前言
MySQL8.0之前,做数据排名统计等相当痛苦,因为没有像Oracle、SQL SERVER 、PostgreSQL等其他数据库那样的窗口函数。但随着MySQL8.0中新增了窗口函数之后,针对这类统计就再也不是事了,本文就以常用的排序实例介绍MySQL的窗口函数。
1、准备工作
创建表及测试数据
mysql> create database testdb; Database changed /* 创建表 */ create table tb_score(id int primary key auto_increment,stu_no varchar(10),course varchar(50),score decimal(4,1),key idx_stuNo_course(stu_no,course)); mysql> show tables; +------------------+ | Tables_in_testdb | +------------------+ | tb_score | +------------------+ /* 新增一批测试数据 */ insert into tb_score(stu_no,course,score)values('2020001','mysql',90),('2020001','C++',85),('2020003','English',100),('2020002','mysql',50),('2020002','C++',70),('2020002','English',99); insert into tb_score(stu_no,course,score)values('2020003','mysql',78),('2020003','C++',81),('2020003','English',80),('2020004','mysql',80),('2020004','C++',60),('2020004','English',100); insert into tb_score(stu_no,course,score)values('2020005','mysql',98),('2020005','C++',96),('2020005','English',70),('2020006','mysql',60),('2020006','C++',90),('2020006','English',70); insert into tb_score(stu_no,course,score)values('2020007','mysql',50),('2020007','C++',66),('2020007','English',76),('2020008','mysql',90),('2020008','C++',69),('2020008','English',86); insert into tb_score(stu_no,course,score)values('2020009','mysql',70),('2020009','C++',66),('2020009','English',86),('2020010','mysql',75),('2020010','C++',76),('2020010','English',81); insert into tb_score(stu_no,course,score)values('2020011','mysql',90),('2020012','C++',85),('2020011','English',84),('2020012','English',75),('2020013','C++',96),('2020013','English',88);
2、统计每门课程分数的排名
根据每门课程的分数从高到低进行排名,此时,会出现分数相同时怎么处理的问题,下面就根据不同的窗口函数来处理不同场景的需求
ROW_NUMBER
由结果可以看出,分数相同时按照学号顺序进行排名
mysql> select stu_no,course,score,row_number() over(PARTITION by course order by score desc) as rn from tb_score; +---------+---------+-------+----+ | stu_no | course | score | rn | +---------+---------+-------+----+ | 2020005 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | | 2020013 | C++ | 96.0 | 2 | | 2020006 | C++ | 90.0 | 3 | | 2020001 | C++ | 85.0 | 4 | | 2020012 | C++ | 85.0 | 5 | | 2020003 | C++ | 81.0 | 6 | | 2020010 | C++ | 76.0 | 7 | | 2020002 | C++ | 70.0 | 8 | | 2020008 | C++ | 69.0 | 9 | | 2020007 | C++ | 66.0 | 10 | | 2020009 | C++ | 66.0 | 11 | | 2020004 | C++ | 60.0 | 12 | | 2020003 | English | 100.0 | 1 | | 2020004 | English | 100.0 | 2 | | 2020002 | English | 99.0 | 3 | | 2020013 | English | 88.0 | 4 | | 2020008 | English | 86.0 | 5 | | 2020009 | English | 86.0 | 6 | | 2020011 | English | 84.0 | 7 | | 2020010 | English | 81.0 | 8 | | 