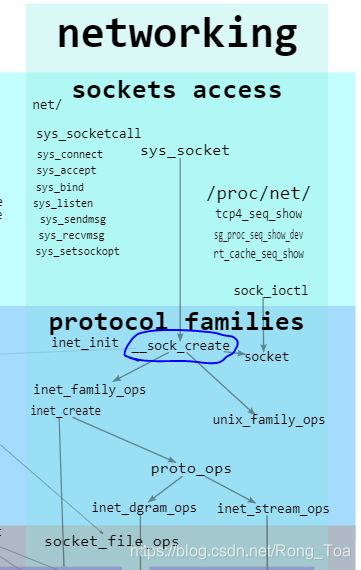
Linux内核协议栈- 创建socket:__sock_create函数调用关系
Table of Contents
__sock_create函数
结构
socket_state
struct socket
struct sock
struct proto_ops
函数原型
__sock_create
security_socket_create
call_int_hook
socket_create
selinux_socket_create
socket_sockcreate_sid
security_transition_sid
sock_alloc
security_socket_post_create
socket_post_create
selinux_socket_post_create
__sock_create函数
int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
struct socket **res, int kern);其在linux内核中的位置:
结构
socket_state
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/latest/source/include/uapi/linux/net.h#L54
typedef enum {
SS_FREE = 0, /* not allocated */
SS_UNCONNECTED, /* unconnected to any socket */
SS_CONNECTING, /* in process of connecting */
SS_CONNECTED, /* connected to socket */
SS_DISCONNECTING /* in process of disconnecting */
} socket_state;struct socket
/**
* struct socket - general BSD socket
* @state: socket state (%SS_CONNECTED, etc)
* @type: socket type (%SOCK_STREAM, etc)
* @flags: socket flags (%SOCK_NOSPACE, etc)
* @ops: protocol specific socket operations
* @file: File back pointer for gc
* @sk: internal networking protocol agnostic socket representation
* @wq: wait queue for several uses
* https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/latest/source/include/linux/net.h#L112
*/
struct socket {
socket_state state;
short type;
unsigned long flags;
struct file *file;
struct sock *sk;
const struct proto_ops *ops;
struct socket_wq wq;
};struct sock
/**
* struct sock - network layer representation of sockets
* @__sk_common: shared layout with inet_timewait_sock
* @sk_shutdown: mask of %SEND_SHUTDOWN and/or %RCV_SHUTDOWN
* @sk_userlocks: %SO_SNDBUF and %SO_RCVBUF settings
* @sk_lock: synchronizer
* @sk_kern_sock: True if sock is using kernel lock classes
* @sk_rcvbuf: size of receive buffer in bytes
* @sk_wq: sock wait queue and async head
* @sk_rx_dst: receive input route used by early demux
* @sk_dst_cache: destination cache
* @sk_dst_pending_confirm: need to confirm neighbour
* @sk_policy: flow policy
* @sk_rx_skb_cache: cache copy of recently accessed RX skb
* @sk_receive_queue: incoming packets
* @sk_wmem_alloc: transmit queue bytes committed
* @sk_tsq_flags: TCP Small Queues flags
* @sk_write_queue: Packet sending queue
* @sk_omem_alloc: "o" is "option" or "other"
* @sk_wmem_queued: persistent queue size
* @sk_forward_alloc: space allocated forward
* @sk_napi_id: id of the last napi context to receive data for sk
* @sk_ll_usec: usecs to busypoll when there is no data
* @sk_allocation: allocation mode
* @sk_pacing_rate: Pacing rate (if supported by transport/packet scheduler)
* @sk_pacing_status: Pacing status (requested, handled by sch_fq)
* @sk_max_pacing_rate: Maximum pacing rate (%SO_MAX_PACING_RATE)
* @sk_sndbuf: size of send buffer in bytes
* @__sk_flags_offset: empty field used to determine location of bitfield
* @sk_padding: unused element for alignment
* @sk_no_check_tx: %SO_NO_CHECK setting, set checksum in TX packets
* @sk_no_check_rx: allow zero checksum in RX packets
* @sk_route_caps: route capabilities (e.g. %NETIF_F_TSO)
* @sk_route_nocaps: forbidden route capabilities (e.g NETIF_F_GSO_MASK)
* @sk_route_forced_caps: static, forced route capabilities
* (set in tcp_init_sock())
