在Tomcat中接收到具体的http请求,请求最后被一个具体的service处理,中间有一系列操作,有service的初始化、监听、过滤器等等操作,今天主要说的是service和URL的映射以及URL的匹配规则。和所有的web框架类似,URL肯定是有一个地方设置,然后关联具体的service,其他web框架有可能是使用正则(例如Django),Tomcat却是使用web.xml关联,接下来就讲讲映射的具体细节以及如何匹配到tomcat的wrap上
以下涉及到的源码版本:java8、Tomcat8.5.4
Tomcat 基础了解
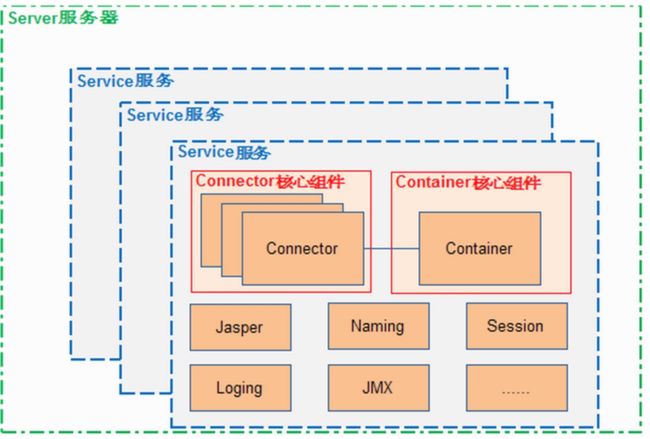
先了解下Tomcat的各个组件的关系吧
Tomcat是有个核心类叫做catalina,在启动的时候就是根据不同的参数加载catalina的不同模块的功能,例如生命周期、事件监听、组件管理等等。
Tomcat的server服务器可以包含多个service服务,每一个service服务都存在一个组件connector接收http请求,然后交给container组件去进行下一步的处理。如图包含了engine、host、context、wrapper四种组件,其中wrapper就是包含了用户实际开发的servlet服务。此外pipeline做为管道,一个组件只持有一个管道,然后管道上可以加上各种各样的阀门valve,通过动态配置valve,我们就可以实现数据的修改,监控等等各种操作。
在servlet规范中有明确的规定,servlet的服务时是使用ServletContext来传递上下文,在Tomcat中是实现了ApplicationContext去绑定service和context组件的,通过这样的绑定就可以间接的绑定connector,使得整个的上下文都可以持有。
public ApplicationContext(StandardContext context) {
super();
this.context = context;
this.service = ((Engine) context.getParent().getParent()).getService();
this.sessionCookieConfig = new ApplicationSessionCookieConfig(context);
// Populate session tracking modes
populateSessionTrackingModes();
}
URL配置
URL配置是通过配置web.xml的URL-pattern设置URL到servlet类的映射关系的,如下样例
ExactServlet
org.test.ExactServlet
ExactServlet
/exact.action
先明确好具体的servlet类,其中servlet-name表示一个servlet的名称,不允许重复,和具体的servlet-mapping对应,url-pattern就是我们关心的URL,现在一个*****/exact.action的URL请求过来,会被关联到org.test.ExactServlet类上。
URL有三种配置方法
- 完全匹配
/index.html - 目录匹配
/news/* - 后缀匹配
*.do
URL读取
在不看源码之前,如果我们实现该功能,第一步肯定是解析xml文件,找到具体的映射之间的关系,然后具体请求就根据某些规则匹配出最合适的servlet服务,如果匹配失败就会提示404错误。
