MySQL数据库管理(数据库的查看方法、MySQL 库和表的创建和删除方法、MySQL 增删改查常见操作、MySQL 用户权限)
文章目录
- 一、 使用数据库
- 1.1 查看数据库结构
- 1.2 查看当前数据库中有哪些表
- 1.3 查看表的结构
- 1.4 SQL语句
- 二、 创建及删除数据库和表
- 2.1 创建新的数据库
- 2.2 创建新的表
- 2.3 删除一个数据表
- 2.4 删除一个数据库
- 三、 MySQL 增删改查常见操作
- 3.1 在表中插入数据
- 3.2 查询数据记录
- 3.3 将筛选的结果另存为一张表
- 3.4 修改数据库记录
- 3.5 MySQL密码破解
- **在配置文件中加入这条命令后,在数据库中不能创建新的用户。**
- 3.5.1 修改密码
- 3.6 删除数据记录
- **注意:如果不加where语句表示删除整个表,谨慎操作!!!**
- 四、 数据库表高级操作
- 4.1 清空表
- 4.2 临时表
- 4.3 克隆表
- 方法一:通过 LIKE 方式克隆表
- 方法二:通过创建表的方式克隆表
- 五、 数据库用户授权
- 5.1 授予权限
- 5.2 查看权限
一、 使用数据库
关于安装与进入数据库的命令在之前已经讲过,这一篇以数据库管理操作来演示。
1.1 查看数据库结构
MySQL 是一套数据库管理系统,在每台MySQL服务器中,均支持运行多个数据库,每个数据库相当于一个容器,其中存放着许多表。
查看当前服务器中的数据库 SHOW DATABASES 语句:用于查看当前 MySQL 服务器中包含的数据库,MySQL 的 每一条操作语句都是以分号“;”结束的。 经初始化后的MySQL服务器 , 默认建立四个数据库:test 、mysql 、information_schema 和 performance_schema(其中 mysql 是 MySQL 服务正常运行所需的数据库,其中包含了用户认证相关的表)。
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p ##使用root用户登录数据库
Enter password: ##输入密码
...
省略部分内容
mysql> show databases; ##查看数据库
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用
1.2 查看当前数据库中有哪些表
SHOW TABLES 语句:用于查看当前所在的数据库中包含的表。在操作之前,需要先使用 USE 语句切换到所使用的数据库。
mysql> use mysql; ##进入到mysql这个数据库中
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables; ##查看当前数据库中有哪些表
+---------------------------+
| Tables_in_mysql |
+---------------------------+
| columns_priv |
| db |
| engine_cost |
| event |
| func |
| general_log |
| gtid_executed |
| help_category |
| help_keyword |
| help_relation |
| help_topic |
| innodb_index_stats |
| innodb_table_stats |
| ndb_binlog_index |
| plugin |
| proc |
| procs_priv |
| proxies_priv |
| server_cost |
| servers |
| slave_master_info |
| slave_relay_log_info |
| slave_worker_info |
| slow_log |
| tables_priv |
| time_zone |
| time_zone_leap_second |
| time_zone_name |
| time_zone_transition |
| time_zone_transition_type |
| user |
+---------------------------+
31 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL 数据库的数据文件存放在/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql目录下,每个数据库对应一个子目录,用于存储数据表文件。每个数据表对应为三个文件,扩展名分别为“.frm”、“.MYD”和 “.MYI”。
-
“.frm”文件是与表相关的元数据(meta)信息都存放在“.frm”文件中,每一个表都会有一个以表名命名的“.frm”文件。
-
“.MYD”文件是 MyISAM 存储引擎专用,存放 MyISAM 表的数据。每一个 MyISAM 表都会有一个“.MYD”文件与之对应,同样存放于所属数据库的文件夹下。
-
“.MYI”文件也是专属于 MyISAM 存储引擎的,主要存放 MyISAM 表的索引相关信息。 对于 MyISAM 存储来说,可以被 cache 的内容主要就是来源于“.MYI”文件中。每一个 MyISAM 表对应一个“.MYI”文件。
-
“.ibd”和 ibdata 文件,这两种文件都是用来存放 Innodb 数据(包括索引)
1.3 查看表的结构
DESCRIBE 语句:用于显示表的结构,即组成表的各字段(列)的信息。需要指定“数据库名.表名”作为参数;若只指定表名参数,则需先通过 USE 语句切换到目标数据库。
mysql> describe user;
+------------------------+-----------------------------------+------+-----+-----------------------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------------------+-----------------------------------+------+-----+-----------------------+-------+
| Host | char(60) | NO | PRI | | |
| User | char(32) | NO | PRI | | |
| Select_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
...