* @sk_gso_type: GSO type (e.g. %SKB_GSO_TCPV4)
* @sk_gso_max_size: Maximum GSO segment size to build
* @sk_gso_max_segs: Maximum number of GSO segments
* @sk_pacing_shift: scaling factor for TCP Small Queues
* @sk_lingertime: %SO_LINGER l_linger setting
* @sk_backlog: always used with the per-socket spinlock held
* @sk_callback_lock: used with the callbacks in the end of this struct
* @sk_error_queue: rarely used
* @sk_prot_creator: sk_prot of original sock creator (see ipv6_setsockopt,
* IPV6_ADDRFORM for instance)
* @sk_err: last error
* @sk_err_soft: errors that don't cause failure but are the cause of a
* persistent failure not just 'timed out'
* @sk_drops: raw/udp drops counter
* @sk_ack_backlog: current listen backlog
* @sk_max_ack_backlog: listen backlog set in listen()
* @sk_uid: user id of owner
* @sk_priority: %SO_PRIORITY setting
* @sk_type: socket type (%SOCK_STREAM, etc)
* @sk_protocol: which protocol this socket belongs in this network family
* @sk_peer_pid: &struct pid for this socket's peer
* @sk_peer_cred: %SO_PEERCRED setting
* @sk_rcvlowat: %SO_RCVLOWAT setting
* @sk_rcvtimeo: %SO_RCVTIMEO setting
* @sk_sndtimeo: %SO_SNDTIMEO setting
* @sk_txhash: computed flow hash for use on transmit
* @sk_filter: socket filtering instructions
* @sk_timer: sock cleanup timer
* @sk_stamp: time stamp of last packet received
* @sk_stamp_seq: lock for accessing sk_stamp on 32 bit architectures only
* @sk_tsflags: SO_TIMESTAMPING socket options
* @sk_tskey: counter to disambiguate concurrent tstamp requests
* @sk_zckey: counter to order MSG_ZEROCOPY notifications
* @sk_socket: Identd and reporting IO signals
* @sk_user_data: RPC layer private data
* @sk_frag: cached page frag
* @sk_peek_off: current peek_offset value
* @sk_send_head: front of stuff to transmit
* @tcp_rtx_queue: TCP re-transmit queue [union with @sk_send_head]
* @sk_tx_skb_cache: cache copy of recently accessed TX skb
* @sk_security: used by security modules
* @sk_mark: generic packet mark
* @sk_cgrp_data: cgroup data for this cgroup
* @sk_memcg: this socket's memory cgroup association
* @sk_write_pending: a write to stream socket waits to start
* @sk_state_change: callback to indicate change in the state of the sock
* @sk_data_ready: callback to indicate there is data to be processed
* @sk_write_space: callback to indicate there is bf sending space available
* @sk_error_report: callback to indicate errors (e.g. %MSG_ERRQUEUE)
* @sk_backlog_rcv: callback to process the backlog
* @sk_validate_xmit_skb: ptr to an optional validate function
* @sk_destruct: called at sock freeing time, i.e. when all refcnt == 0
* @sk_reuseport_cb: reuseport group container
* @sk_bpf_storage: ptr to cache and control for bpf_sk_storage
* @sk_rcu: used during RCU grace period
* @sk_clockid: clockid used by time-based scheduling (SO_TXTIME)
* @sk_txtime_deadline_mode: set deadline mode for SO_TXTIME
* @sk_txtime_report_errors: set report errors mode for SO_TXTIME
* @sk_txtime_unused: unused txtime flags
* https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/latest/source/include/net/sock.h#L346
*/
struct sock {
/*
* Now struct inet_timewait_sock also uses sock_common, so please just
* don't add nothing before this first member (__sk_common) --acme
*/
struct sock_common __sk_common;
#define sk_node __sk_common.skc_node
