HI3556V200 Linux+Liteos双系统学习(4)----双系统通信 IPCM/virt_tty/sharefs
文章目录
- 1 IPCM
- 1.1 IPCMSG
- 1.1.1 Linux端示例代码
- 1.1.2 Liteos端示例代码
- 1.2 DATAFIFO
- 1.2.1 Linux端示例代码
- 1.2.2 Liteos端示例代码
- 2 virt_tty
- 3 sharefs
双系统之间进行交互主要有以下三种方式:
ipcm:用于双系统之间数据传输、信令交互;
virt_tty:虚拟终端功能,用于在Linux端调试Liteos;
sharefs:共享文件系统。
1 IPCM
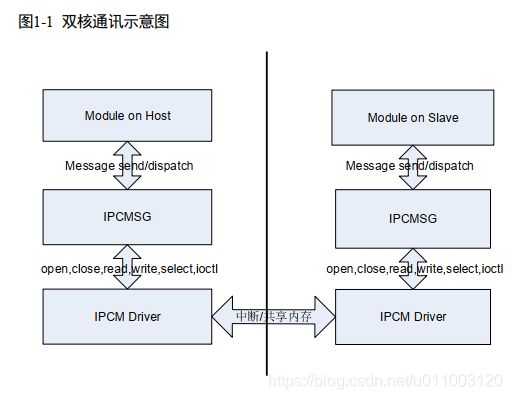
HiSysLink 包含两个模块:IPCMSG 和 DATAFIFO。一个用于小量数据间通信,一个用于大量数据间传输。
1.1 IPCMSG
IPCMSG适应于小数据,数据一次性传输不大于1024个字节,例如信令交互,音频数据传输。延时比较低,毫秒甚至微秒级延时,另外,IPCMSG是双向通信的。
1.1.1 Linux端示例代码
示例代码如下,通过IPCMSG_CLIENT_SendMsg函数将数据发送给Liteos端,通过CLIENT_HandleRecvMsg函数接收Liteos发送过来的数据。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static HI_S32 s_s32CommonIPCMsgID = 0; //消息ID
static pthread_t s_CommonRecvThrdId = 0;
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
//回复消息给liteos
int MSG_USER_LinuxResponse(HI_S32 s32MsgId, HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S * pstMsg, int ret)
{
HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *respMsg;
//创建回复消息
respMsg = HI_IPCMSG_CreateRespMessage(pstMsg, ret, NULL, 0);
//发送异步消息 不需要等待liteos响应
HI_IPCMSG_SendAsync(s32MsgId, respMsg, NULL);
//销毁消息 释放指针
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(respMsg);
return 0;
}
//发送指令给liteos端
//userCmd 自定义的指令
//pBody 数据指针
//u32BodyLen 数据长度
HI_S32 IPCMSG_CLIENT_SendMsg(COMM_USER_CMD_E userCmd, void* pBody, HI_S32 u32BodyLen)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *pReq = NULL;
HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *pResp = NULL;
//创建消息
pReq = HI_IPCMSG_CreateMessage(IPCMSG_COMMON_MODID, userCmd, pBody, u32BodyLen);
if(NULL == pReq)
{
printf("HI_IPCMSG_CreateMessage failed!\n");
return HI_FAILURE;
}
//发送消息 阻塞等待回应
//s_s32CommonIPCMsgID 消息ID
//AVPLAY_MSG_LONG_TIMEOUT timeout时间
s32Ret = HI_IPCMSG_SendSync(s_s32CommonIPCMsgID, pReq, &pResp, AVPLAY_MSG_LONG_TIMEOUT);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("HI_IPCMSG_SendSync failed!\n");
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pReq);
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pResp);
return s32Ret;
}
s32Ret = pResp->s32RetVal;
//销毁消息
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pReq);
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pResp);
return s32Ret;
}
//接收Liteos端的信息,并进行处理
//s32MsgId 消息ID
//pstMsg 消息体
HI_S32 CLIENT_HandleRecvMsg(HI_S32 s32MsgId, HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *pstMsg)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
if (s32MsgId != s_s32CommonIPCMsgID)
{
printf( "ipcmsg receive msg from error id: %d\n", s32MsgId);
return s32Ret;
}
//IPCMSG_COMMON_MODID 自定义 用于简单校验指令
if (pstMsg->u32Module != IPCMSG_COMMON_MODID)
{
printf( "ipcmsg receive msg from error module id: %d\n", pstMsg->u32Module);
return s32Ret;
}
//根据消息类型处理消息
switch(pstMsg->u32CMD)
{
case 1:
break;
default:
printf("linux error cmd %#x\n", pstMsg->u32CMD);
break;
}
MSG_USER_LinuxResponse(s32MsgId, pstMsg, s32Ret);
return s32Ret;
}
static HI_VOID* IPCMSG_CLIENT_RecvThread(void* arg)
{
prctl(15, "common_ipcmsg_cli_rcvThread", 0, 0, 0);
HI_S32* s32Id = (HI_S32*)arg;
LOGD_print("common receive from %d\n", *s32Id);
HI_IPCMSG_Run(*s32Id);
return NULL;
}
HI_S32 IPCMSG_CLIENT_Init()
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
HI_IPCMSG_CONNECT_S stIpcMsgConnect;
stIpcMsgConnect.u32RemoteId = 1; //1:连接Liteos的CPU
stIpcMsgConnect.u32Port = IPMSG_COMMON_PORT; //IPMSG_COMMON_PORT:端口号 自定义
stIpcMsgConnect.u32Priority = 0; //0:普通优先级
//添加服务 IPCMSG_COMMON:服务名称指针 自定义
if (HI_IPCMSG_AddService(IPCMSG_COMMON,&stIpcMsgConnect) != HI_SUCCESS)
{
