我们在实际的应用开发过程中有几种常见的页面展示方式
1:activity的setContentView方式来加载我们自己的布局
2:dialog的形式,setContentView
3:PopupWindow,PopupWindow初始化的时候可以传入一个View
4:通过WindowManager的addView方法添加到窗口管理器
Android中View是以树的形式来管理的,每个窗口上都对应着一个DecorView(根View),我们通过上面的前三个方法设置的view都被添加到DecorView下面的一个id为:android.R.id.Content的子view上
1:DecorView被添加到Window的过程
DecorView本质上是一个FrameLayout,它下面有四个子view
1:action_bar
2:content
3:navgationbarbackgroundview
4:statusbarbackgroundview
其中34既可以在systemui进程中绘制也可以在应用进程中绘制
在启动activity的过程中我们知道ActivityManagerService会回调Activity相关的生命周期,在ActivityThread中有一个方法叫handleResumeActivity
@Override
public void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean finalStateRequest, boolean isForward,
String reason) {
...............................
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);-------------------------------------->设置成不可见
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (r.mPreserveWindow) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
r.mPreserveWindow = false;
// Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity
// in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing
// the decor view we have to notify the view root that the
// callbacks may have changed.
ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl();
if (impl != null) {
impl.notifyChildRebuilt();
}
}
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
if (!a.mWindowAdded) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);------------------------------------------->添加到窗口管理器
} else {
// The activity will get a callback for this {@link LayoutParams} change
// earlier. However, at that time the decor will not be set (this is set
// in this method), so no action will be taken. This call ensures the
// callback occurs with the decor set.
a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l);
}
}
// If the window has already been added, but during resume
// we started another activity, then don't yet make the
// window visible.
} else if (!willBeVisible) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Launch " + r + " mStartedActivity set");
r.hideForNow = true;
}
// Get rid of anything left hanging around.
cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r, false /* force */);
// The window is now visible if it has been added, we are not
// simply finishing, and we are not starting another activity.
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible && r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
if (r.newConfig != null) {
performConfigurationChangedForActivity(r, r.newConfig);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming activity " + r.activityInfo.name + " with newConfig "
+ r.activity.mCurrentConfig);
}
r.newConfig = null;
}
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming " + r + " with isForward=" + isForward);
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION)
!= forwardBit) {
l.softInputMode = (l.softInputMode
& (~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION))
| forwardBit;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();---------->windowManager是一个接口,实现类是WindowManagerImpl
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l);
}
}
r.activity.mVisibleFromServer = true;
mNumVisibleActivities++;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
r.activity.makeVisible();----------------------------------------->设置成可见
}
}
......................................
}
WindowManagerImpl::addView
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);----->通过WindowManagerGlobal来实现
}
WindowManagerglobal的addView方法实现
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...............................................................................
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);---------->如果有父窗口,调整窗口参数
} else {
// If there's no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is
// set from the application's hardware acceleration setting.
final Context context = view.getContext();
if (context != null
&& (context.getApplicationInfo().flags
& ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) {
wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
}
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Start watching for system property changes.
if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) {
mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
synchronized (mLock) {
for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties();
}
}
}
};
SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater);
}
int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) {
// Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue.
mRoots.get(index).doDie();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view
+ " has already been added to the window manager.");
}
// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.
}
// If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being
// attached to for future reference.