2020003 | English | 80.0 | 9 | | 2020007 | English | 76.0 | 10 | | 2020012 | English | 75.0 | 11 | | 2020005 | English | 70.0 | 12 | | 2020006 | English | 70.0 | 13 | | 2020005 | mysql | 98.0 | 1 | | 2020001 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020008 | mysql | 90.0 | 3 | | 2020011 | mysql | 90.0 | 4 | | 2020004 | mysql | 80.0 | 5 | | 2020003 | mysql | 78.0 | 6 | | 2020010 | mysql | 75.0 | 7 | | 2020009 | mysql | 70.0 | 8 | | 2020006 | mysql | 60.0 | 9 | | 2020002 | mysql | 50.0 | 10 | | 2020007 | mysql | 50.0 | 11 | +---------+---------+-------+----+
DENSE_RANK
为了让分数相同时排名也相同,则可以使用DENSE_RANK函数,结果如下:
mysql> select stu_no,course,score,DENSE_RANK() over(partition by course order by score desc) rn from tb_score; +---------+---------+-------+----+ | stu_no | course | score | rn | +---------+---------+-------+----+ | 2020005 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | | 2020013 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | | 2020006 | C++ | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020001 | C++ | 85.0 | 3 | | 2020012 | C++ | 85.0 | 3 | | 2020003 | C++ | 81.0 | 4 | | 2020010 | C++ | 76.0 | 5 | | 2020002 | C++ | 70.0 | 6 | | 2020008 | C++ | 69.0 | 7 | | 2020007 | C++ | 66.0 | 8 | | 2020009 | C++ | 66.0 | 8 | | 2020004 | C++ | 60.0 | 9 | | 2020003 | English | 100.0 | 1 | | 2020004 | English | 100.0 | 1 | | 2020002 | English | 99.0 | 2 | | 2020013 | English | 88.0 | 3 | | 2020008 | English | 86.0 | 4 | | 2020009 | English | 86.0 | 4 | | 2020011 | English | 84.0 | 5 | | 2020010 | English | 81.0 | 6 | | 2020003 | English | 80.0 | 7 | | 2020007 | English | 76.0 | 8 | | 2020012 | English | 75.0 | 9 | | 2020005 | English | 70.0 | 10 | | 2020006 | English | 70.0 | 10 | | 2020005 | mysql | 98.0 | 1 | | 2020001 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020008 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020011 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020004 | mysql | 80.0 | 3 | | 2020003 | mysql | 78.0 | 4 | | 2020010 | mysql | 75.0 | 5 | | 2020009 | mysql | 70.0 | 6 | | 2020006 | mysql | 60.0 | 7 | | 2020002 | mysql | 50.0 | 8 | | 2020007 | mysql | 50.0 | 8 | +---------+---------+-------+----+
RANK
DENSE_RANK的结果是分数相同时排名相同了,但是下一个名次是紧接着上一个名次的,如果2个并列的第1之后,下一个我想是第3名,则可以使用RANK函数实现