#define sk_nulls_node __sk_common.skc_nulls_node
#define sk_refcnt __sk_common.skc_refcnt
#define sk_tx_queue_mapping __sk_common.skc_tx_queue_mapping
#ifdef CONFIG_XPS
#define sk_rx_queue_mapping __sk_common.skc_rx_queue_mapping
#endif
#define sk_dontcopy_begin __sk_common.skc_dontcopy_begin
#define sk_dontcopy_end __sk_common.skc_dontcopy_end
#define sk_hash __sk_common.skc_hash
#define sk_portpair __sk_common.skc_portpair
#define sk_num __sk_common.skc_num
#define sk_dport __sk_common.skc_dport
#define sk_addrpair __sk_common.skc_addrpair
#define sk_daddr __sk_common.skc_daddr
#define sk_rcv_saddr __sk_common.skc_rcv_saddr
#define sk_family __sk_common.skc_family
#define sk_state __sk_common.skc_state
#define sk_reuse __sk_common.skc_reuse
#define sk_reuseport __sk_common.skc_reuseport
#define sk_ipv6only __sk_common.skc_ipv6only
#define sk_net_refcnt __sk_common.skc_net_refcnt
#define sk_bound_dev_if __sk_common.skc_bound_dev_if
#define sk_bind_node __sk_common.skc_bind_node
#define sk_prot __sk_common.skc_prot
#define sk_net __sk_common.skc_net
#define sk_v6_daddr __sk_common.skc_v6_daddr
#define sk_v6_rcv_saddr __sk_common.skc_v6_rcv_saddr
#define sk_cookie __sk_common.skc_cookie
#define sk_incoming_cpu __sk_common.skc_incoming_cpu
#define sk_flags __sk_common.skc_flags
#define sk_rxhash __sk_common.skc_rxhash
socket_lock_t sk_lock;
atomic_t sk_drops;
int sk_rcvlowat;
struct sk_buff_head sk_error_queue;
struct sk_buff *sk_rx_skb_cache;
struct sk_buff_head sk_receive_queue;
/*
* The backlog queue is special, it is always used with
* the per-socket spinlock held and requires low latency
* access. Therefore we special case it's implementation.
* Note : rmem_alloc is in this structure to fill a hole
* on 64bit arches, not because its logically part of
* backlog.
*/
struct {
atomic_t rmem_alloc;
int len;
struct sk_buff *head;
struct sk_buff *tail;
} sk_backlog;
#define sk_rmem_alloc sk_backlog.rmem_alloc
int sk_forward_alloc;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
unsigned int sk_ll_usec;
/* ===== mostly read cache line ===== */
unsigned int sk_napi_id;
#endif
int sk_rcvbuf;
struct sk_filter __rcu *sk_filter;
union {
struct socket_wq __rcu *sk_wq;
/* private: */
struct socket_wq *sk_wq_raw;
/* public: */
};
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct xfrm_policy __rcu *sk_policy[2];
#endif
struct dst_entry *sk_rx_dst;
struct dst_entry __rcu *sk_dst_cache;
atomic_t sk_omem_alloc;
int sk_sndbuf;
/* ===== cache line for TX ===== */
int sk_wmem_queued;
refcount_t sk_wmem_alloc;
unsigned long sk_tsq_flags;
union {
struct sk_buff *sk_send_head;
struct rb_root tcp_rtx_queue;
};
struct sk_buff *sk_tx_skb_cache;
struct sk_buff_head sk_write_queue;
__s32 sk_peek_off;
int sk_write_pending;
__u32 sk_dst_pending_confirm;
u32 sk_pacing_status; /* see enum sk_pacing */
long sk_sndtimeo;
struct timer_list sk_timer;
__u32 sk_priority;
__u32 sk_mark;
unsigned long sk_pacing_rate; /* bytes per second */
unsigned long sk_max_pacing_rate;
struct page_frag sk_frag;
netdev_features_t sk_route_caps;
netdev_features_t sk_route_nocaps;
netdev_features_t sk_route_forced_caps;
int sk_gso_type;
unsigned int sk_gso_max_size;
gfp_t sk_allocation;
__u32 sk_txhash;
/*
* Because of non atomicity rules, all
* changes are protected by socket lock.
