程序设计与算法(三)第05周测验(2020春季)
题目链接:http://cxsjsxmooc.openjudge.cn/2020t3spring5/
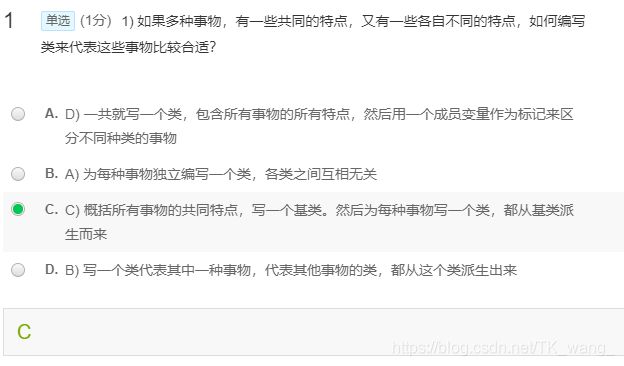
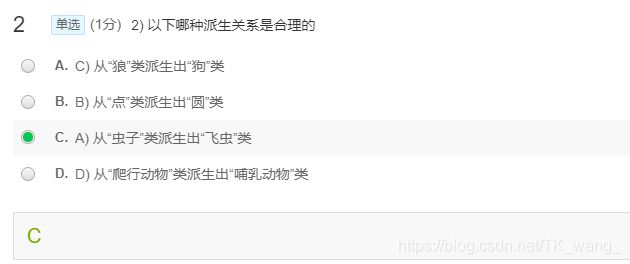
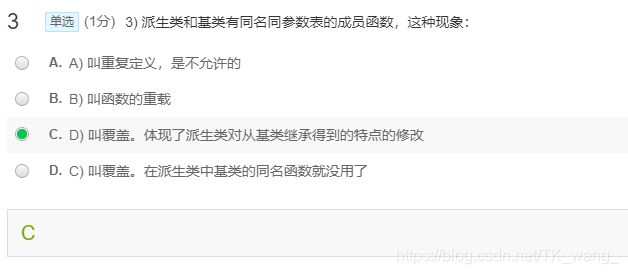
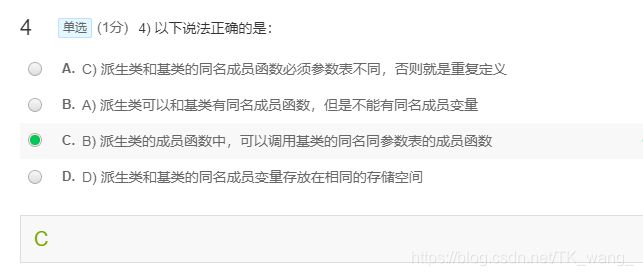
001:全面的MyString
输入
无
输出
- abcd-efgh-abcd-
- abcd-
- abcd-efgh-
- efgh-
- c
- abcd-
- ijAl-
- ijAl-mnop
- qrst-abcd-
- abcd-qrst-abcd- uvw xyz
about
big
me
take
abcd
qrst-abcd-
样例输入
无
样例输出- abcd-efgh-abcd-
- abcd-
- abcd-efgh-
- efgh-
- c
- abcd-
- ijAl-
- ijAl-mnop
- qrst-abcd-
- abcd-qrst-abcd- uvw xyz
about
big
me
take
abcd
qrst-abcd-
注意出现过的运算符都要重载
代码如下:
#include 002:继承自string的MyString
代码如下:
#include 003:魔兽世界之二:装备
总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB
描述
魔兽世界的西面是红魔军的司令部,东面是蓝魔军的司令部。两个司令部之间是依次排列的若干城市。
红司令部,City 1,City 2,……,City n,蓝司令部
两军的司令部都会制造武士。武士一共有 dragon 、ninja、iceman、lion、wolf 五种。每种武士都有编号、生命值这两种属性。
有的武士可以拥有武器。武器有三种,sword, bomb,和arrow,编号分别为0,1,2。
双方的武士编号都是从1开始计算。红方制造出来的第 n 个武士,编号就是n。同样,蓝方制造出来的第 n 个武士,编号也是n。
不同的武士有不同的特点。
dragon 可以拥有一件武器。编号为n的dragon降生时即获得编号为 n%3 的武器。dragon还有“士气”这个属性,是个浮点数,其值为它降生后其司令部剩余生命元的数量除以造dragon所需的生命元数量。
ninja可以拥有两件武器。编号为n的ninja降生时即获得编号为 n%3 和 (n+1)%3的武器。
iceman有一件武器。编号为n的iceman降生时即获得编号为 n%3 的武器。
lion 有“忠诚度”这个属性,其值等于它降生后其司令部剩余生命元的数目。
wolf没特点。
请注意,在以后的题目里,武士的士气,生命值,忠诚度在其生存期间都可能发生变化,都有作用,武士手中的武器随着使用攻击力也会发生变化。
武士在刚降生的时候有一个生命值。
在每个整点,双方的司令部中各有一个武士降生。
红方司令部按照 iceman、lion、wolf、ninja、dragon 的顺序循环制造武士。
蓝方司令部按照 lion、dragon、ninja、iceman、wolf 的顺序循环制造武士。
制造武士需要生命元。
制造一个初始生命值为 m 的武士,司令部中的生命元就要减少 m 个。
如果司令部中的生命元不足以制造某个按顺序应该制造的武士,那么司令部就试图制造下一个。如果所有武士都不能制造了,则司令部停止制造武士。
给定一个时间,和双方司令部的初始生命元数目,要求你将从0点0分开始到双方司令部停止制造武士为止的所有事件按顺序输出。
一共有两种事件,其对应的输出样例如下:
- 武士降生