省略部分内容
45 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.4 SQL语句
数据库目前标准的指令集是SQL。SQL是Structured Query Language的缩写,即结构化查询语言。它是1974年由 Boyce 和 Chamberlin 提出来的,1975~1979 年 IBM 公司 研制的关系数据库管理系统原型 System R 实现了这种语言。经过多年的发展,SQL 语言得到了广泛的应用。
SQL 语言主要由以下几部分组成。
- DDL(Data Definition Language,数据定义语言):用来建立数据库、数据库对象和 定义字段,如 CREATE、ALTER、DROP。
- DML(DataManipulationLanguage,数据操纵语言):用来插入、删除和修改数据库 中的数据,如 INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE。
- DQL(DataQueryLanguage,数据查询语言):用来查询数据库中的数据,如 SELECT。
- DCL(Data Control Language,数据控制语言):用来控制数据库组件的存取许可、 存取权限等,如 COMMIT、ROLLBACK、GRANT、REVOKE。
二、 创建及删除数据库和表
2.1 创建新的数据库
CREATEDATABASE 语句:用于创建一个新的数据库,需指定数据库名称作为参数。
mysql> create database home; ##新建一个数据库命名为home
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show databases; ##查看数据库
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| home |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use home; ##进入数据库home
Database changed
mysql> show tables; ##查看表
Empty set (0.00 sec) ##为空
2.2 创建新的表
mysql> use home;
Database changed
mysql> create table infom (id int(4) not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10) not null,score decimal(5,2),address varchar(50) default '未知');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
- int:数据类型为整型
- not null:非空
- primary key:主键,具有唯一性,类似于人的身份证号,一般一个表内要有一个,作为该字段的唯一标识。
- auto_increment:自动递增
- decimal(5,2):表示取值范围是 -999.99 到 999.99,
其中整数的位数必须小于等于(5-2),不然报错。小数的位数可以大于2位。多出2位时会做四舍五入,截取到5位。
以上均不包括小数点、符号的位数。数字的总长度是5位,保存后的小数位最多是2位。如果保存后是整数,小数位不会补0。 - varchar:数据类型为字符串类型,VARCHAR可以保存可变长度的字符串。
- default:表示使用默认参数
mysql> show tables; ##查看我们刚刚创建的表是否创建成功
+----------------+
| Tables_in_home |
+----------------+
| infom |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> describe infom; ##查看表结构
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(4) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
| score | decimal(5,2) | YES | | NULL | |
| address | varchar(50) | YES | | 未知 | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
2.3 删除一个数据表
DROPTABLE 语句:用于删除数据库中的表,需要指定“数据库名.表名”作为参数;若 只指定表名参数,则需先通过执行“USE”语句切换到目标数据库。
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_home |
+----------------+
| infom |
| tmp |
+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop table tmp;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_home |
+----------------+
| infom |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.4 删除一个数据库
DROPDATABASE 语句:用于删除指定的数据库,需要指定数据库名作为参数
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| home |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| school |
| sys |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> drop database school;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| home |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
三、 MySQL 增删改查常见操作
3.1 在表中插入数据
mysql> insert into infom (id,name,score,address) values (1,'老大',99,'nanjing'); ##在表中添加第一个数据
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from infom;
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into infom values (2,'老二',88,'beijing'); ##添加第二条数据,如果不写表结构,就默认是所有的表结构,按顺序依次进行插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from infom;
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | 老二 | 88.00 | beijing |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
验证自动递增功能