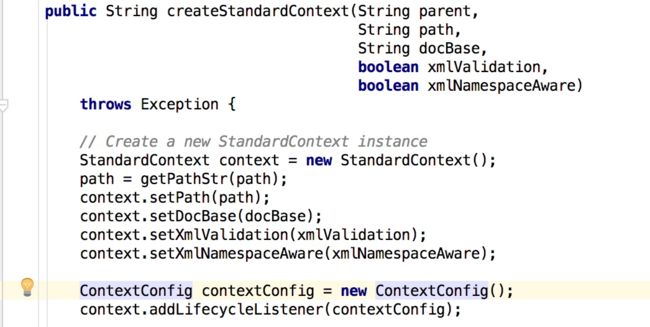
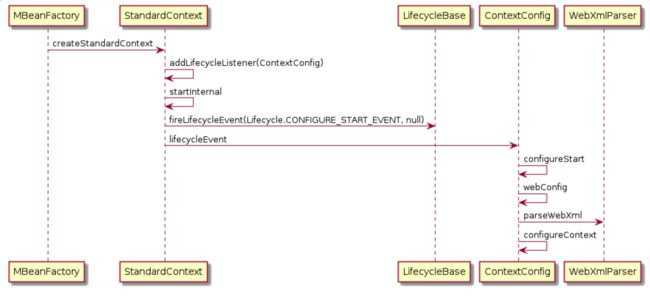
现在就看看源码具体的细节是如何操作的,其实Tomcat的具体实现和我们说的也基本类似(基本上的URL映射都是这个套路吧),入口是mbeanfactory类的createStandardContext方法,其中context加上了ContextConfig监听者
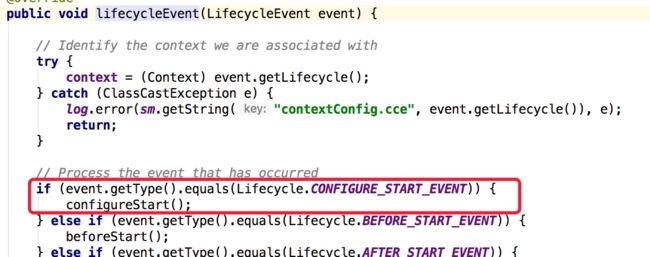
然后就是StandardContext类的启动,按照链路分析,发现在startInternal方法中有进行CONFIG_START_EVENT的监听事件触发
又因为上面加入的监听者是ContextConfig类,那么最后就进入到该类的事件处理方法上
configStart这个方法的名字就很直观,表示的是属性开始配置,又来到webConfig方法
通过WebXmlParse类的即系以及WebXml数据的存储,依旧是采用了digester的方式解析xml数据,中间通过各种操作,最后把数据存储到了StandardContext的servletMappings键值对中。
通过上述操作,就完成了URL从xml文件中到context的过渡工作。下面这个图简要的介绍下上面的整个流程(有些细节还未完全处理好)
URL映射
这一节介绍接收到一个http请求,URL是如何从socket被解析出来,映射到具体的servlet的一整个过程,包括了URL匹配的细节
作为一个http容器,必然存在接受socket套接字的数据,我们可以看到在Tomcat的启动时候的代码
其中getConnector()方法就是创建一个connector,使用配置好的端口号,http1.1的协议,并且把这个连接器组件绑定到service上。再回看上面的框架图,肯定知道在service中包含了一个engine组件,重点是在Mapper,关于解析socket数据不在此次介绍中。
Mapper的作用就是通过一系列的规则,最后匹配到合适的servlet去执行相应功能,具体的调用是由MapperListener监听器完成。在MapperListener类中监听到容器事件
@Override
public void containerEvent(ContainerEvent event) {
if (Container.ADD_CHILD_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
Container child = (Container) event.getData();
addListeners(child);
// 添加子容器
if (child.getState().isAvailable()) {
if (child instanceof Host) {
registerHost((Host) child);
} else if (child instanceof Context) {
registerContext((Context) child);
} else if (child instanceof Wrapper) {
// Only if the Context has started. If it has not, then it
// will have its own "after_start" life-cycle event later.
