C++线性表
C++线性表(arrayList)
一、线性表的定义
线性表是由一个或多个数据元素组成的有限序列
线性表根据存储方式分为:
1、顺序存储(数组描述):元素的地址是连续的
2、链式存储(链表描述):节点地址不连续,通过指针连起来
二、线性表的抽象数据类型
线性表的抽象类(常用的API):
- 判断是否为空;
- 返回元素个数;
- 返回索引元素;
- 返回指定元素第一次出现的索引值;
- 删除索引元素;
- 将指定元素插入指定索引位置;
#include三、线性表的顺序存储
对于顺序存储方式一般用数组实现,事实上就是在内存中找个初始地址,然后通过占位的形式,把一定连续的内存空间给占了,然后把相同数据类型的数据元素依次放在这块空地中,数组大小有两种方式指定,一是静态分配,二是动态扩展。
顺序表相关的操作跟数组有关,一般都是移动数组元素。
 顺序存储的实现方式:
顺序存储的实现方式:
//子类线性表,通过数组实现
template<class T>
class arrayList : public LineList<T>
{
public:
arrayList(int initialCapacity = 10);
arrayList(const arrayList<T>&);
~arrayList() { delete[] element; }
bool empty() const
{
if (ListSize == 0)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int size() const { return ListSize; }
T& get(int theIndex) const;
int index(const T& theElement) const;
void erase(int theIndex);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
void output() const;
int capacity() const { return arrayLength; }
protected:
void checkIndex(int theIndex) const;
T* element;
int arrayLength;
int ListSize;
};
各成员函数:
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int initialCapacity)
{
if (initialCapacity < 1)
cout<<"Capability must be greater than 1"<<endl;
arrayLength = initialCapacity;
element = new T[arrayLength];
ListSize = 0;
}
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList<T>& theList)
{
arrayLength = theList.arrayLength;
ListSize = theList.ListSize;
element = new T[arrayLength];
copy(theList.element, theList.element + ListSize, element);
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{
if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= ListSize)
cout << "illegalindex" << endl;
}
template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
return element[theIndex];
}
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::index(const T& theElement) const
{
int theIndex = (int)(find(element, element + ListSize, theElement) - element);
if (theIndex == ListSize)
{
return -1;
}
else return theIndex;
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
copy(element + theIndex + 1, element + ListSize, element + theIndex);
element[--ListSize].~T();
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{
if (theIndex<0 || theIndex>ListSize)
cout << "illegalindex" << endl;
if (ListSize == arrayLength)
{
T* temp = new T[2 * arrayLength];
copy(element, element + arrayLength, temp);
delete[]element;
element = temp;
arrayLength = 2 * arrayLength;
}
copy_backward(element + theIndex, element + ListSize, element + ListSize + 1);
element[theIndex] = theElement;
ListSize++;
}
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::output() const
{
for (int i = 0; i <= arrayLength; i++)
{
cout << element[i] << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
}
测试:
int main()
{
using namespace std;
arrayList<int> a(20);
cout << "数组的容量为:" << a.capacity() << endl;
cout << "数组的大小为:" << a.size() << endl;
a.output();
a.insert(0, 1);
a.insert(1, 3);
a.insert(2, 5);
a.insert(3, 7);
a.insert(4, 9);
cout << "数组的容量为:" << a.capacity() << endl;
cout << "数组的大小为:" << a.size() << endl;
a.output();
cout << "索引为2的元素为:" << a.get(2) << endl;
cout << "元素为5的索引为:" << a.index(5) << endl;
a.erase(3);
a.output();
cout << "索引为3的元素为:" << a.get(3) << endl;
cout << "数组的大小为:" << a.size() << endl;
a.insert(4, 11);
a.output();
system("pause");
return (0);
}
顺序存储的优缺点
- 优点:
随机访问特性,查找O(1)时间,存储密度高;
逻辑上相邻的元素,物理上也相邻;
无须为表中元素之间的逻辑关系而增加额外的存储空间; - 缺点:
插入和删除需移动大量元素;
当线性表长度变化较大时,难以确定存储空间的容量;
造成存储空间的“碎片”
四、线性表的链式存储
线性表的链式存储结构的特点是用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素,这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的。这就意味着,这些元素可以存在内存未被占用的任意位置。
链表的定义是递归的,它或者为空null,或者指向另一个节点node的引用,这个节点含有下一个节点或链表的引用,线性链表的最后一个结点指针为“空”(通常用NULL或“^”符号表示)。
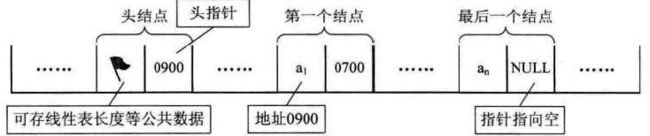
特点:
- 用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素, 这组存储单元可以存在内存中未被占用的任意位置