mysql> insert into infom (name,score,address) values ('老三',77,'guiyang'); ##插入第三条数据,不写入id选项的数据
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from infom; ##数据成功存入
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | 老二 | 88.00 | beijing |
| 3 | 老三 | 77.00 | guiyang |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.2 查询数据记录
SELECT 语句:用于从指定的表中查找符合条件的数据记录。MySQL数据库支持标准的SQL查询语句。
也可以使用WHERE进行条件查询
mysql> select * from infom where score > 80; ##将表中score选项中大于80的筛选出来
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | 老二 | 88.00 | beijing |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from infom where name = '老大' ; ##将表中name选项中’老大‘的记录输出
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3.3 将筛选的结果另存为一张表
mysql> create table tmp as select * from infom where score > 80; ##将score选项中大于80的记录筛选出来存在新建的tmp表中
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_home |
+----------------+
| infom |
| tmp |
+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from tmp;
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | 老二 | 88.00 | beijing |
+----+--------+-------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.4 修改数据库记录
UPDATE 语句:用于修改、更新表中的数据记录.
UPDATE 语句格式
UPDATE 表名 SET 字段名1=字段值1[,字段名2=字段值 2] WHERE 条件表达式
mysql> update infom set name='dogzhen' where score=88; ##将score=88的,name改为dogzhen
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from infom; ##查看表中记录
+----+---------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+---------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | dogzhen | 88.00 | beijing |
| 3 | 老三 | 77.00 | guiyang |
+----+---------+-------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.5 MySQL密码破解
mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
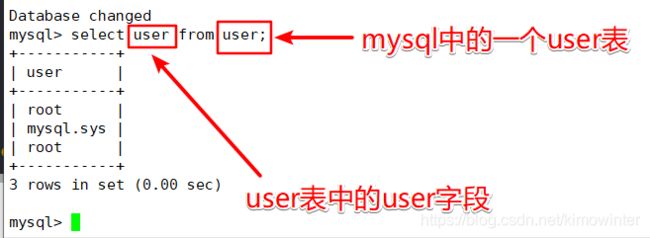
mysql> select user from user; ##查看可以登录数据库的用户
+-----------+
| user |
+-----------+
| root |
| mysql.sys |
| root |
+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
在配置文件中加入这条命令后,在数据库中不能创建新的用户。
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'tom'@'localhost' identified by 'abc123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit; ##退出数据库
Bye
如果我们使用tom用户登录数据库忘记了密码,可以通过修改配置文件来进行登录。
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u tom -p ##模拟忘记密码报错
Enter password:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'tom'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
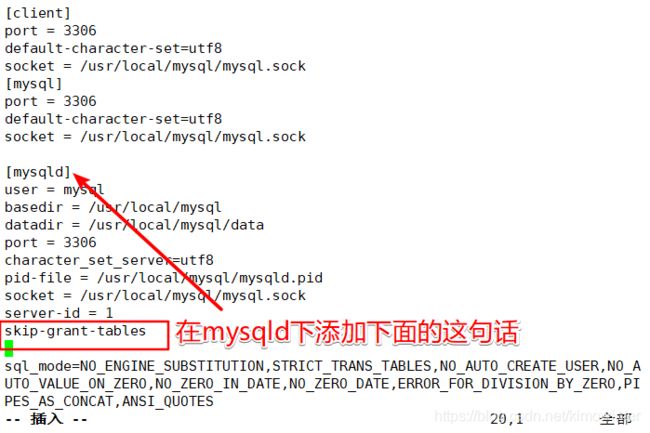
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf
skip-grant-tables ##跳过密码验证
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart mysqld
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u tom -p ##用tom登录数据库
Enter password: ##没有密码,直接回车
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
3.5.1 修改密码
mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from user; ##用户的信息在mysql库中的user表中
mysql> update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='tom'; ##重新设置tom的密码
Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 1
mysql> flush privileges; ##刷新数据库
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
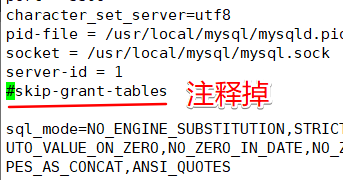
然后在配置文件中开启密码验证
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart mysqld
用密码’123456‘登陆成功
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u tom -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
3.6 删除数据记录
DELETE 语句:用于删除表中指定的数据记录
DELETE FROM 表名 WHERE 条件表达式
注意:如果不加where语句表示删除整个表,谨慎操作!!!