*/
u8 sk_padding : 1,
sk_kern_sock : 1,
sk_no_check_tx : 1,
sk_no_check_rx : 1,
sk_userlocks : 4;
u8 sk_pacing_shift;
u16 sk_type;
u16 sk_protocol;
u16 sk_gso_max_segs;
unsigned long sk_lingertime;
struct proto *sk_prot_creator;
rwlock_t sk_callback_lock;
int sk_err,
sk_err_soft;
u32 sk_ack_backlog;
u32 sk_max_ack_backlog;
kuid_t sk_uid;
struct pid *sk_peer_pid;
const struct cred *sk_peer_cred;
long sk_rcvtimeo;
ktime_t sk_stamp;
#if BITS_PER_LONG==32
seqlock_t sk_stamp_seq;
#endif
u16 sk_tsflags;
u8 sk_shutdown;
u32 sk_tskey;
atomic_t sk_zckey;
u8 sk_clockid;
u8 sk_txtime_deadline_mode : 1,
sk_txtime_report_errors : 1,
sk_txtime_unused : 6;
struct socket *sk_socket;
void *sk_user_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *sk_security;
#endif
struct sock_cgroup_data sk_cgrp_data;
struct mem_cgroup *sk_memcg;
void (*sk_state_change)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_data_ready)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_write_space)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_error_report)(struct sock *sk);
int (*sk_backlog_rcv)(struct sock *sk,
struct sk_buff *skb);
#ifdef CONFIG_SOCK_VALIDATE_XMIT
struct sk_buff* (*sk_validate_xmit_skb)(struct sock *sk,
struct net_device *dev,
struct sk_buff *skb);
#endif
void (*sk_destruct)(struct sock *sk);
struct sock_reuseport __rcu *sk_reuseport_cb;
#ifdef CONFIG_BPF_SYSCALL
struct bpf_sk_storage __rcu *sk_bpf_storage;
#endif
struct rcu_head sk_rcu;
};struct proto_ops
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Rong_Toa/article/details/105327127
struct proto_ops {
int family;
struct module *owner;
int (*release) (struct socket *sock);
int (*bind) (struct socket *sock,
struct sockaddr *myaddr,
int sockaddr_len);
int (*connect) (struct socket *sock,
struct sockaddr *vaddr,
int sockaddr_len, int flags);
int (*socketpair)(struct socket *sock1,
struct socket *sock2);
int (*accept) (struct socket *sock,
struct socket *newsock, int flags, bool kern);
int (*getname) (struct socket *sock,
struct sockaddr *addr,
int peer);
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *file, struct socket *sock,
struct poll_table_struct *wait);
int (*ioctl) (struct socket *sock, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
int (*compat_ioctl) (struct socket *sock, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg);
#endif
int (*gettstamp) (struct socket *sock, void __user *userstamp,
bool timeval, bool time32);
int (*listen) (struct socket *sock, int len);
int (*shutdown) (struct socket *sock, int flags);
int (*setsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval, unsigned int optlen);
int (*getsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval, int __user *optlen);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
int (*compat_setsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval, unsigned int optlen);
int (*compat_getsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval, int __user *optlen);
#endif
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct socket *sock);
int (*sendmsg) (struct socket *sock, struct msghdr *m,
size_t total_len);
/* Notes for implementing recvmsg:
* ===============================
* msg->msg_namelen should get updated by the recvmsg handlers
* iff msg_name != NULL. It is by default 0 to prevent
* returning uninitialized memory to user space. The recvfrom
* handlers can assume that msg.msg_name is either NULL or has
* a minimum size of sizeof(struct sockaddr_storage).
