tensorflow基础教程学习笔记
目录
Tensorflow计算模型——计算图
计算图的使用
Tensorflow数据模型——张量(Tensor)
一 Tensor 类简介
Tensor 定义
Tensor-like objects
Some special tensors
二 Tensor 创建
2.1 常量 Tensor 的创建
2.2 变量 Tensor 的创建
三 Tensor 初始化及访问
3.1 Constants 初始化
3.2 Variables 初始化
3.3 Tensor 的访问
Tensorflow运行模型——会话(Session)
Tensorflow实现神经网络
Tensorflow计算模型——计算图
计算图是TensorFlow中最基本的一个概念,TensorFlow中的所有计算都会被转化为计算图上的节点。在学习计算图之前,我们先来了解一下TensorFlow中两个最重要的基本概念:Tensor和Flow。
- Tensor:即张量,在TensorFlow的范畴里,可将其简单的理解为多维数组
- Flow:中文翻译过来是“流”,它形象的表达了张量之间通过计算相互转化的过程
Tensor表明了TensorFlow中的数据结构,而Flow则体现了它的计算模型。
计算图的使用
在使用TensorFlow的过程中,通常需要定义两个阶段:
- 阶段1:定义计算图中所有的计算
- 阶段2:执行计算
本篇文章中我们不对执行计算的阶段展开,下面给一个定义计算阶段的Demo:
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant([1.0,2.0], name='a')
b = tf.constant([3.0,4.0], name='b')
result = a + b在上述代码中,TensorFlow会自动将定义的计算a和b转化为计算图中的节点。在TensorFlow中,系统会自动维护一个默认的计算图。除了使用默认的计算图,TensorFlow支持通过tf.Graph函数来生成新的计算图。不同计算图上的张量和运算都不会共享,这里我们可以简单的将其理解为作用域的概念。
下面给出一个在不同计算图定义和使用便利的Demo:
g1 = tf.Graph()
g2 = tf.Graph()
with g1.as_default():
# 在计算图g1中定义变量v,并将其初始化值设为0
v = tf.get_variable("v", initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(shape = [1]))
with g2.as_default():
# 在计算图g2中定义变量v,并将其初始化值设为1
v = tf.get_variable("v", initializer=tf.ones_initializer(shape = [1]))
# 在计算图g1中读取变量v的值
with tf.Session( graph = g1) as sess:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
with tf.variable_scope("", reuse= True):
# 这里会输出[0.]
print( sess.run(tf.get_variable("v") ))
# 在计算图g2中读取变量v的值
with tf.Session( graph = g2) as sess:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
with tf.variable_scope("", reuse= True):
# 这里会输出[1.]
print( sess.run(tf.get_variable("v") ))
上述代码设置了两个计算图,每个计算图均定义一个变量“v”。由于变量v的值在初始化时设置的值是不同的,所以当运行不同的计算图时,变量v的值也是不一样的。TensorFlow中的计算图不仅仅可以用于隔离张量和计算,它还提供了用于管理张量和计算的机制。快速有效的整理TensorFlow程序中的资源是计算图的一个重要功能。在计算图中,可以通过集合collection来管理不同类别的资源。比如通过tf.add_to_collection函数可以将资源加入一个或多个集合中,然后通过tf.get_collection获取一个集合里面的所有资源。这里的资源可以是张量、变量或者运行TensorFlow程序所需要的队列资源等等。
为了方便使用,TensorFlow也自动管理了一些最常用的集合,最常用的几个自动维护的集合:
| 集合名词 | 集合内容 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| tf.GraphKeys.VARIABLES | 所有变量 | 持久化TensorFlow模型 |
| tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES | 可学习的变量(一般指神经网络中的参数) | 模型训练、生成模型可视化内容 |
| tf.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES | 日志生成相关的张量 | TensorFlow计算可视化 |
| tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS | 处理输入的QueueRunner | 输入处理 |
| tf.GraphKeys.MOVING_AVERAGE_VARIABLES | 所有计算了滑动平均值的变量 | 计算变量的滑动平均值 |
Tensorflow数据模型——张量(Tensor)
一 Tensor 类简介
-
Tensor 定义
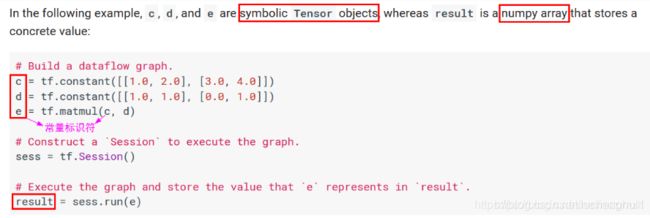
A Tensor is a symbolic handle to one of the outputs of an Operation. It does not hold the values of that operation’s output, but instead provides a means of computing those values in a TensorFlow tf.Session
在 TensorFlow 中,所有在节点之间传递的数据都为 Tensor 对象(可以看作 n 维的数组),常用图像数据的表示形式 为:batch*height*width*channel
-
Tensor-like objects
-
Some special tensors
tf.constant():返回一个常量 tensor
tf.Variable():返回一个 tensor-like 对象,表示变量
tf.SparseTensor():返回一个tensor-like 对象
tf.placeholder():return a tensor that may be used as a handle for feeding a value, but not evaluated directly.