```handlebars
mysql> show databases; ##查看数据库
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| home |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| school |
| sys |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> use school; ##进入新建的数据库
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables; ##查看创建的表
+------------------+
| Tables_in_school |
+------------------+
| infom |
+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from infom; ##查看表中的数据
+----+----------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+----------+-------+---------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 99.00 | nj |
| 3 | lisi | 99.00 | nj |
| 5 | wangwu | 99.00 | nj |
| 6 | 666 | 99.00 | nj |
| 8 | 777 | 99.00 | nj |
+----+----------+-------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
删除表中name是’666‘的记录
mysql> delete from school.infom where name='666'; ##school.infom表示是数据库school中的infom表
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from infom;
+----+----------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+----------+-------+---------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 99.00 | nj |
| 3 | lisi | 99.00 | nj |
| 5 | wangwu | 99.00 | nj |
| 8 | 777 | 99.00 | nj |
+----+----------+-------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
四、 数据库表高级操作
包括清空表、使用临时表和克隆表。
4.1 清空表
清空一个数据表就是删除这个表内的所有数据,除了 DELETE FROM 语句,可以删除表内的数据,除此之外还可以使用 TRUNCATE TABLE 语句实现清 空表内记录。
与DROP语句相比,TRUNCATE TABLE 语句是删除表中所有记录数据,表的数据结构仍然存在;而DROP语句则是删除整张表。
mysql> use home; ##进入home数据库
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables ##查看数据库中的表
-> ;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_home |
+----------------+
| infom |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table hello like infom; ##创建一个新的表hello,结构像infom表一样
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> select * from hello; ##查看hello表内容
Empty set (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into hello select * from infom; ##将infom表中的内容插入到hello表中
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from hello;
+----+---------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+---------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | dogzhen | 88.00 | beijing |
| 3 | 老三 | 77.00 | guiyang |
+----+---------+-------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> truncate table hello; ##清空表内容
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) ##这里没有显示被清空表的具体条目
mysql> select * from hello;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> describe hello; ##查看表结构
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(4) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
| score | decimal(5,2) | YES | | NULL | |
| address | varchar(50) | YES | | 未知 | |
+---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.2 临时表
临时建立的表,并不会长期存在,主要用于保存一些临时数据。临时表只在当前连接可见,当前连接下可执行增删改查等操作, 当连接被关闭后,临时表就会被 MySQL 删除,相关的资源也会被释放。
mysql> create temporary table temp_info (id int(4) not null auto_increment,name varchar(10) not null,hobby varchar(50) not null,primary key(id))engine=innodb default charset=utf8; ##temporary表示创建的是临时表;设置的引擎为innodb,默认字符集为中文,引擎会在下一篇博客中介绍
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
然后我们在表中写入数据
mysql> insert into temp_info (name,hobby) values ('xiaohei','look cat');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from temp_info; ##查看插入临时表中的数据
+----+---------+----------+
| id | name | hobby |
+----+---------+----------+
| 1 | xiaohei | look cat |
+----+---------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
这时候退出数据库
mysql> quit;
Bye
临时表在我们退出数据库后重新登录就没有了,然后我们重新登录查看临时表temp_info是否还存在。
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -p'abc123' ##登录数据库
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 9
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
...