if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW &&
wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {
final int count = mViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) {
panelParentView = mViews.get(i);
}
}
}
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);-------------------->创建ViewRootImpl对象
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);--------------------->调用ViewRootImpl的setView方法
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
在这里我们需要了解的是ViewRootImpl,PhoneWindow,PhoneWindow是Window目前唯一的实现类,在Activity的attch方法中创建,对应Dialog是在其构造函数中创建的,对于PopupWindow是没有直接持有Phonewindow对象的,这些都不重要,PhoneWindow并不是应用程序端的窗口(Window),PhoneWindow更多的是充当一个桥梁的作用,ViewRootImpl一端连接的是view,另一端连接的是windowmanager,ViewRootImpl里面有一个相当重要的成员: final W mWindow;这个才是应用程序段的窗口对象,其本质是一个binder对象,在应用程序向wms申请分配请求窗口的时候会传递给wms,以便wms能够回调窗口的各种状态
2:ViewRootImpl的setView方法
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();----------------------------->第一次请求布局
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
mForceDecorViewVisibility = (mWindowAttributes.privateFlags
& PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DECOR_VIEW_VISIBILITY) != 0;
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
//请求添加到窗口,最终是调到wms的addWindow方法
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mWinFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
requestlayout便是view绘制的入口,我们从这个方法开始分析
3:View的整体绘制流程
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
final TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable = new TraversalRunnable();
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);
if (mProfile) {
Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor");
}
performTraversals();---------------------->从performTraversals方法开始
if (mProfile) {
Debug.stopMethodTracing();
mProfile = false;
}
}
}
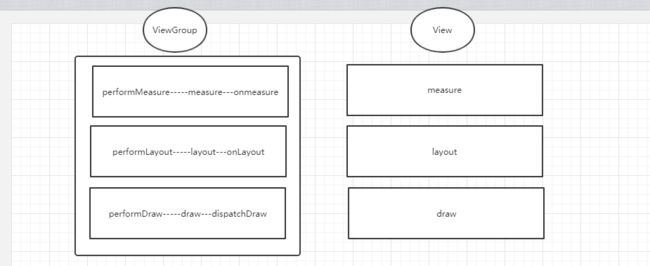
绘制会从ViewRootImpl的performTraversals方法开始,从上到下遍历整个视图树,每个View控件负责绘制自己,而ViewGroup还需要负责通知自己的子View进行绘制操作
private void performTraversals() {
...
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
...
//执行测量流程
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
//执行布局流程
performLayout(lp, desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
...
//执行绘制流程
performDraw();
}
performTraversals的大致流程是
3.1:performMeasure的流程
performMeasure主要是负责测量的
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);---->也就是decorView
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
View的measure方法
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
........................................
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);-------------->onMeasure
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
....................................
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
DecorView本身是一个FrameLayout,ViewGroup是一个抽象类,并没有重写onMeasure方法,我们从FrameLayout的onMeasure方法开始分析
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 子view结合父view的MeasureSpec和自己的layoutparms来计算自己的measureSpec
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
//父view下的所有子view测量完成再来测量自己
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);------>子view测量
}
}
}
measureChildWithMargins方法是ViewGroup的方法
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);---->
}
这样便完成了整个view的测量过程
3.2:performLayout的流程
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
int desiredWindowHeight) {
············································
try {
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
mInLayout = false;
int numViewsRequestingLayout = mLayoutRequesters.size();
if (numViewsRequestingLayout > 0) {
// requestLayout() was called during layout.
// If no layout-request flags are set on the requesting views, there is no problem.
// If some requests are still pending, then we need to clear those flags and do
// a full request/measure/layout pass to handle this situation.
ArrayList validLayoutRequesters = getValidLayoutRequesters(mLayoutRequesters,
false);
if (validLayoutRequesters != null) {
························
}·
mInLayout = false;
}
View的layout方法
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
..........................
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);---------------------->view的矩形区域发生了变化,onlayout方法
if (shouldDrawRoundScrollbar()) {
if(mRoundScrollbarRenderer == null) {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = new RoundScrollbarRenderer(this);
}
} else {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = null;
}
...........................................
}
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
onlayout方法是一个空方法,子类如果是ViewGroup的话则需要重写该方法,实现子view中所有视图的布局
实际上onLayout在ViewGroup中是一个抽象方法,必须去实现
3.3:performDraw的流程
private void performDraw() {
try {
boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
if (usingAsyncReport && !canUseAsync) {
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.setFrameCompleteCallback(null);
usingAsyncReport = false;
}
} finally {
mIsDrawing = false;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
.....................
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset,
scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) {
return false;
}
}
}
..................................
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty, Rect surfaceInsets) {
...........................
mView.draw(canvas);
..........................
drawAccessibilityFocusedDrawableIfNeeded(canvas);
} finally {
}
进入到View.java的draw方法
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// Step 7, draw the default focus highlight
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
if (debugDraw()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
总结
View的绘制流程主要是从ViewRootImpl的requestLayout开始的,后续分为三大流程performMeasure,performLayout,performDraw