输出样例: 004 blue lion 5 born with strength 5,2 lion in red headquarter
表示在 4点整,编号为5的蓝魔lion武士降生,它降生时生命值为5,降生后蓝魔司令部里共有2个lion武士。(为简单起见,不考虑单词的复数形式)注意,每制造出一个新的武士,都要输出此时司令部里共有多少个该种武士。
如果造出的是dragon,那么还要输出一行,例:
It has a arrow,and it’s morale is 23.34
表示该dragon降生时得到了arrow,其士气是23.34(为简单起见,本题中arrow前面的冠词用a,不用an,士气精确到小数点后面2位,四舍五入)
如果造出的是ninja,那么还要输出一行,例:
It has a bomb and a arrow
表示该ninja降生时得到了bomb和arrow。
如果造出的是iceman,那么还要输出一行,例:
It has a sword
表示该iceman降生时得到了sword。
如果造出的是lion,那么还要输出一行,例:
It’s loyalty is 24
表示该lion降生时的忠诚度是24。 - 司令部停止制造武士
输出样例: 010 red headquarter stops making warriors
表示在 10点整,红方司令部停止制造武士
输出事件时:
首先按时间顺序输出;
同一时间发生的事件,先输出红司令部的,再输出蓝司令部的。
输入
第一行是一个整数,代表测试数据组数。
每组测试数据共两行。
第一行,一个整数M。其含义为: 每个司令部一开始都有M个生命元( 1 <= M <= 10000)
第二行:五个整数,依次是 dragon 、ninja、iceman、lion、wolf 的初始生命值。它们都大于0小于等于10000
输出
对每组测试数据,要求输出从0时0分开始,到双方司令部都停止制造武士为止的所有事件。
对每组测试数据,首先输出“Case:n" n是测试数据的编号,从1开始
接下来按恰当的顺序和格式输出所有事件。每个事件都以事件发生的时间开头,时间以小时为单位,有三位。
样例输入
1
20
3 4 5 6 7
样例输出
Case:1
000 red iceman 1 born with strength 5,1 iceman in red headquarter
It has a bomb
000 blue lion 1 born with strength 6,1 lion in blue headquarter
It’s loyalty is 14
001 red lion 2 born with strength 6,1 lion in red headquarter
It’s loyalty is 9
001 blue dragon 2 born with strength 3,1 dragon in blue headquarter
It has a arrow,and it’s morale is 3.67
002 red wolf 3 born with strength 7,1 wolf in red headquarter
002 blue ninja 3 born with strength 4,1 ninja in blue headquarter
It has a sword and a bomb
003 red headquarter stops making warriors
003 blue iceman 4 born with strength 5,1 iceman in blue headquarter
It has a bomb
004 blue headquarter stops making warriors
#include004:编程填空:统计动物数量
代码如下:
#include