printf("HI_IPCMSG_AddService IPCMSG_COMMON fail\n");
return HI_FAILURE;
}
//阻塞方式建立连接
//s_s32CommonIPCMsgID 消息ID
//IPCMSG_COMMON 服务名称指针
//CLIENT_HandleRecvMsg 消息处理函数
if (HI_SUCCESS != HI_IPCMSG_Connect(&s_s32CommonIPCMsgID, IPCMSG_COMMON, (HI_IPCMSG_HANDLE_FN_PTR)CLIENT_HandleRecvMsg))
{
printf("HI_IPCMSG_Connect IPCMSG_COMMON fail\n");
HI_IPCMSG_DelService(IPCMSG_COMMON);
return HI_FAILURE;
}
//创建消息处理函数
s32Ret = pthread_create(&s_CommonRecvThrdId, NULL, IPCMSG_CLIENT_RecvThread, &s_s32CommonIPCMsgID);
if(s32Ret != HI_SUCCESS)
{
s_s32CommonIPCMsgID = 0;
HI_IPCMSG_Disconnect(s_s32CommonIPCMsgID);
HI_IPCMSG_DelService(IPCMSG_COMMON);
return HI_FAILURE;
}
return HI_SUCCESS;
}
int main()
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
s32Ret = IPCMSG_CLIENT_Init();
if (s32Ret != 0)
{
printf("Media_Msg_Init Error!\n");
return s32Ret;
}
while(1)
sleep(10);
return s32Ret;
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
1.1.2 Liteos端示例代码
示例代码如下,通过IPCMSG_SVR_SendMsg函数将数据发送给Linux端,通过IPCMSG_SVR_HandleRecvMsg函数接收Linux端发送过来的数据。
//双系统通信模块
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static pthread_t s_CommonRecvThrdId = 0;
static HI_S32 s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID = 0;
static HI_BOOL bCommonSvrInited = HI_FALSE;
#define COMMON_IPCMSG_THREAD_PRIORITY (7)
#define COMMON_IPCMSG_THREAD_STACKSIZE (0x10000)
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
//回复消息给linux
int MSG_USER_Response(HI_S32 s32MsgId, HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S * pstMsg, HI_S32 ret)
{
HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *respMsg;
//创建回复消息
respMsg = HI_IPCMSG_CreateRespMessage(pstMsg, ret, NULL, 0);
//发送异步消息 不需要等待linux响应
HI_IPCMSG_SendAsync(s32MsgId, respMsg, NULL);
//销毁消息 释放指针
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(respMsg);
return 0;
}
//发送指令给liunx端
//userCmd 自定义的指令
//pBody 数据指针
//u32BodyLen 数据长度
int IPCMSG_SVR_SendMsg(COMM_USER_CMD_E userCmd, void* pBody, int u32BodyLen)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *pReq = NULL;
HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S *pResp = NULL;
//创建消息
pReq = HI_IPCMSG_CreateMessage(IPCMSG_COMMON_MODID, userCmd, pBody, u32BodyLen);
if(NULL == pReq)
{
printf("HI_IPCMSG_CreateMessage failed!\n");
return HI_FAILURE;
}
//发送消息 阻塞等待回应
//s_s32CommonIPCMsgID 消息ID
//AVPLAY_MSG_LONG_TIMEOUT timeout时间
s32Ret = HI_IPCMSG_SendSync(s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID, pReq, &pResp, AVPLAY_MSG_LONG_TIMEOUT);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("HI_IPCMSG_SendSync failed!\n");
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pReq);
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pResp);
return s32Ret;
}
s32Ret = pResp->s32RetVal;
//销毁消息
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pReq);
HI_IPCMSG_DestroyMessage(pResp);
return s32Ret;
}
//接收Liteos端的信息,并进行处理
//s32MsgId 消息ID
//pstMsg 消息体
static void IPCMSG_SVR_HandleRecvMsg(HI_S32 s32Id, HI_IPCMSG_MESSAGE_S* pMsg)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_FAILURE;
printf("common ipcmsg, receive msg id:%d, msg cmd %d \n", s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID, pMsg->u32CMD );
if(s32Id != s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID)
{
printf ("ipcmsg receive msg from error id: %d\n", s32Id);
return;
}
//IPCMSG_COMMON_MODID 自定义 用于简单校验指令 和linux端保持一致
if(pMsg->u32Module != IPCMSG_COMMON_MODID)
{
printf ("ipcmsg receive msg from error module id: %d\n", pMsg->u32Module);
return;
}
//根据消息类型处理消息
switch(pMsg->u32CMD)
{
case 1:
break;
default:
printf ("unsupported cmd request from client\n");
break;
}
//回复消息给linux端
MSG_USER_Response(s32Id, pMsg, s32Ret);
}
//创建消息处理函数
static void* IPCMSG_SVR_RecvThread(void *arg)
{
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "Hi_pTCommonMsg", 0, 0, 0);
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
do
{
if(HI_TRUE == HI_IPCMSG_IsConnected(s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID))
{
HI_IPCMSG_Run(s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID);
}
else
{
s32Ret = HI_IPCMSG_Disconnect(s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID);
if(s32Ret != HI_SUCCESS)
{
printf ("SVR RecvThread HI_IPCMSG_Disconnect fail\n");
}
s32Ret = HI_IPCMSG_Connect(&s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID, IPCMSG_COMMON, IPCMSG_SVR_HandleRecvMsg);
if(s32Ret != HI_SUCCESS)
{
printf ("RecvThread HI_IPCMSG_Connect fail\n");
}
}
}while(1);
return NULL;
}
static void* IPCMSG_SVR_WaitClientConnect(void *arg)
{
pthread_attr_t attr;
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "Hi_pCommonMsgwait", 0, 0, 0);
HI_IPCMSG_CONNECT_S stIpcMsgConnect;
stIpcMsgConnect.u32RemoteId = 0; //连接Linux的CPU
stIpcMsgConnect.u32Port = IPMSG_COMMON_PORT; //IPMSG_COMMON_PORT:端口号 自定义 和linux端一致
stIpcMsgConnect.u32Priority = 0; //0:普通优先级 和linux端一致
//添加服务 IPCMSG_COMMON:服务名称指针 自定义 和linux端一致
if(HI_IPCMSG_AddService(IPCMSG_COMMON, &stIpcMsgConnect) != HI_SUCCESS)
{
printf ("HI_IPCMSG_AddService fail\n");
return NULL;
}
printf("thread wait for player client connect.......\n");
//阻塞方式建立连接
//s_s32CommonIPCMsgID 消息ID
//IPCMSG_COMMON 服务名称指针 和linux端保持一致
//IPCMSG_SVR_HandleRecvMsg 消息处理函数
if (HI_SUCCESS != HI_IPCMSG_Connect(&s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID,IPCMSG_COMMON, IPCMSG_SVR_HandleRecvMsg))
{
printf ("HI_IPCMSG_Connect fail\n");
HI_IPCMSG_DelService(IPCMSG_COMMON);
return NULL;
}
printf("player ipc msg client&server connected id: %d\n", s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID);
if(0 != pthread_attr_init(&attr))
{
printf ("Error pthread_attr_init()!");
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return NULL; //Thread attribute initialise error, then exit
}
if(0 != pthread_attr_setstacksize(&attr, COMMON_IPCMSG_THREAD_STACKSIZE))
{
printf ("Error pthread_attr_setstacksize()!");
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return NULL; //Thread attribute initialise error, then exit
}
attr.inheritsched = PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED;
attr.schedparam.sched_priority = COMMON_IPCMSG_THREAD_PRIORITY;
//创建消息处理函数
if (0 != pthread_create(&s_CommonRecvThrdId, &attr, IPCMSG_SVR_RecvThread, &s32CommonSvrIPCMsgID))
{
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
printf ("pthread_create HI_AVPLAY_IPCMSG_SVR_RecvThread failed\n");
return NULL;
}
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); //Destroying threads attribute structure, cannot be used again before restarting the initialization
return NULL;
}
int IPCMSG_SVR_Init()
{
int ret = 0;
extern int _ipcm_vdd_init(void);
printf("ipcm init ...\n");
_ipcm_vdd_init();
pthread_t waitConThrd;
if (0 != pthread_create(&waitConThrd, NULL, IPCMSG_SVR_WaitClientConnect, NULL))
{
printf( "pthread_create HI_AVPLAY_IPCMSG_SVR_WaitClientConnect failed\n");
return HI_FAILURE;
}
return ret;
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
1.2 DATAFIFO
datafifo用于频繁传输大量数据。datafifo只能单向传输,写端只能作为写端,读端只能作为读端。
示例代码如下,在下面代码中,Linux端作为写端,将数据写入datafifo。liteos作为读端,从datafifo中读取数据进行处理。
1.2.1 Linux端示例代码
Linux端调用IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_Data函数写入数据。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