二 Tensor 创建
2.1 常量 Tensor 的创建
Constant Value Tensors(常量张量)
#产生全0的张量
tf.zeros(shape,dtype=tf.float32,name=None)
tf.zeros_like(tensor, dtype=None, name=None)
'''
tf.zeros([2,3],dtype=tf.float32,name="zeros") =>
[[0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0.]]
'''
# 产生全 1 的张量
tf.ones(shape, dtype=tf.float32, name=None)
tf.ones_like(tensor, dtype=None, name=None)
# Creates a tensor of shape and fills it with value
tf.fill(dims, value, name=None)
tf.fill([2, 3], 9) ==> [[9, 9, 9]
[9, 9, 9]]
# 产生常量 Tensor, value值可为python标准数据类型、Numpy 等
tf.constant(value, dtype=None, shape=None, name='Const')
tf.constant(-1.0, shape=[2, 3]) => [[-1., -1., -1.] # Note: 注意 shape 的用法(广播机制)
[-1., -1., -1.]]
tf.constant([1,2,3,4,5,6], shape=[2,3]) => [[1, 2, 3]
[4, 5, 6]]Sequences(序列张量)
# 产生 num 个等距分布在 [start, stop] 间元素组成的数组,包括 start & stop (需为 float 类型)
# increase by (stop - start) / (num - 1)
tf.linspace(start, stop, num,, name=None)
# []为可选参数,步长 delta 默认为 1,start 默认为 0, limit 的值取不到,它产生一个数字序列
tf.range([start], limit, delta=1, dtype=None, name='range')
# eg
tf.range(start=3, limit=18, delta=3) # [3, 6, 9, 12, 15]
tf.range(limit=5) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Random Tensors(随机张量)
# 正态分布,默认均值为0,标准差为1.0,数据类型为float32
tf.random_normal(shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32, seed=None, name=None)
# 正态分布,但那些到均值的距离超过2倍标准差的随机数将被丢弃,然后重新抽取,直到取得足够数量的随机数为止, 随机数 x
# 的取值范围是$[mean - 2*stddev, mean + 2*stddev]$, 从而可以防止有元素与该张量中的其他元素显著不同的情况出现
tf.truncated_normal(shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32, seed=None, name=None)
# 产生在[minval, maxval)之间形状为 shape 的均匀分布, 默认是[0, 1)之间形状为 shape 的均匀分布
tf.random_uniform(shape, minval=0.0, maxval=1, dtype=tf.float32, seed=None, name=None)
# Randomly crops a tensor to a given size
tf.random_crop(value, size, seed=None, name=None)
# Note:If a dimension should not be cropped, pass the full size of that dimension.
# For example, RGB images can be cropped with size = [crop_height, crop_width, 3]
# Randomly shuffles a tensor along its first dimension
# 若要几个 op 以同样的顺序 shuffle,设置相同的 seed 即可
tf.random_shuffle(value, seed=None, name=None)
# Sets the graph-level random seed
tf.set_random_seed(seed)
# 1. To generate the same repeatable sequence for an op across sessions
# set the seed for the op, a = tf.random_uniform([1], seed=1)
# 2. To make the random sequences generated by all ops be repeatable across sessions
# set a graph-level seed, tf.set_random_seed(1234)
# 其它
tf.multinomial(logits, num_samples, seed=None, name=None)
tf.random_gamma(shape,alpha,beta=None,dtype=tf.float32,seed=None,name=None)
2.2 变量 Tensor 的创建
1.Class tf.Variable()
- 常用属性
-
dtype、shape、name
-
initial_value:Returns the Tensor used as the initial value for the variable.
-
initializer:The initializer operation for this variable,用于初始化此变量 sess.run(v.initializer)
-
op:The Operation that produces this tensor as an output.
-
device:The name of the device on which this tensor will be produced, or None.
-
graph:The Graph that contains this tensor.