if (child.getParent().getState().isAvailable()) {
registerWrapper((Wrapper) child);
}
}
}
} else if (Container.REMOVE_CHILD_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
Container child = (Container) event.getData();
removeListeners(child);
// No need to unregister - life-cycle listener will handle this when
// the child stops
} else if (Host.ADD_ALIAS_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically adding host aliases
mapper.addHostAlias(((Host) event.getSource()).getName(),
event.getData().toString());
} else if (Host.REMOVE_ALIAS_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically removing host aliases
mapper.removeHostAlias(event.getData().toString());
} else if (Wrapper.ADD_MAPPING_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically adding wrappers
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) event.getSource();
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
String version = context.getWebappVersion();
String hostName = context.getParent().getName();
String wrapperName = wrapper.getName();
String mapping = (String) event.getData();
boolean jspWildCard = ("jsp".equals(wrapperName)
&& mapping.endsWith("/*"));
mapper.addWrapper(hostName, contextPath, version, mapping, wrapper,
jspWildCard, context.isResourceOnlyServlet(wrapperName));
} else if (Wrapper.REMOVE_MAPPING_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically removing wrappers
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) event.getSource();
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
String version = context.getWebappVersion();
String hostName = context.getParent().getName();
String mapping = (String) event.getData();
mapper.removeWrapper(hostName, contextPath, version, mapping);
} else if (Context.ADD_WELCOME_FILE_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically adding welcome files
Context context = (Context) event.getSource();
String hostName = context.getParent().getName();
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
String welcomeFile = (String) event.getData();
mapper.addWelcomeFile(hostName, contextPath,
context.getWebappVersion(), welcomeFile);
} else if (Context.REMOVE_WELCOME_FILE_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically removing welcome files
Context context = (Context) event.getSource();
String hostName = context.getParent().getName();
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
String welcomeFile = (String) event.getData();
mapper.removeWelcomeFile(hostName, contextPath,
context.getWebappVersion(), welcomeFile);
} else if (Context.CLEAR_WELCOME_FILES_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically clearing welcome files
Context context = (Context) event.getSource();
String hostName = context.getParent().getName();
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
mapper.clearWelcomeFiles(hostName, contextPath,
context.getWebappVersion());
}
}
仔细看这个代码没发现什么异常,可以细看会觉得有些不对劲,MapperListener作为service的监听器怎么可能接收到添加wrapper的,中间还嵌套了engine、host等容器,按照逻辑肯定是不能挂载wrapper的。回过头来再看StandardService类的启动方法
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
// 启动了engine
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
mapperListener.start();
// 当前standardservice的监听器也启动了
上述代码可知,在engine.start()的时候,engine以及engine的子容器,子容器的子容器也都顺利启动了,各个组件的嵌套关系也很明确,细看mapperListener.start()
public void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
Engine engine = service.getContainer();
if (engine == null) {
return;
}
findDefaultHost();
addListeners(engine);
// 比较关键的一步,加上监听器,也是我们当前关注的重点
Container[] conHosts = engine.findChildren();
// 开始处理engine的子容器
for (Container conHost : conHosts) {
Host host = (Host) conHost;
if (!LifecycleState.NEW.equals(host.getState())) {
// Registering the host will register the context and wrappers
registerHost(host);
// 注册host组件
}
}
}
private void addListeners(Container container) {
container.addContainerListener(this);
// 把该mapperlistener加入到容器的监听者中
container.addLifecycleListener(this);
for (Container child : container.findChildren()) {
// 针对engine而言子容器就是host,给每个host加上该mapperlistener
// 遍历所有的容器组件,给每个组件都加上mapperlistener监听器
addListeners(child);
}
}
上述代码已经很清楚的告诉我们,每一个容器都持有同一个mapperlistener监听器对象,所以上述的可以添加wrapper容器也可以很好的解释了,每一个组件都可以调用该方法,自然就存在挂载wrapper的情况了。
该函数内容较多,大部分事件都是在容器内插入新的子容器,以及插入子容器后续的事情,就以addMapping为例子
// 调用该addMapping的方法在StandardContext的addServletMapping方法内
// fireContainerEvent("addServletMapping", decodedPattern);
} else if (Wrapper.ADD_MAPPING_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Handle dynamically adding wrappers
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) event.getSource();
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
String version = context.getWebappVersion();
String hostName = context.getParent().getName();
String wrapperName = wrapper.getName();
String mapping = (String) event.getData();
boolean jspWildCard = ("jsp".equals(wrapperName)
&& mapping.endsWith("/*"));
mapper.addWrapper(hostName, contextPath, version, mapping, wrapper,
jspWildCard, context.isResourceOnlyServlet(wrapperName));
// mapper的addwrapper方法
protected void addWrapper(ContextVersion context, String path,
Wrapper wrapper, boolean jspWildCard, boolean resourceOnly) {
synchronized (context) {
if (path.endsWith("/*")) {
// Wildcard wrapper
String name = path.substring(0, path.length() - 2);
MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(name, wrapper,
jspWildCard, resourceOnly);
MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.wildcardWrappers;
MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1];