省略部分内容
mysql> show databases; ##查看数据库
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| home |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use home; ##进入建立临时表的数据库中
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables; ##查看表,发现刚刚创建的临时表不见了
+----------------+
| Tables_in_home |
+----------------+
| hello |
| infom |
+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.3 克隆表
有的时候我们会有原样拷贝某个数据表的需求,解决这样的需求的方法有两种,方法如下。
方法一:通过 LIKE 方式克隆表
-
在创建表时使用 LIKE 方法,完整复制表结构。LIKE 方法可以将源表完全
一样的复制生成一个新表,包括表的备注、索引、主键、存储引擎等,但是不会复制源表内数据记录。 -
通过 INSERTINTO…SELECT 方法,将源表内的数据写入新表内。
这个方法在做清空表时候已经演示过了,就不再进行演示
方法二:通过创建表的方式克隆表
-
使用 SHOW CREATETABLE 命令来获取源表的表结构、索引等信息。
-
复制源表结构并修改表名为目标名字,然后执行创建新表的语句。通过这步操作,就可以获得一个和源表结构一样的克隆表了。
-
执行 INSERTINTO…SELECT 语句,从源表复制数据到新表内。
第一步:
mysql> show create table infom\G; ##获取源表的表结构、索引等信息。\G表示以
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: infom
Create Table: CREATE TABLE "infom" (
"id" int(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
"name" varchar(10) NOT NULL,
"score" decimal(5,2) DEFAULT NULL,
"address" varchar(50) DEFAULT '未知',
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified
第二步:
mysql> CREATE TABLE "new" (
-> "id" int(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> "name" varchar(10) NOT NULL,
-> "score" decimal(5,2) DEFAULT NULL,
-> "address" varchar(50) DEFAULT '未知',
-> PRIMARY KEY ("id")
-> ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-> ;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
第三步:
mysql> insert into new select * from infom;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
查看克隆的new表
mysql> select * from new;
+----+---------+-------+---------+
| id | name | score | address |
+----+---------+-------+---------+
| 1 | 老大 | 99.00 | nanjing |
| 2 | dogzhen | 88.00 | beijing |
| 3 | 老三 | 77.00 | guiyang |
+----+---------+-------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
五、 数据库用户授权
MySQL 数据库的 root 用户账号拥有对所有数据库、表的全部权限,频繁使用 root 账号会给数据库服务器带来一定的安全风险。
实际工作中,通常会建立一些低权限的用户,只负责一部分数据库、表的管理和维护操作,甚至可以对查询、修改、删除记录等各种操作做进一步的细化限制,从而将数据库的风险降至最低。
5.1 授予权限
GRANT 语句:专门用来设置数据库用户的访问权限。当指定的用户名不存在时, GRANT 语句将会创建新的用户;当指定的用户名存在时,GRANT 语句用于修改用户信息。
使用 GRANT 语句授权的用户 记录,会保存到 mysql 库的 user、db、host、tables_priv 等相关表中,无须刷新即可生效。
grant语句格式
GRANT 权限列表 ON 数据库名.表名 TO 用户名@来源地址 [IDENTIFIED BY'密码']
- 权限列表:用于列出授权使用的各种数据库操作,以逗号进行分隔,如“select,insert, update”。使用“all”表示所有权限,可授权执行任何操作。
- 数据库名.表名:用于指定授权操作的数据库和表的名称,其中可以使用通配符“*”。
- 用户名@来源地址:用于指定用户名称和允许访问的客户机地址
- IDENTIFIED BY:用于设置用户连接数据库时所使用的密码字符串。在新建用户时, 若省略“IDENTIFIED BY”部分,则用户的密码将为空。
创建一个jerry用户,允许访问所有库中的所有表,允许从本地登录
mysql> grant all on *.* to 'jerry'@'localhost' identified by 'abc123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
5.2 查看权限
SHOW GRANTS 语句:专门用来查看数据库用户的授权信息,通过 FOR 子句可指定查看的用户对象(必须与授权时使用的对象名称一致)。
mysql> show grants for 'jerry'@'localhost';
+----------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for jerry@localhost |
+----------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'jerry'@'localhost' |
+----------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)