- 顺序存储结构每个数据元素只需要存储一个位置就可以了,而链式存储结构中,除了要存储数据信息外,还要存储它的后继元素的存储地址
父类虚函数
class LineList
{
public:
virtual ~LineList() {}; //虚析构函数
virtual bool empty() const = 0; //判断线性表是否为空
virtual int size() const = 0; //返回线性表大小
virtual T& get(int theIndex) const = 0; //按索引查找元素
virtual int index(const T& theElement) const = 0; //按值查找元素
virtual void erase(int theIndex) = 0; //删除索引元素
virtual void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) = 0; //按索引插入元素
};
链表节点的结构定义
template <class T>
struct chainNode
{
T element; //存储数据
chainNode<T>* next; //下一个节点的地址
};
链表派生类
template <class T>
class chain :public LineList<T>
{
public:
//构造函数
chain();
chain(T a[],int n);
~chain();
//抽象数据类型
bool empty() const { return 0; }
int size() const;
T& get(int theIndex) const;
int index(const T& theElement) const;
void erase(int theIndex);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
void output() const;
protected:
chainNode<T>* firstNode; //指向链表第一个节点的指针
};
无参构造函数
chain<T>::chain()
{
firstNode = new chainNode<T>;
firstNode->next = NULL;
}
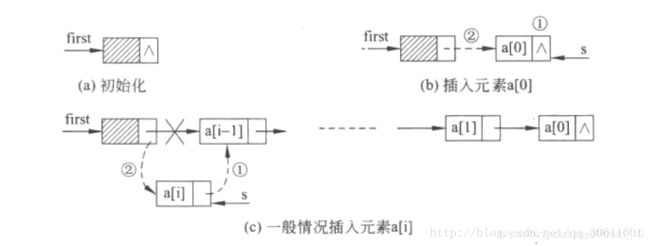
头插法的拷贝构造函数
template <class T>
chain<T>::chain(T a[],int n)
{
firstNode = new chainNode<T>;
firstNode->next = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
chainNode<T>* s = new chainNode<T>;
s->element = a[i];
s->next = firstNode->next;
firstNode->next = s;
}
}
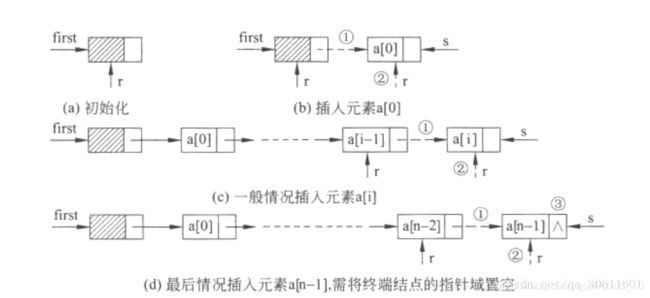
template<class T>
chain<T>::chain(T a[], int n)
{
firstNode = new chainNode<T>;
chainNode<T> *r = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
chainNode<T>* s = new chainNode<T>;
s->element = a[i];
r->next = s;
r = s;
}
r->next = NULL;
}
template<class T>
chain<T>::~chain()
{
while (firstNode != NULL)
{
chainNode<T>* q = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
delete q;
}
}
成员方法函数
//返回长度
template<class T>
int chain<T>::size() const
{
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode->next;
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
//按位查找
template<class T>
T& chain<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode->next;
int count = 1;
while (p != NULL && count < theIndex)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL)
throw"Wrong_Index";
else
return p->element;
}
//按值查找
template<class T>
int chain<T>::index(const T& theElement) const
{
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode->next;
int count = 1;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->element == theElement)
return count;
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return 0;
}
//删除
template<class T>
void chain<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode;
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL && count < theIndex - 1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL || p->next == NULL)
throw"Wrong_Index";
else
{
chainNode<T>* q = p->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
delete q;
}
}
//插入
template<class T>
void chain<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode;
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL && count < theIndex - 1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (theIndex!=1&&p == NULL)
throw"Wrong_Index";
else
{
chainNode<T>* s = new chainNode<T>;
s->element = theElement;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
}
}
//输出
template<class T>
void chain<T>::output() const
{
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
cout << p->element << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
测试主函数
int main()
{
chain<int> p;
p.insert(1, 1);
p.insert(2, 5);
p.insert(3, 7);
p.output();
p.insert(2, 3);
p.output();
cout << "元素5位于:" << p.index(5) << endl;
cout << "元素9位于:" << p.index(9) << endl;
cout << "第2号元素为:" << p.get(2) << endl;
cout << "链表长度为:" << p.size() << endl;
p.erase(2);
p.output();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
链式存储的优缺点
- 优点:1.插入、删除不需要移除其他元素,只需改变指针。2.内存空间不需要连续,空间利用率高
- 缺点:查找需要遍历操作,效率低