mysql> select stu_no,course,score,rank() over(partition by course order by score desc) rn from tb_score; +---------+---------+-------+----+ | stu_no | course | score | rn | +---------+---------+-------+----+ | 2020005 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | | 2020013 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | | 2020006 | C++ | 90.0 | 3 | | 2020001 | C++ | 85.0 | 4 | | 2020012 | C++ | 85.0 | 4 | | 2020003 | C++ | 81.0 | 6 | | 2020010 | C++ | 76.0 | 7 | | 2020002 | C++ | 70.0 | 8 | | 2020008 | C++ | 69.0 | 9 | | 2020007 | C++ | 66.0 | 10 | | 2020009 | C++ | 66.0 | 10 | | 2020004 | C++ | 60.0 | 12 | | 2020003 | English | 100.0 | 1 | | 2020004 | English | 100.0 | 1 | | 2020002 | English | 99.0 | 3 | | 2020013 | English | 88.0 | 4 | | 2020008 | English | 86.0 | 5 | | 2020009 | English | 86.0 | 5 | | 2020011 | English | 84.0 | 7 | | 2020010 | English | 81.0 | 8 | | 2020003 | English | 80.0 | 9 | | 2020007 | English | 76.0 | 10 | | 2020012 | English | 75.0 | 11 | | 2020005 | English | 70.0 | 12 | | 2020006 | English | 70.0 | 12 | | 2020005 | mysql | 98.0 | 1 | | 2020001 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020008 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020011 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | | 2020004 | mysql | 80.0 | 5 | | 2020003 | mysql | 78.0 | 6 | | 2020010 | mysql | 75.0 | 7 | | 2020009 | mysql | 70.0 | 8 | | 2020006 | mysql | 60.0 | 9 | | 2020002 | mysql | 50.0 | 10 | | 2020007 | mysql | 50.0 | 10 | +---------+---------+-------+----+
这样就实现了各种排序需求。
NTILE
NTILE函数的作用是对每个分组排名后,再将对应分组分成N个小组,例如
mysql> select stu_no,course,score,rank() over(partition by course order by score desc) rn,NTILE(2) over(partition by course order by score desc) rn_group from tb_score; +---------+---------+-------+----+----------+ | stu_no | course | score | rn | rn_group | +---------+---------+-------+----+----------+ | 2020005 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | 1 | | 2020013 | C++ | 96.0 | 1 | 1 | | 2020006 | C++ | 90.0 | 3 | 1 | | 2020001 | C++ | 85.0 | 4 | 1 | | 2020012 | C++ | 85.0 | 4 | 1 | | 2020003 | C++ | 81.0 | 6 | 1 | | 2020010 | C++ | 76.0 | 7 | 2 | | 2020002 | C++ | 70.0 | 8 | 2 | | 2020008 | C++ | 69.0 | 9 | 2 | | 2020007 | C++ | 66.0 | 10 | 2 | | 2020009 | C++ | 66.0 | 10 | 2 | | 2020004 | C++ | 60.0 | 12 | 2 | | 2020003 | English | 100.0 | 1 | 1 | | 2020004 | English | 100.0 | 1 | 1 | | 2020002 | English | 99.0 | 3 | 1 | | 2020013 | English | 88.0 | 4 | 1 | | 2020008 | English | 86.0 | 5 | 1 | | 2020009 | English | 86.0 | 5 | 1 | | 2020011 | English | 84.0 | 7 | 1 | | 2020010 | English | 81.0 | 8 | 2 | | 2020003 | English | 80.0 | 9 | 2 | | 2020007 | English | 76.0 | 10 | 2 | | 2020012 | English | 75.0 | 11 | 2 | | 2020005 | English | 70.0 | 12 | 2 | | 2020006 | English | 70.0 | 12 | 2 | | 2020005 | mysql | 98.0 | 1 | 1 | | 2020001 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | 1 | | 2020008 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | 1 | | 2020011 | mysql | 90.0 | 2 | 1 | | 2020004 | mysql | 80.0 | 5 | 1 | | 2020003 | mysql | 78.0 | 6 | 1 | | 2020010 | mysql | 75.0 | 7 | 2 | | 2020009 | mysql | 70.0 | 8 | 2 | | 2020006 | mysql | 60.0 | 9 | 2 | | 2020002 | mysql | 50.0 | 10 | 2 | | 2020007 | mysql | 50.0 | 10 | 2 | +---------+---------+-------+----+----------+
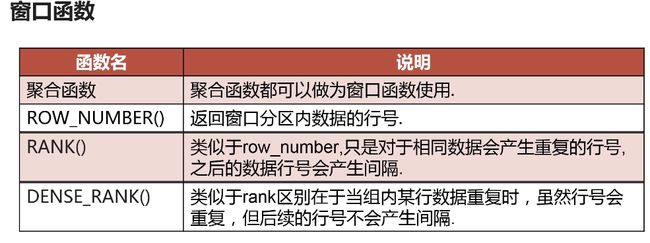
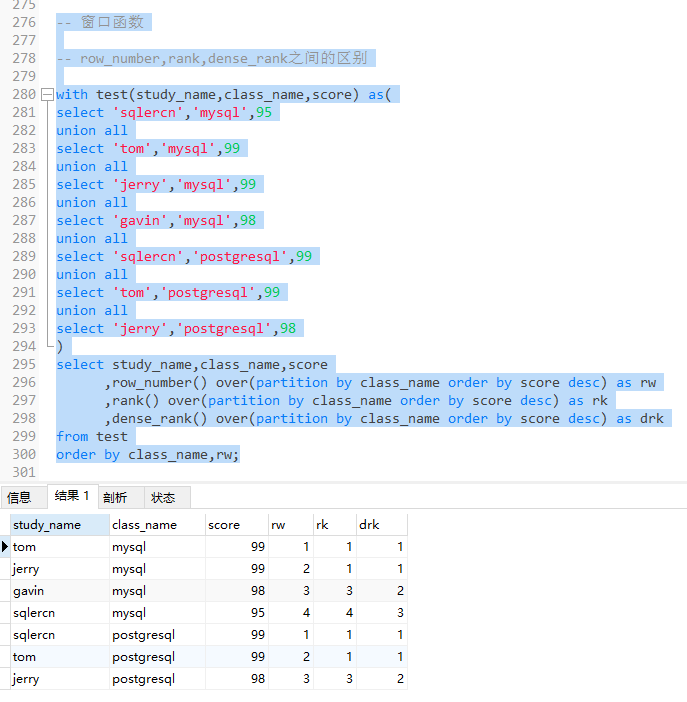
-- 窗口函数 -- row_number,rank,dense_rank之间的区别 with test(study_name,class_name,score) as( select 'sqlercn','mysql',95 union all select 'tom','mysql',99 union all select 'jerry','mysql',99 union all select 'gavin','mysql',98 union all select 'sqlercn','postgresql',99 union all select 'tom','postgresql',99 union all select 'jerry','postgresql',98 ) select study_name,class_name,score ,row_number() over(partition by class_name order by score desc) as rw ,rank() over(partition by class_name order by score desc) as rk ,dense_rank() over(partition by class_name order by score desc) as drk from test order by class_name,rw; 排名显示的方式不同
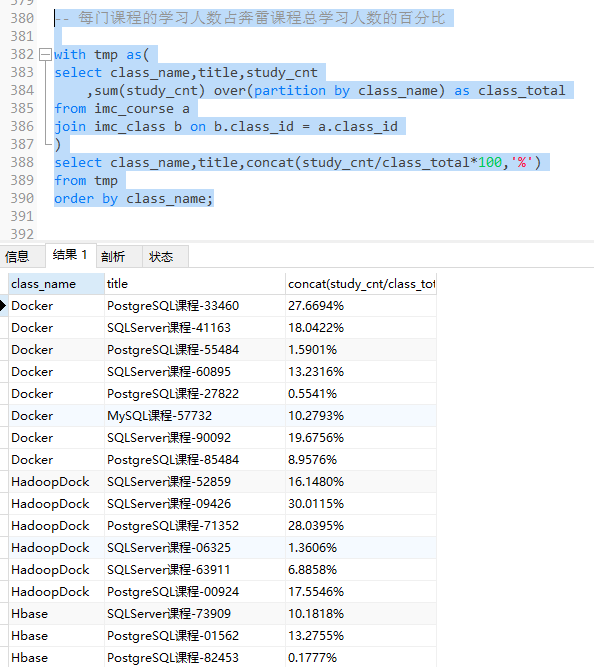
-- 按学习人数对课程进行排名,并列出每类课程学习人数排名前3的课程名称,学习人数以及名次 with tmp as( select class_name,title,score ,rank() over(partition by class_name order by score desc) as cnt from imc_course a join imc_class b on a.class_id = b.class_id ) select * from tmp where cnt<=3; -- 每门课程的学习人数占奔雷课程总学习人数的百分比 with tmp as( select class_name,title,study_cnt ,sum(study_cnt) over(partition by class_name) as class_total from imc_course a join imc_class b on b.class_id = a.class_id ) select class_name,title,concat(study_cnt/class_total*100,'%') from tmp order by class_name;
-- 学习人数等于1000人的课程有哪些,列出他们的课程标题和学习人数 select title,study_cnt from imc_course where study_cnt = 1000; -- 学习人数大于1000人的课程有哪些,列出他们的课程标题和学习人数 select title,study_cnt from imc_course where study_cnt > 1000; 开发sql容易发生的问题
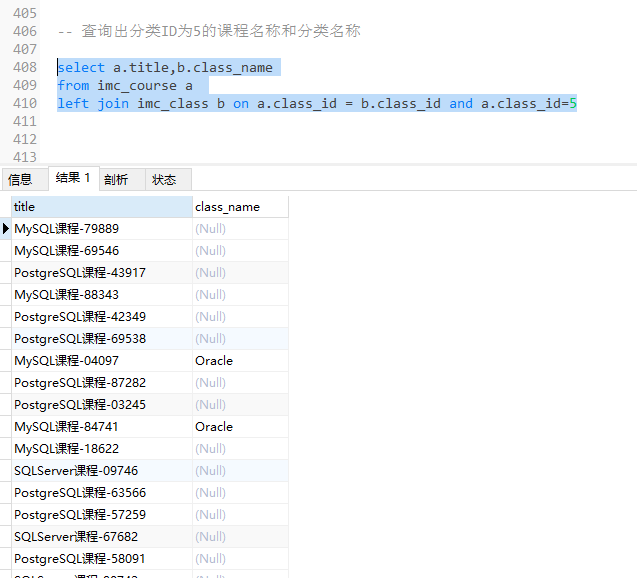
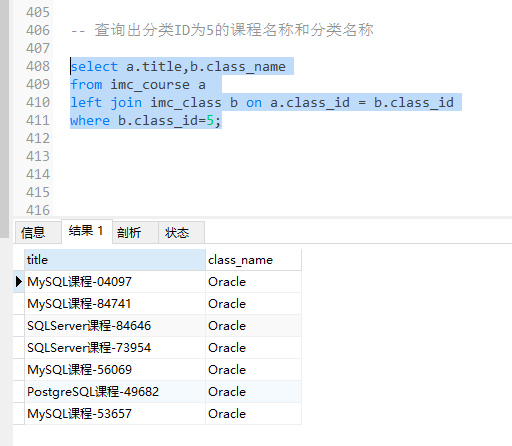
-- 查询出分类ID为5的课程名称和分类名称 错误一: 在on中使用and进行过滤 select a.title,b.class_name from imc_course a join imc_class b on a.class_id = b.class_id and a.class_id=5;
把内连接变更为左外连接,起不到过滤出我们需要的数据的效果 select a.title,b.class_name from imc_course a left join imc_class b on a.class_id = b.class_id and a.class_id=5
使用where条件语句就没有这样的问题 select a.title,b.class_name from imc_course a left join imc_class b on a.class_id = b.class_id where b.class_id=5;
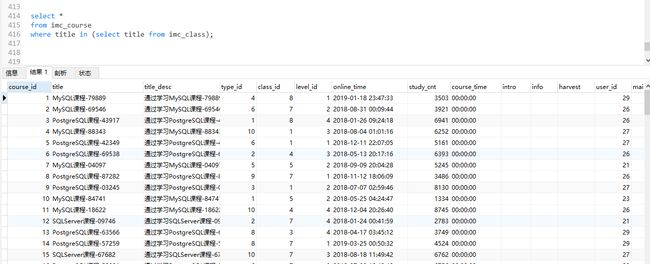
select * from imc_course where title in (select title from imc_class);
如何避免
这样就实现了各种排序需求。
NTILE
NTILE函数的作用是对每个分组排名后,再将对应分组分成N个小组,例如