- 常用方法
- eval(session=None):Evaluates this tensor in a Session. Returns A numpy ndarray with a copy of the value of this variable
- get_shape():Alias of Tensor.shape.
- set_shape(shape): It can be used to provide additional information about the shape of this tensor that cannot be inferred from the graph alone。
- initialized_value():Returns the value of the initialized variable.
- read_value():Returns the value of this variable, read in the current context.
- assign(value, use_locking=False):Assigns a new value to the variable.
- assign_add(delta, use_locking=False)
- assign_sub(delta, use_locking=False)
- Class Variable 定义
# tf.constant 是 op,而 tf.Variable() 是一个类,初始化的对象有多个op
var_obj = tf.Variable(
initial_value,
dtype=None,
name=None,
trainable=True,
collections=None,
validate_shape=True
)
# 初始化参数
initial_value:可由 Python 内置数据类型提供,也可由常量 Tensor 的内置 op 来快速构建,但所有这些 op 都需要提供 shape
trainable:指明了该变量是否可训练, 会加入 `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` collection 中去。
collections: List of graph collections keys. The new variable is added to these collections. Defaults to [GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES].
validate_shape: If False, allows the variable to be initialized with a value of unknown shape. If True, the default, the shape of initial_value must be known.
# 返回值
变量实例对象(Tensor-like)
2.tf.get_variable()
# Gets an existing variable with these parameters or create a new one
tf.get_variable(
name,
shape=None,
dtype=None,
initializer=None,
trainable=True,
regularizer=None,
collections=None,
caching_device=None,
partitioner=None,
validate_shape=True,
use_resource=None,
custom_getter=None
)
# 初始化参数
name: The name of the new or existing variable.
shape: Shape of the new or existing variable.
dtype: Type of the new or existing variable (defaults to DT_FLOAT).
initializer: Initializer for the variable if one is created.
trainable: If True also add the variable to the graph collection tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES.
regularizer: A (Tensor -> Tensor or None) function; the result of applying it on a newly created variable will be added to the collection tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES and can be used for regularization.
collections: List of graph collections keys to add the Variable to. Defaults to [GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES] (see tf.Variable).
# 返回值
The created or existing Variable, 拥有变量类的所有属性和方法。
# Note:
>>> name 参数必须要指定,如果仅给出 shape 参数而未指定 initializer,那么它的值将由 tf.glorot_uniform_initializer 随机产生,数据类型为tf.float32;
>>> 另外,initializer 可以为一个张量,这种情况下,变量的值和形状即为此张量的值和形状(就不必指定shape 了)。
>>> 此函数经常和 tf.variable_scope() 一起使用,产生共享变量
三 Tensor 初始化及访问
3.1 Constants 初始化
- Constants are initialized when you
call tf.constant, and their value can never change.
3.2 Variables 初始化
Variables are not initialized when you call tf.Variable. To initialize all the variables in a TensorFlow program, you must explicitly call a special operation as follows:
# 变量使用前一定要初始化
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 初始化全部变量
sess.run(init)
# 使用变量的 initializer 属性初始化
sess.run(v.initializer)
用另一个变量的初始化值给当前变量初始化
- 由于tf.global_variables_initializer()是并行地初始化所有变量,所以直接使用另一个变量的初始化值来初始化当前变量会报错(因为你用另一个变量的值时,它没有被初始化)
- 在这种情况下需要使用另一个变量的initialized_value()方法。你可以直接把已初始化的值作为新变量的初始值,或者把它当做tensor计算得到一个值赋予新变量。
# Create a variable with a random value.
weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 200], stddev=0.35), name="weights")
# Create another variable with the same value as 'weights'.
w2 = tf.Variable(weights.initialized_value(), name="w2")
# Create another variable with twice the value of 'weights'
w_twice = tf.Variable(weights.initialized_value() * 0.2, name="w_twice")
改变变量的值:通过 TF 中的赋值操作,update = tf.assign(old_variable, new_value) or v.assign(new_value)
3.3 Tensor 的访问
- 索引
- 一维 Tensor 的索引和 Python 列表类似(可以逆序索引(arr[ : : -1])和负索引arr[-3])
- 二维 Tensor 的索引: arr[i, j] == arr[i][j]
- 在多维 Tensor 中,如果省略了后面的索引,则返回的对象会是一个维度低一点的ndarray(但它含有高一级维度上的某条轴上的所有数据)
- 条件索引:arr[conditon] # conditon 可以使用 & | 进行多条件组合
- 切片
- 一维 Tensor 的切片和 Python 列表类似
- 二维 Tensor 的索引:arr[r1:r2, c1:c2:step] # 也可指定 step 进行切片
- RGB 与 BGR 相互转换
- img_bgr = tf.reverse(img_rgb, axis=[-1])
- img_rgb = tf.reverse(img_bgr, axis=[-1])
Tensorflow运行模型——会话(Session)
a、Session 的简介
- 图必须通过
创建一个 Session 对象来执行计算任务,会话将图的 op分发到诸如 CPU 或 GPU 之类的设备上, 同时提供执行 op 的方法。 - 这些方法执行后,将产生
