为什么要使用线程池?dubbo是如何扩展的?
为什么要使用线程池
多线程能够提高系统的并发性,充分利用服务的资源。但是,如果无限制的创建线程,反而会拖垮服务器的性能。一是创建线程是一个耗资源的操作,二是过多的线程会加剧线程上下文切换,竞争CPU。所以,会对线程使用池化的方案,重复的利用已经创建的线程。在Java中使用ThreadPoolExecutor定义线程池,其部分的源码如下:
/**
* ThreadPoolExecutor 初始化方法
*/
// ThreadPoolExecutor.class
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
} 属性介绍分别如下:
- corePoolSize,核心线程数。
- maximumPoolSize,最大线程数。
- workQueue,阻塞任务队列。
- threadFactory,线程工厂。
- handler,拒绝策略。
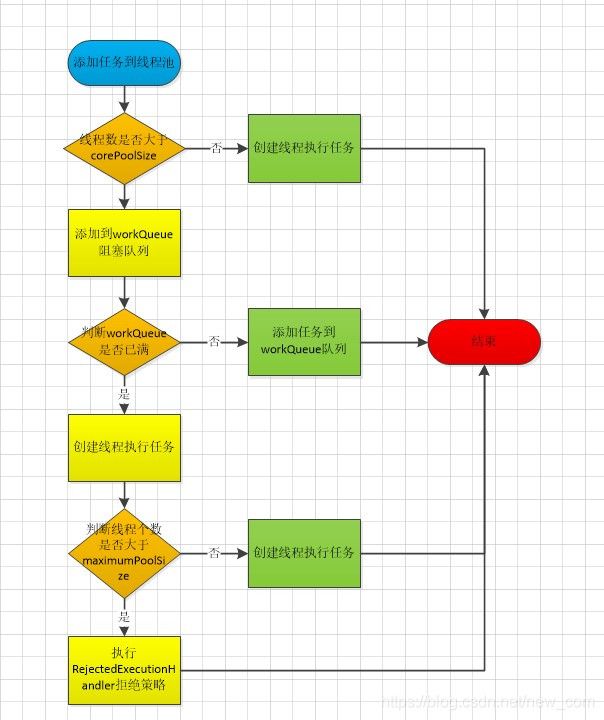
线程池执行任务的步骤如图:
- 当添加任务时,检测是否存在线程或者空闲线程,如果都没有线程则创建线程。
- 当继续添加任务时,如果都没有空闲线程,则继续创建,直到创建corePoolSize个核心线程数。
- 当继续添加任务时,创建的任务数大于corePoolSize个数时,就不会把未执行的任务加入workQueue阻塞队列排队,直到填满队列。此时,如果有线程执行完毕处于空闲状态,就从workQueue阻塞队列中获取任务执行。
- 当继续添加任务时,创建的任务个数大于满足2,并且workQueue阻塞队列已满,则继续创建新的线程,直到maximumPoolSize指定的最大线程数。
- 当继续添加任务时,创建任务的满足步骤4,并且创建的个数大于maximumPoolSize指定的最大线程数,这时,就会执行handler拒绝策略,拒绝执行新增的任务。
线程池执行任务的部分其源码如下:
/**
* 线程池执行任务
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor.class
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
// 创建的线程数小于corePoolSize核心线程数
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
// 添加新的任务到新的线程
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 添加任务到阻塞队列
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 创建线程到maximumPoolSize个数,如果继续创建失败则拒绝执行任务
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
/**
* 创建worker任务并绑定线程
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor.class
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
for (;;) {
// 已经创建的线程个数
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// 大于指定个数的线程设置个数(corePoolSize 或者maximumPoolSize)
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
// 修改执行线程的个数成功,则退出循环
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
// 创建Worker 任务,并创建新的线程
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (workerAdded) {
//执行任务
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
/**
* 创建Worker,设置任务,通过threadFactory创建线程
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor.class
Worker(Runnable firstTask) {
setState(-1); // inhibit interrupts until runWorker
this.firstTask = firstTask;
// 创建线程
this.thread = getThreadFactory().newThread(this);
}dubbo是如何扩展线程池
在dubbo的服务发布过程中,使用Netty的NioEventLoopGroup基于NIO的线程模式来监听连接客户端的各类事件。当监听到客户端的事件时,会使用线程池执行各类时间的任务。按照特性,dubbo扩展了4类线程池,分别如下:
- FixedThreadPool,固定线程数的线程池,核心线程(corePoolSize)与最大线程数(maximumPoolSize)相同,启动时建立线程,并且线程不会被回收。
- CachedThreadPool,可缓存corePoolSize个数的线程,当创建了更多的线程,在达到失效时间时会被回收。
- LimitedThreadPool,可缓存corePoolSize个数的线程,当创建的线程数小于maximumPoolSize个数的线程时,线程不会被回收。
- EagerThreadPool,当创建的任务超过corePoolSize个数的线程,会继续创建线程执行任务,直到maximumPoolSize个的线程。
其线程池的源码分别如下:
/**
* Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
*
* @see java.util.concurrent.Executors#newFixedThreadPool(int)
*/
public class FixedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
String name = url.getParameter(THREAD_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
int threads = url.getParameter(THREADS_KEY, DEFAULT_THREADS);
int queues = url.getParameter(QUEUES_KEY, DEFAULT_QUEUES);
// 核心线程(corePoolSize)与最大线程数(maximumPoolSize)相同,并且不会过期
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(threads, threads, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue() :
(queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}
}
/**
* This thread pool is self-tuned. Thread will be recycled after idle for one minute, and new thread will be created for
* the upcoming request.
