Pytorch的gather和scatter
最近在看pytorch的gather与scatter函数,现在详细记录一下
1、Gather
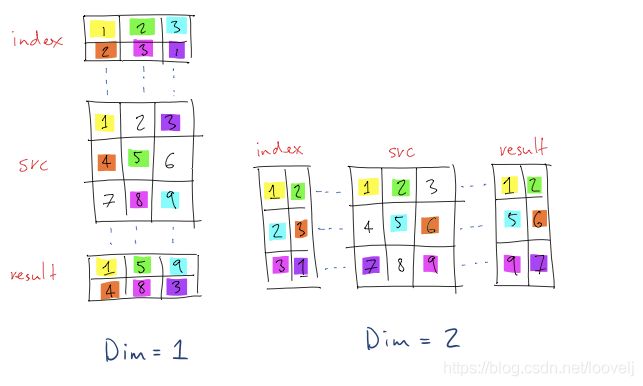
gather是根据索引取数据,下图可以表示gather,具体见[gather]的介绍(https://stackoverflow.com/a/54706716)
但是要注意的是,dim为0和1时,index是有区别的,要转置一下
index = torch.as_tensor([[0,1,2],[1,2,0]])
src = torch.arange(9).reshape(3,3)
torch.gather(src,0,index)
torch.gather(src,1,index.T) #dim 为1时,index要转置
2、Scatter
scatter是将数据根据索引回填到新的矩阵里面,这个适合做onehot矩阵
1)对于2D转3D
如下图,进行回填,参考知乎
a = torch.rand(2, 5)
print(a)
b = torch.zeros(3, 5).scatter_(0, torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 0, 0], [2, 0, 0, 1, 2]]), a)
print(b)

制作one-hot的代码,参考PyTorch笔记之 scatter() 函数
class_num = 10
batch_size = 4
label = torch.LongTensor(batch_size, 1).random_() % class_num
#tensor([[6],
# [0],
# [3],
# [2]])
torch.zeros(batch_size, class_num).scatter_(1, label, 1)
#tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
# [1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
1)对于3D转4D的
这个对于图像分割的onehot制作比较多,这时,每个类别在一个面上设置为0或1,具体参考PyTorch One-Hot Labels
def make_one_hot(labels, C=2):
'''
Converts an integer label torch.autograd.Variable to a one-hot Variable.
Parameters
----------
labels : torch.autograd.Variable of torch.cuda.LongTensor
N x 1 x H x W, where N is batch size.
Each value is an integer representing correct classification.
C : integer.
number of classes in labels.
Returns
-------
target : torch.autograd.Variable of torch.cuda.FloatTensor
N x C x H x W, where C is class number. One-hot encoded.
'''
one_hot = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(labels.size(0), C, labels.size(2), labels.size(3)).zero_()
target = one_hot.scatter_(1, labels.data, 1)
target = Variable(target)
return target
具体结果为
>> labels = torch.LongTensor(4,4) % 3
2 1 0 0
1 0 0 0
2 0 0 1
2 0 0 1
[torch.LongTensor of size 4x4]
>> make_one_hot(labels)
(0 ,0 ,.,.) =
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0
(0 ,1 ,.,.) =
0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1
(0 ,2 ,.,.) =
1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
[torch.LongTensor of size 1x3x4x4]