HI_U64 gDataFifoPhyAddr; //数据通路在Linux端的物理地址
HI_DATAFIFO_HANDLE gDataFifoHandle = HI_DATAFIFO_INVALID_HANDLE; //数据通路句柄
HI_U32 gDataFifoSize = DATAFIFO_NUM*DATAFIFO_NUM_SIZE;
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
//判断datafifo是否为空
static HI_BOOL Is_DatafifoFull()
{
HI_S32 s32Ret;
HI_U32 u32AvailWriteLen = 0;
//NULL 触发写端的数据释放回调函数,同时更新写端的读尾指针
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_Write(gDataFifoHandle, NULL);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("write error:%x\n", s32Ret);
return HI_TRUE;
}
//获取可以写入的数据长度
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_CMD(gDataFifoHandle, DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_WRITE_LEN, &u32AvailWriteLen);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("get available write len error:%x\n", s32Ret);
return HI_TRUE;
}
printf("write len is %d\n", u32AvailWriteLen);
if (u32AvailWriteLen >= gDataFifoSize)
{
return HI_FALSE;
}
else
{
return HI_TRUE;
}
}
//数据释放回调
void IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_DataRelease(char* pDataBuf)
{
if (NULL == pDataBuf)
return;
//memset(pDataBuf, 0, gDataFifoSize);
}
//将数据传输给liteos端
//pDataBuf 数据指针
HI_S32 IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_Data(char* pDataBuf)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
if (NULL == pDataBuf)
return HI_FAILURE;
//等待datafifo为空
while (Is_DatafifoFull())
{
usleep(10000); //10ms
//continue;
}
//写数据
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_Write(gDataFifoHandle, pDataBuf);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("write error:%x\n", s32Ret);
return HI_FAILURE;
}
//通知写入完成
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_CMD(gDataFifoHandle, DATAFIFO_CMD_WRITE_DONE, NULL);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("write done error:%x\n", s32Ret);
return HI_FAILURE;
}
return s32Ret;
}
//linux端 写入者 初始化
HI_S32 IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_Init()
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
HI_DATAFIFO_PARAMS_S stDatafifo;
stDatafifo.u32EntriesNum = DATAFIFO_NUM+1; //循环buf数据个数 自定义
stDatafifo.u32CacheLineSize = DATAFIFO_NUM_SIZE; //每个数据的大小 自定义
stDatafifo.bDataReleaseByWriter = HI_TRUE;
stDatafifo.enOpenMode = DATAFIFO_WRITER; //角色写入者
//打开数据通路
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_Open(&gDataFifoHandle, &stDatafifo);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("open datafifo error:%x\n", s32Ret);
return s32Ret;
}
//获取数据通路在Linux端的物理地址
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_CMD(gDataFifoHandle, DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_PHY_ADDR, &gDataFifoPhyAddr);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("get datafifo phy addr error:%x\n", s32Ret);
return s32Ret;
}
//设置数据释放回调函数
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_CMD(gDataFifoHandle, DATAFIFO_CMD_SET_DATA_RELEASE_CALLBACK, IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_DataRelease);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("register callback funtion fail! s32Ret: 0x%x\n", s32Ret);
return s32Ret;
}
return s32Ret;
}
//liteos端 读出者 初始化
//即将linux端写入者创建的datafifo的物理地址通过IPCMSG告诉liteos端
HI_S32 IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Init()
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
printf("IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Init phy addr is %llu!\n", gDataFifoPhyAddr);
//COMM_USER_CMD_DATA_FIFO_INIT 自定义的指令
s32Ret = IPCMSG_CLIENT_SendMsg(COMM_USER_CMD_DATA_FIFO_INIT, (void *)&gDataFifoPhyAddr, sizeof(HI_U64));