if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) {
context.wildcardWrappers = newWrappers;
int slashCount = slashCount(newWrapper.name);
if (slashCount > context.nesting) {
context.nesting = slashCount;
}
}
} else if (path.startsWith("*.")) {
// Extension wrapper
String name = path.substring(2);
MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(name, wrapper,
jspWildCard, resourceOnly);
MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.extensionWrappers;
MappedWrapper[] newWrappers =
new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1];
if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) {
context.extensionWrappers = newWrappers;
}
} else if (path.equals("/")) {
// Default wrapper
MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper("", wrapper,
jspWildCard, resourceOnly);
context.defaultWrapper = newWrapper;
} else {
// Exact wrapper
final String name;
if (path.length() == 0) {
// Special case for the Context Root mapping which is
// treated as an exact match
name = "/";
} else {
name = path;
}
MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(name, wrapper,
jspWildCard, resourceOnly);
MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.exactWrappers;
MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1];
if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) {
context.exactWrappers = newWrappers;
}
}
}
}
这里,我们可以看到路径分成4类,其中包含了我们上面说的三种分类情况,其实细看源码会发现,不同匹配规则会被放到不同类型的wrapper中,其中有
- /* 放在wildcardWrappers中
- *. 放在extensionWrappers中
- / 放在defaultWrapper中
- 其他 放在exactWrappers中
以上就完成了wrapper以及一系列容器的关联嵌套。
HTTP处理
一个新来的http请求,也需要找到合适的engine、host、context、wrapper进行处理,在接收到新的请求之后,在CoyoteAdapt类中调用map方法,再调用internalMap方法,这个方法中可以为mappingdata设置整个链路的容器(除了wrapper),最后的internalMapWrapper 明确最后的wrapper
// CoyoteAdapt
connector.getService().getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI,
version, request.getMappingData());
private final void internalMap(CharChunk host, CharChunk uri,
String version, MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
if (mappingData.host != null) {
// The legacy code (dating down at least to Tomcat 4.1) just
// skipped all mapping work in this case. That behaviour has a risk
// of returning an inconsistent result.
// I do not see a valid use case for it.
throw new AssertionError();
}
uri.setLimit(-1);
// Virtual host mapping
MappedHost[] hosts = this.hosts;
MappedHost mappedHost = exactFindIgnoreCase(hosts, host);
if (mappedHost == null) {
if (defaultHostName == null) {
return;
}
mappedHost = exactFind(hosts, defaultHostName);
if (mappedHost == null) {
return;
}
}
mappingData.host = mappedHost.object;
// Context mapping
ContextList contextList = mappedHost.contextList;
MappedContext[] contexts = contextList.contexts;
int pos = find(contexts, uri);
if (pos == -1) {
return;
}
int lastSlash = -1;
int uriEnd = uri.getEnd();
int length = -1;
boolean found = false;
MappedContext context = null;
while (pos >= 0) {
context = contexts[pos];
if (uri.startsWith(context.name)) {
length = context.name.length();
if (uri.getLength() == length) {
found = true;
break;
} else if (uri.startsWithIgnoreCase("/", length)) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (lastSlash == -1) {
lastSlash = nthSlash(uri, contextList.nesting + 1);
} else {
lastSlash = lastSlash(uri);
}
uri.setEnd(lastSlash);
pos = find(contexts, uri);
}
uri.setEnd(uriEnd);
if (!found) {
if (contexts[0].name.equals("")) {
context = contexts[0];
} else {
context = null;
}
}
if (context == null) {
return;
}
mappingData.contextPath.setString(context.name);
ContextVersion contextVersion = null;
ContextVersion[] contextVersions = context.versions;
final int versionCount = contextVersions.length;
if (versionCount > 1) {
Context[] contextObjects = new Context[contextVersions.length];
for (int i = 0; i < contextObjects.length; i++) {
contextObjects[i] = contextVersions[i].object;
}
mappingData.contexts = contextObjects;
if (version != null) {
contextVersion = exactFind(contextVersions, version);
}
}
if (contextVersion == null) {
// Return the latest version
// The versions array is known to contain at least one element
contextVersion = contextVersions[versionCount - 1];
}
mappingData.context = contextVersion.object;
mappingData.contextSlashCount = contextVersion.slashCount;
// Wrapper mapping
if (!contextVersion.isPaused()) {
internalMapWrapper(contextVersion, uri, mappingData);
}
}
// 根据URL匹配具体的wrapper规则
private final void internalMapWrapper(ContextVersion contextVersion,
CharChunk path,
MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {
int pathOffset = path.getOffset();
int pathEnd = path.getEnd();
boolean noServletPath = false;
int length = contextVersion.path.length();
if (length == (pathEnd - pathOffset)) {
noServletPath = true;
}
int servletPath = pathOffset + length;
path.setOffset(servletPath);
// Rule 1 -- Exact Match
MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = contextVersion.exactWrappers;
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 2 -- Prefix Match
boolean checkJspWelcomeFiles = false;
MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = contextVersion.wildcardWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
internalMapWildcardWrapper(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
if (mappingData.wrapper != null && mappingData.jspWildCard) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/') {
/*
* Path ending in '/' was mapped to JSP servlet based on
* wildcard match (e.g., as specified in url-pattern of a
* jsp-property-group.
