时对应的$G_q$的点顺序即为最终四个点的关系(此时,第一个点可以认为是top-left点)。如下图所示,左图比右图距离和更小,故采用左图的点顺序关系。
使用$(x, y, w, h, \theta)$还是$(x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, h)$?
使用$\theta$具有数据集的偏向性(某些数据集可能水平文字比较多,$\theta$普遍比较小,那么模型学出来的$\theta$也比较小),而采用$(x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, h)$方式则会避免该问题。
However, due to the bias of the dataset, there is usually an uneven distribution on θ, which may make the model dataset-dependent.
在data augmentation时,除了用Jaccard overlap作为crop的标准外(小目标仅用IOU会导致小目标可能占了全图比例过大?),增加object overlap标准来判断是否crop。->个人认为,其实是增加一个指标/参数,控制目标在整张图中的比例不至于过大。
Fig. 5: Data augmentation by random cropping based on Jaccard overlap (a-b) and object coverage constraints (c-d). Images in (b) and (d) are the corresponding resized crops.
训练的前期可以用小的scale,后期用大的scale,可以加速
NMS加速
先使用四边形的boundingBox来做NMS_bb(速度更快),阈值可取大如0.5。再在剩下的四边形做NMS_polygon,阈值可取小一些如0.2。
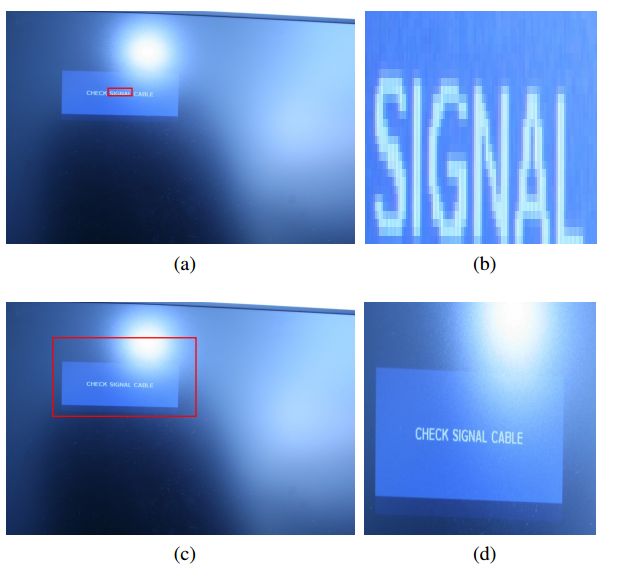
检测+识别的综合打分
$s_d = 0.6,s_r = 0.005$,使用指数更平滑,检测+识别取平均更好。
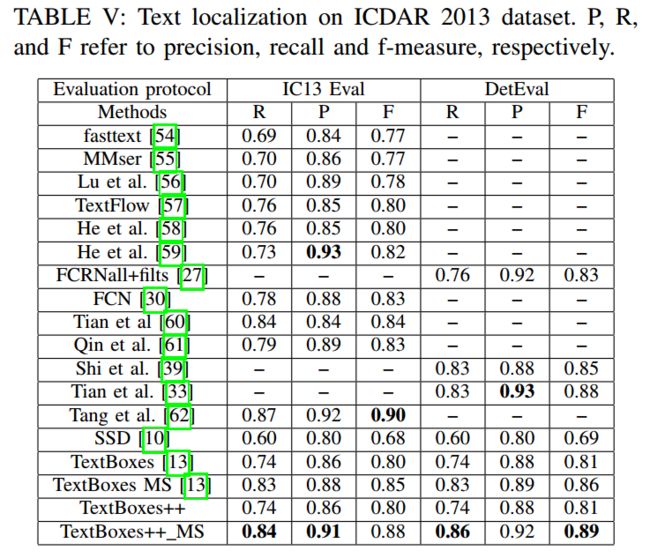
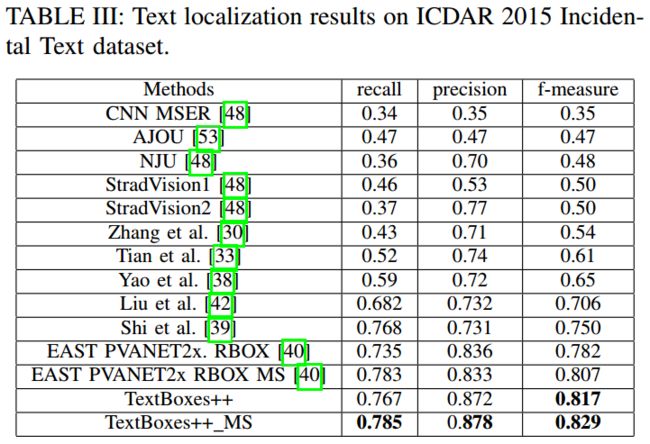
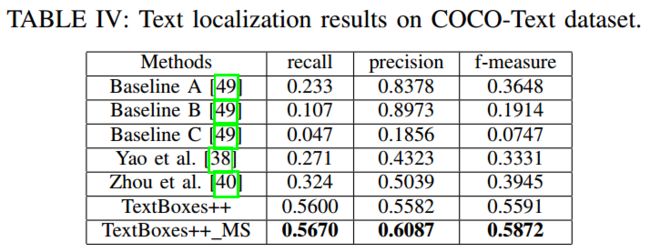
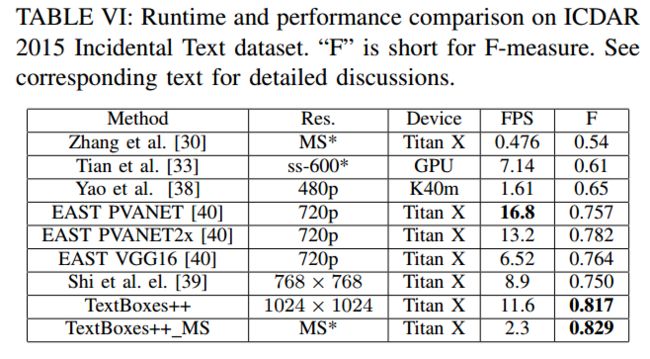
实验结果
- COCO-Text
- 速度
总结与收获
这篇和其他水平转倾斜方法进行改进的文章相比,细节介绍的比较有趣,增加boundingbox的regression loss思路也很直观(监督信息越多,效果应该是会越好)。