*/
int (*recvmsg) (struct socket *sock, struct msghdr *m,
size_t total_len, int flags);
int (*mmap) (struct file *file, struct socket *sock,
struct vm_area_struct * vma);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct socket *sock, struct page *page,
int offset, size_t size, int flags);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct socket *sock, loff_t *ppos,
struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, size_t len, unsigned int flags);
int (*set_peek_off)(struct sock *sk, int val);
int (*peek_len)(struct socket *sock);
/* The following functions are called internally by kernel with
* sock lock already held.
*/
int (*read_sock)(struct sock *sk, read_descriptor_t *desc,
sk_read_actor_t recv_actor);
int (*sendpage_locked)(struct sock *sk, struct page *page,
int offset, size_t size, int flags);
int (*sendmsg_locked)(struct sock *sk, struct msghdr *msg,
size_t size);
int (*set_rcvlowat)(struct sock *sk, int val);
};函数原型
__sock_create
/**
* __sock_create - creates a socket
* @net: net namespace
* @family: protocol family (AF_INET, ...)
* @type: communication type (SOCK_STREAM, ...)
* @protocol: protocol (0, ...)
* @res: new socket
* @kern: boolean for kernel space sockets
*
* Creates a new socket and assigns it to @res, passing through LSM.
* Returns 0 or an error. On failure @res is set to %NULL. @kern must
* be set to true if the socket resides in kernel space.
* This function internally uses GFP_KERNEL.
*/
int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
struct socket **res, int kern)
{
int err;
struct socket *sock;
const struct net_proto_family *pf;
/*
* Check protocol is in range
*/
if (family < 0 || family >= NPROTO)
return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (type < 0 || type >= SOCK_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
/* Compatibility.
This uglymoron is moved from INET layer to here to avoid
deadlock in module load.
*/
if (family == PF_INET && type == SOCK_PACKET) {
pr_info_once("%s uses obsolete (PF_INET,SOCK_PACKET)\n",
current->comm);
family = PF_PACKET;
}
err = security_socket_create(family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
return err;
/*
* Allocate the socket and allow the family to set things up. if
* the protocol is 0, the family is instructed to select an appropriate
* default.
*/
sock = sock_alloc();
if (!sock) {
net_warn_ratelimited("socket: no more sockets\n");
return -ENFILE; /* Not exactly a match, but its the
closest posix thing */
}
sock->type = type;
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULES
/* Attempt to load a protocol module if the find failed.
*
* 12/09/1996 Marcin: But! this makes REALLY only sense, if the user
* requested real, full-featured networking support upon configuration.
* Otherwise module support will break!
*/
if (rcu_access_pointer(net_families[family]) == NULL)
request_module("net-pf-%d", family);
#endif
rcu_read_lock();
pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]);
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (!pf)
goto out_release;
/*
* We will call the ->create function, that possibly is in a loadable
* module, so we have to bump that loadable module refcnt first.
*/
if (!try_module_get(pf->owner))
goto out_release;
/* Now protected by module ref count */
rcu_read_unlock();
err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern);
if (err < 0)
goto out_module_put;
/*
* Now to bump the refcnt of the [loadable] module that owns this
* socket at sock_release time we decrement its refcnt.