*
* @see java.util.concurrent.Executors#newCachedThreadPool()
*/
public class CachedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
String name = url.getParameter(THREAD_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
int cores = url.getParameter(CORE_THREADS_KEY, DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
int threads = url.getParameter(THREADS_KEY, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
int queues = url.getParameter(QUEUES_KEY, DEFAULT_QUEUES);
int alive = url.getParameter(ALIVE_KEY, DEFAULT_ALIVE);
// 大于corePoolSize个数小于等于maximumPoolSize个数的线程,在空闲alive毫秒后会被回收
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(cores, threads, alive, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue() :
(queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}
}
/**
* Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed until limits reaches. This thread pool will not shrink
* automatically.
*/
public class LimitedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
String name = url.getParameter(THREAD_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
int cores = url.getParameter(CORE_THREADS_KEY, DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
int threads = url.getParameter(THREADS_KEY, DEFAULT_THREADS);
int queues = url.getParameter(QUEUES_KEY, DEFAULT_QUEUES);
// 创建指定的核心线程数和最大线程数,并且空闲线程不会被回收
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(cores, threads, Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue() :
(queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}
}
public class EagerThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
String name = url.getParameter(THREAD_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
int cores = url.getParameter(CORE_THREADS_KEY, DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
int threads = url.getParameter(THREADS_KEY, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
int queues = url.getParameter(QUEUES_KEY, DEFAULT_QUEUES);
int alive = url.getParameter(ALIVE_KEY, DEFAULT_ALIVE);
// init queue and executor
TaskQueue taskQueue = new TaskQueue(queues <= 0 ? 1 : queues);
// 自定义的EagerThreadPoolExecutor,会在刚大于cores个数的线程时,继续创建线程
EagerThreadPoolExecutor executor = new EagerThreadPoolExecutor(cores,
threads,
alive,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
taskQueue,
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true),
new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
taskQueue.setExecutor(executor);
return executor;
}
}
/**
* EagerThreadPoolExecutor执行任务的逻辑
*/
// EagerThreadPoolExecutor.class
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// do not increment in method beforeExecute!
submittedTaskCount.incrementAndGet();
try {
super.execute(command);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) {
// 队列已满,任务被拒绝后,继续从队列中获取任务
final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue) super.getQueue();
try {
// 重试从队列中获取任务失败,抛出RejectedExecutionException
if (!queue.retryOffer(command, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Queue capacity is full.", rx);
}
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(x);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// decrease any way
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
throw t;
}
}
/**
* EagerThreadPool 中使用的任务队列的添加任务(offer)方法
*/
//TaskQueue.class
@Override
public boolean offer(Runnable runnable) {
if (executor == null) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("The task queue does not have executor!");
}
int currentPoolThreadSize = executor.getPoolSize();
// have free worker. put task into queue to let the worker deal with task.
// 当有空闲线程时,添加任务到队列中,让线程继续执行
if (executor.getSubmittedTaskCount() < currentPoolThreadSize) {
return super.offer(runnable);
}
// return false to let executor create new worker.
// 当创建的线程大于corePoolSize核心线程数,并且小于maximumPoolSize最大线程数时,返回添加失败,让线程池继续创建新的线程执行
if (currentPoolThreadSize < executor.getMaximumPoolSize()) {
return false;
}
// currentPoolThreadSize >= max
// 当执行线程数大于maximumPoolSize最大线程数,则添加任务到队列
return super.offer(runnable);
}