if (s32Ret != HI_SUCCESS)
{
printf("IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Init Error!\n");
}
return s32Ret;
}
int main()
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
printf(" init\n");
s32Ret = IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_Init();
if (s32Ret != 0)
{
printf("IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_Init Error!\n");
return s32Ret;
}
s32Ret = IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Init();
if (s32Ret != 0)
{
printf("IPCDATAFIFO_WRITE_Init Error!\n");
return s32Ret;
}
return s32Ret;
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
1.2.2 Liteos端示例代码
Liteos端在IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Read函数中读取数据。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
HI_U64 gDataPhyAddr; //写入端创建的datafifo的物理地址
HI_DATAFIFO_HANDLE gDataHandle = HI_DATAFIFO_INVALID_HANDLE;
HI_U32 gDataSize = 400*1024;
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
static void* IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Read(void *arg)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret;
HI_U32 readLen;
HI_DATAFIFO_PARAMS_S stDatafifo;
char* recvData = NULL;
stDatafifo.u32EntriesNum = DATAFIFO_NUM+1; //循环buf数据个数 自定义 和Linux端保持一致
stDatafifo.u32CacheLineSize = DATAFIFO_NUM_SIZE;//每个数据的大小 自定义 和Linux端保持一致
stDatafifo.bDataReleaseByWriter = HI_TRUE;
stDatafifo.enOpenMode = DATAFIFO_READER; //角色 读者
//通过物理地址打开
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_OpenByAddr(&gDataHandle, &stDatafifo, gDataPhyAddr);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("open datafifo error:%x\n", s32Ret);
//return HI_FAILURE;
}
printf("IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Read\n");
while(1)
{
readLen = 0;
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_CMD(gDataHandle, DATAFIFO_CMD_GET_AVAIL_READ_LEN, &readLen);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("get available read len error:%x\n", s32Ret);
//break;
}
if (readLen > 0)
{
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_Read(gDataHandle, (HI_VOID **)&recvData);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("read error:%x\n", s32Ret);
//break;
}
//数据处理
//todo...
s32Ret = HI_DATAFIFO_CMD(gDataHandle, DATAFIFO_CMD_READ_DONE, recvData);
if (HI_SUCCESS != s32Ret)
{
printf("break: read done error:%x\n", s32Ret);
//break;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
//datafifo 读端初始化
//pAddr 写端创建的datafifo的物理地址
HI_S32 IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Init(HI_VOID* pAddr)
{
HI_S32 s32Ret = HI_SUCCESS;
unsigned int dataReadThrd;
gDataPhyAddr = *((HI_U64 *)pAddr);
printf("IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Init addr is %llu\n",gDataPhyAddr);
//读线程
LOS_TASK_CREATE(dataReadThrd, "dataRead", IPCDATAFIFO_READ_Read, NULL, 0x19000, 11);
return s32Ret;
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
#if __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* End of #ifdef __cplusplus */
###1.3 驱动安装
在使用IPCMSG以及DATAFIFO前,需要在linux和liteos端分别调用对应的驱动。
在linux端需要安装驱动hi_ipcm.ko ,驱动安装成功之后,会生成设备文件/dev/ipcm。
在liteos端调用_ipcm_vdd_init进行初始化初始化。
2 virt_tty
由于硬件资源限制,设备只有一个debug串口在Linux端部署,因此在代码调试阶段无法使用这个debug口查看liteos端的打印信息。所以可以在Linux端使用虚拟串口功能来调试Liteos端。
在Linux端需要安装驱动hi_virt-tty.ko,并且在需要使用虚拟串口时候,使用指令virt-tty a7,然后就可以在终端上调试Liteos端的信息。
在Liteos端调用virt_tty_dev_init()进行初始化工作。
3 sharefs
在Liteos端因为使用的是虚拟文件系统,所以不太方便存放一些文件,例如动态库之类的。
因此,需要启动共享机制,将Liteos需要的一些文件存放在Linux相应的目录下,然后Liteos就可以访问Linux上的目录。
在Linux端设备执行指令sharefs &,或者在应用程序中使用sharefs_server_init() 函数并链接libsharefs 库也可以。
在Liteos端使用sharefs_client_init函数进行初始化即可。