Python | 多项式回归的实现
多项式回归是一种线性回归形式,其中自变量x和因变量y之间的关系被建模为n次多项式。多项式回归拟合x的值与y的相应条件均值之间的非线性关系,表示为E(y | x)
为什么多项式回归:
- 研究人员假设的某些关系是曲线的。显然,这种类型的案例将包括多项式项。
- 检查残差。如果我们尝试将线性模型拟合到曲线数据,则预测变量(X轴)上的残差(Y轴)的散点图将在中间具有许多正残差的斑块。因此,在这种情况下,这是不合适的。
- 通常的多元线性回归分析的假设是所有自变量都是独立的。在多项式回归模型中,不满足该假设。
多项式回归的使用:
这些基本上用于定义或描述非线性现象,例如:
- 组织生长速度。
- 疾病流行病的进展
- 湖泊沉积物中碳同位素的分布
回归分析的基本目标是根据自变量x的值来模拟因变量y的期望值。在简单回归中,我们使用以下等式 -
| y = a + bx + e |
|---|
这里y是因变量,a是y截距,b是斜率,e是误差率。
在许多情况下,这种线性模型将无法解决。例如,如果我们在这种情况下根据合成温度分析化学合成的产生,我们使用二次模型
| y = a + b1x + b2 ^ 2 + e |
|---|
这里y是x的因变量,a是y截距,e是误差率。
通常,我们可以将其建模为第n个值。
| y = a + b1x + b2x ^ 2 + … + bnx ^ n |
|---|
由于回归函数在未知变量方面是线性的,因此这些模型从估计的角度来看是线性的。
因此,通过最小二乘技术,让我们计算y的响应值。
Python中的多项式回归:
要获得用于分析多项式回归的数据集,请单击此处。
- **步骤1:**导入库和数据集
导入重要的库和我们用于执行多项式回归的数据集。
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the dataset
datas = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
datas
- **第2步:**将数据集分为2个组件
将数据集划分为两个组件,即X和yX将包含1到2之间的列.y将包含2列。
X = datas.iloc[:, 1:2].values
y = datas.iloc[:, 2].values
- **第3步:**将线性回归拟合到数据集
拟合线性回归模型在两个组件上。
# Fitting Linear Regression to the dataset
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lin = LinearRegression()
lin.fit(X, y)
- **第4步:**将多项式回归拟合到数据集
将多项式回归模型拟合到两个分量X和y上。
# Fitting Polynomial Regression to the dataset
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 4)
X_poly = poly.fit_transform(X)
poly.fit(X_poly, y)
lin2 = LinearRegression()
lin2.fit(X_poly, y)
- **步骤5:**在此步骤中,我们使用散点图可视化线性回归结果。
# Visualising the Linear Regression results
plt.scatter(X, y, color = 'blue')
plt.plot(X, lin.predict(X), color = 'red')
plt.title('Linear Regression')
plt.xlabel('Temperature')
plt.ylabel('Pressure')
plt.show()
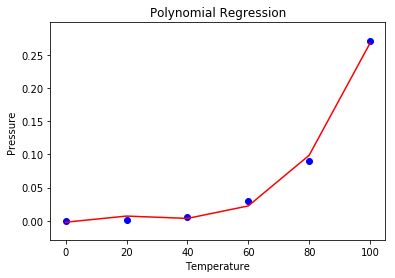
- **步骤6:**使用散点图可视化多项式回归结果。
# Visualising the Polynomial Regression results
plt.scatter(X, y, color = 'blue')
plt.plot(X, lin2.predict(poly.fit_transform(X)), color = 'red')
plt.title('Polynomial Regression')
plt.xlabel('Temperature')
plt.ylabel('Pressure')
plt.show()
- **步骤7:**使用线性和多项式回归预测新结果。
# Predicting a new result with Linear Regression
lin.predict(110.0)
# Predicting a new result with Polynomial Regression
lin2.predict(poly.fit_transform(110.0))
使用多项式回归的优点:
- 广泛的功能可以适应它。
- 多项式基本上适合宽范围的曲率。
- 多项式提供了依赖变量和自变量之间关系的最佳近似。
使用多项式回归的缺点
- 这些对异常值过于敏感。
- 数据中存在一个或两个异常值会严重影响非线性分析的结果。
- 此外,遗憾的是,用于检测非线性回归中的异常值的模型验证工具少于线性回归。