Servlet八大监听器+统计网站在线人数Demo
引入:
Servlet监听器可以让Web容器在特定的事件发生时,执行特定的操作,采取适当的动作进行反馈。
在Servlet规范中定义了多种类型的监听器,它们用于监听的事件源分别 HttpSession,ServletContext和ServletRequest这三个域对象,和其它事件监听器略有不同的是,servlet监听器的注册不是直接注册在事件源上,而是由WEB容器负责注册,开发人员只需在web.xml文件中使用
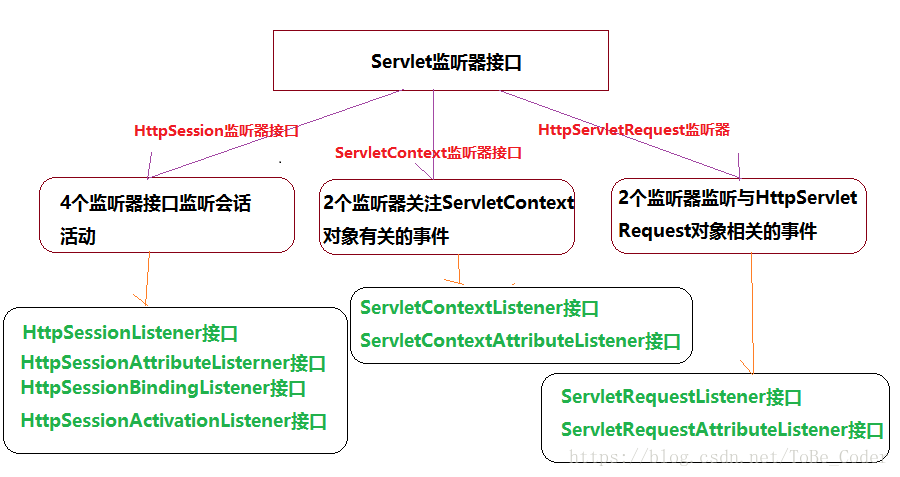
监听器中定义了web容器会自动调用的方法,其中有4个监听器接口监听session活动,有两个监听器关注与ServletContext对象有关的事件,还有两个监听器接口监听与HttpServletRequest对象有关的事件。
以下分别对其进行介绍:
HttpSession监听器接口:
HttpSessionListener(javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener)
此接口中定义了两个需要实现的方法:两个方法都接收HttpSessionEvent类型的事件。
注:如果web应用中使用了实现该监听器接口的类,需要修改web.xml文件。类似如下:
webbook.CounterListener
- sessionCreated():在会话对象被Servlet与JSP创建时,Web容器会自动调用该实现类的此方法。
- sessionDestoryed():会话对象被销毁时,会自动调用此方法。
HttpSessionAttributeListener(javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionAttributeListener)
此接口定义了定义了三个需要实现的方法,他们都接收HttpSessionBindingEvent类型的事件。
注:如果web应用中使用了实现该监听器接口的类,需要修改web.xml文件。与HttpSessionListener修改相同。
- attributeAdded():当session对象增加属性时,Web容器会自动调用此方法。
- attributeReplaced():当session对象的同名属性被替换时,Web容器会自动调用此方法。
- attributeRemoved():当session对象属性被移除时,Web容器会自动调用此方法。
拓展:在HttpSessionBindingEvent类中定义了三个方法,getSession(),getName()和getValue()。getSession()方法获得当前触发事件的session对象,getName()方法获得被操作的session的属性的名字,getValue()方法获得被操作的session属性的值。
HttpSessionBindingListener(javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener)
实现HttpSessionBindingListener接口,JavaBean 对象可以感知自己被绑定到 Session 中和从 Session 中删除的事件。
此接口中定义了两个方法,他们都接收HttpSessionBindingEvent类型的事件。
注:使用这个接口的实现类不需要配置web,xml文件,可以直接使用。
- valueBound():一个类实现了此接口,则当这个类的对象通过session.setAttributr()被绑定到session对象中时,该对象的词=此方法被调用。
- valueUnbound():一个类实现了此接口,则当这个类的对象从session中删除时,此方法会被自动调用。
HttpSessionActivationListener(javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionActivationListener)
实现HttpSessionActivationListener接口,JavaBean 对象可以感知自己被活化和钝化的事件。
此接口中定义了两个方法,他们都接收HttpSessionEvent类型的事件。
注:如果web应用中使用了实现该监听器接口的类,需要配置web.xml文件。
- sessionDidActivate():session对象活化后由容器自动调用。
- sessionWillPassivate():session对象钝化前由容器自动调用。
说明:Activate(活化)与Passivate(钝化)是web容器为了更好的利用资源或者进行服务器负载平衡等原因而对 特定对象采取的措施。session对象的钝化指的是:session对象通过序列化的方式存储到硬盘,而会话对象的活化与钝化相反,web容器把硬盘上存储的会话对象重新加载到web容器。
ServletContext监听器接口:
拓展:一个web应用就是由一系列的Servlet,Jsp和其他相关文件的集合,这些文件的组织采用特定的目录结构,并且会有一个web.xml文件作为配置文件。每个在web容器中运行的web应用都会有一个对应的javax.servlet.ServletContext对象。在JSP文件中这个对象化身成application对象;在Servlet中,该对象可以通过this.getServletContext()方法获取,servletContext对象在同一个应用中是共享的,它总是用来保存生命周期非常长的全局变量或者全局对象。
ServletContextListener(javax.servlet.ServletContextListener)
此接口定义两个方法:contextInitialized(); contextDestroyed();
注:此两个方法,接收ServletContextEvent类型的事件。需要配置web.xml文件。
ServletContextAttributeListener(javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeListener)
此接口定义三个方法:addributeAdded(); attributeReplaced(); attributeRemoved();
注:此三个方法接收ServletContextAttributeEvent类型的事件。需要配置web.xml文件。
HttpServletRequest监听器接口:
ServletRequestListener(javax.servlet.HttpSessionActivationListener)
此接口定义两个方法:requestInitialized(); requestDestroyed();
注:此两个方法,接收ServletRequestEvent类型的事件。需要配置web.xml文件。
ServletRequestAttributeListener(javax.servlet.ServletRequestAttributeListener)
此接口定义三个方法:addributeAdded(); attributeReplaced(); attributeRemoved()
注:此三个方法接收ServletRequestAttributeEvent类型的事件。需要配置web.xml文件。
说明:ServletContext和ServletRequest监听器中的接口方法,与HttpSession监听器中(HttpSessionLister和HttpSessionAttributeListener)的方法调用时机一致,因此不进行赘述。
应用Demo:
HttpSessionListener:收集在线者信息
package webbook;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
public class CounterListener implements HttpSessionListener {
private static long onlineNumber=0;
public static long getOnlineNumber(){
return onlineNumber;
}
@Override
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent arg0) {
onlineNumber++;
}
@Override
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent arg0) {
onlineNumber--;
}
}
在web.xml中加入配置:
webbook.CounterListener
访问页面:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ page import="webbook.CounterListener" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
web应用在线人数监听
当前应用中有<%= CounterListener.getOnlineNumber() %>人在线
注:本篇文章纯属笔记,没有侵权意图。感兴趣的可以看书《Java+Web开发与实战-Eclipse+Tomcat+Servlet+JSP整合应用》。