*/
if (!try_module_get(sock->ops->owner))
goto out_module_busy;
/*
* Now that we're done with the ->create function, the [loadable]
* module can have its refcnt decremented
*/
module_put(pf->owner);
err = security_socket_post_create(sock, family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
goto out_sock_release;
*res = sock;
return 0;
out_module_busy:
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
out_module_put:
sock->ops = NULL;
module_put(pf->owner);
out_sock_release:
sock_release(sock);
return err;
out_release:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out_sock_release;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__sock_create);security_socket_create
int security_socket_create(int family, int type, int protocol, int kern)
{
return call_int_hook(socket_create, 0, family, type, protocol, kern);
}call_int_hook
#define call_int_hook(FUNC, IRC, ...) ({ \
int RC = IRC; \
do { \
struct security_hook_list *P; \
\
hlist_for_each_entry(P, &security_hook_heads.FUNC, list) { \
RC = P->hook.FUNC(__VA_ARGS__); \
if (RC != 0) \
break; \
} \
} while (0); \
RC; \
})socket_create
翻阅linux4.20.11源码hooks.c,找到
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_create, selinux_socket_create),selinux_socket_create
static int selinux_socket_create(int family, int type,
int protocol, int kern)
{
const struct task_security_struct *tsec = current_security();
u32 newsid;
u16 secclass;
int rc;
if (kern)
return 0;
secclass = socket_type_to_security_class(family, type, protocol);
rc = socket_sockcreate_sid(tsec, secclass, &newsid);
if (rc)
return rc;
return avc_has_perm(&selinux_state,
tsec->sid, newsid, secclass, SOCKET__CREATE, NULL);
}socket_sockcreate_sid
/* socket security operations */
static int socket_sockcreate_sid(const struct task_security_struct *tsec,
u16 secclass, u32 *socksid)
{
if (tsec->sockcreate_sid > SECSID_NULL) {
*socksid = tsec->sockcreate_sid;
return 0;
}
return security_transition_sid(&selinux_state, tsec->sid, tsec->sid,
secclass, NULL, socksid);
}security_transition_sid
int security_transition_sid(struct selinux_state *state,
u32 ssid, u32 tsid, u16 tclass,
const struct qstr *qstr, u32 *out_sid)
{
return security_compute_sid(state, ssid, tsid, tclass,
AVTAB_TRANSITION,
qstr ? qstr->name : NULL, out_sid, true);
}sock_alloc
该函数中创建了inode
/**
* sock_alloc - allocate a socket
*
* Allocate a new inode and socket object. The two are bound together
* and initialised. The socket is then returned. If we are out of inodes
* NULL is returned. This functions uses GFP_KERNEL internally.
*/
struct socket *sock_alloc(void)
{
struct inode *inode;
struct socket *sock;
inode = new_inode_pseudo(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
if (!inode)
return NULL;
sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
inode->i_ino = get_next_ino();
inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
inode->i_op = &sockfs_inode_ops;
return sock;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sock_alloc);security_socket_post_create
socket_post_create
int security_socket_post_create(struct socket *sock, int family,
int type, int protocol, int kern)
{
return call_int_hook(socket_post_create, 0, sock, family, type,
protocol, kern);
}
...
LSM_HOOK_INIT(socket_post_create, selinux_socket_post_create),selinux_socket_post_create
static int selinux_socket_post_create(struct socket *sock, int family,
int type, int protocol, int kern)
{
const struct task_security_struct *tsec = current_security();
struct inode_security_struct *isec = inode_security_novalidate(SOCK_INODE(sock));
struct sk_security_struct *sksec;
u16 sclass = socket_type_to_security_class(family, type, protocol);
u32 sid = SECINITSID_KERNEL;
int err = 0;
if (!kern) {
err = socket_sockcreate_sid(tsec, sclass, &sid);
if (err)
return err;
}
isec->sclass = sclass;
isec->sid = sid;
isec->initialized = LABEL_INITIALIZED;
if (sock->sk) {
sksec = sock->sk->sk_security;
sksec->sclass = sclass;
sksec->sid = sid;
/* Allows detection of the first association on this socket */
if (sksec->sclass == SECCLASS_SCTP_SOCKET)
sksec->sctp_assoc_state = SCTP_ASSOC_UNSET;
err = selinux_netlbl_socket_post_create(sock->sk, family);
}
return err;
}
参考链接:
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/latest/source/net/socket.c#L1362
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/latest/source/security/security.c#L2010
详解请听下回分解。