* Force the context's welcome files, which are interpreted
* as JSP files (since they match the url-pattern), to be
* considered. See Bugzilla 27664.
*/
mappingData.wrapper = null;
checkJspWelcomeFiles = true;
} else {
// See Bugzilla 27704
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars(buf, path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.pathInfo.recycle();
}
}
}
if(mappingData.wrapper == null && noServletPath &&
contextVersion.object.getMapperContextRootRedirectEnabled()) {
// The path is empty, redirect to "/"
path.append('/');
pathEnd = path.getEnd();
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), pathOffset, pathEnd - pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd - 1);
return;
}
// Rule 3 -- Extension Match
MappedWrapper[] extensionWrappers = contextVersion.extensionWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData,
true);
}
// Rule 4 -- Welcome resources processing for servlets
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles;
if (!checkWelcomeFiles) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/');
}
if (checkWelcomeFiles) {
for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length)
&& (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) {
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0,
contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length());
path.setOffset(servletPath);
// Rule 4a -- Welcome resources processing for exact macth
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 4b -- Welcome resources processing for prefix match
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
internalMapWildcardWrapper
(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
}
// Rule 4c -- Welcome resources processing
// for physical folder
if (mappingData.wrapper == null
&& contextVersion.resources != null) {
String pathStr = path.toString();
WebResource file =
contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr);
if (file != null && file.isFile()) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path,
mappingData, true);
if (mappingData.wrapper == null
&& contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) {
mappingData.wrapper =
contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object;
mappingData.requestPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
}
}
}
path.setOffset(servletPath);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
}
/* welcome file processing - take 2
* Now that we have looked for welcome files with a physical
* backing, now look for an extension mapping listed
* but may not have a physical backing to it. This is for
* the case of index.jsf, index.do, etc.
* A watered down version of rule 4
*/
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles;
if (!checkWelcomeFiles) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/');
}
if (checkWelcomeFiles) {
for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length)
&& (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) {
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0,
contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length());
path.setOffset(servletPath);
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path,
mappingData, false);
}
path.setOffset(servletPath);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
}
// Rule 7 -- Default servlet
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
if (contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) {
mappingData.wrapper = contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object;
mappingData.requestPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
mappingData.matchType = MappingMatch.DEFAULT;
}
// Redirection to a folder
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (contextVersion.resources != null && buf[pathEnd -1 ] != '/') {
String pathStr = path.toString();
WebResource file;
// Handle context root
if (pathStr.length() == 0) {
file = contextVersion.resources.getResource("/");
} else {
file = contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr);
}
if (file != null && file.isDirectory() &&
contextVersion.object.getMapperDirectoryRedirectEnabled()) {
// Note: this mutates the path: do not do any processing
// after this (since we set the redirectPath, there
// shouldn't be any)
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.append('/');
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
} else {
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
}
}
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
以上过程也知道了,只要一个http请求解析出http协议的字段信息,就立马明确了其整个的执行链路过程,链路数据是存储在mappingdata中,这点和Tomcat4有些不一样