numpy.ndarray类型的数据返回。
# 通过 Python 的上下文管理器来管理这个会话,不需要再调用Session.close()函数来关闭会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(...)
b、Session 的初始化参数
- target:specifies the execution engine to use.
- graph:specifies the Graph object that will be launched in the Session. If no, the default graph will be launched
- config:allows users to specify options to configure the session, such as limiting the number of CPUs or GPUs to use, setting optimization parameters for graphs, and logging options.
c、Session 对象的 run 方法
- Runs operations and evaluates tensors in fetches
- 必选参数(fetches):A single graph element, a list of graph elements, or a dictionary whose values are graph elements or lists of graph elements
- 可选参数(feed_dict):A dictionary that maps graph elements to values,用于为数据流图喂数据或者覆盖数据流图中的 Tensor 对象值
Tensorflow实现神经网络
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os
INPUT_NODE = 784
OUTPUT_NODE = 10
LAYER1_NODE = 500
BATCH_SIZE = 128
LEARNING_RATE_BASE = 0.8
REGULARIZER_RATE = 0.01 #正则化权重
TRAINING_STEPS = 30000
MODEL_SAVE_PATH = "d:\data\model"
MODEL_NAME = "model.ckpt"
def get_weight_variable(shape,regularizer):
weights = tf.get_variable(
"weights",shape,
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
#增加权重参数进行正则化,tf.add_to_collection()将tensor对象放入同一个集合
if regularizer != None:
tf.add_to_collection("losses",regularizer(weights))
return weights
#定义神经网络的前向传播过程
def inference(input_tensor,regularizer):
#tf.variable_scope()用来指定变量的作用域,作为变量名的前缀,支持嵌套
with tf.variable_scope("layer1"):
weights = get_weight_variable([INPUT_NODE,LAYER1_NODE],regularizer)
biases = tf.get_variable("biases",[LAYER1_NODE],initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
#tf.matmul()将矩阵a乘以矩阵b,生成a*b;tf.multiply()两个矩阵中对应元素各自相乘
layer1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(input_tensor,weights) + biases)
with tf.variable_scope("layer2"):
weights = get_weight_variable([LAYER1_NODE,OUTPUT_NODE],regularizer)
biases = tf.get_variable("biases",[OUTPUT_NODE],initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
layer2 = tf.matmul(layer1,weights) + biases
return layer2
def train(mnist):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,INPUT_NODE],name = "x-input")
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,OUTPUT_NODE],name = "y-input")
regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(REGULARIZER_RATE)
y = inference(x,regularizer)
#tf.argmax(input,axis)根据axis取值的不同返回每行或者每列最大值的索引,axis=1,返回行最大值说因
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels = tf.argmax(y_,1),logits = y))
#tf.get_collection()主要作用:从一个集合中取出变量,获取key集合中的所有元素,返回一个列表;
#tf.add_n()将list中的数值相加
loss = cross_entropy_mean + tf.add_n(tf.get_collection("losses"))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LEARNING_RATE_BASE).minimize(loss)
#初始化tensorflow持久化类
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(TRAINING_STEPS):
xs,ys = mnist.train.next_batch(BATCH_SIZE)
_,loss_value = sess.run([train_step,loss],feed_dict = {x:xs,y_:ys})
if i % 5000 == 0:
print("After %d training step,loss on training batch is %f" % (i,loss_value))
saver.save(sess,os.path.join(MODEL_SAVE_PATH,MODEL_NAME))
def evaluate(mnist):
with tf.Graph().as_default() as g:
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,INPUT_NODE],name = "x-input")
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,OUTPUT_NODE],name = "y-input")
valid_feed = {x:mnist.validation.images,
y_:mnist.validation.labels}
y = inference(x,None)
#tf.equal()逐个元素进行判断,如果相等就是True,不相等就是False =>[True,True,....False]。
correct_predict = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1))
#tf.cast(x)将x的数据格式转化成dtype.例如,原来x的数据格式是bool,那么将其转化成float以后,就能够将其转化成0和1的序列,反之也可以.
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predict,tf.float32))
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess,ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
accurac_score = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict=valid_feed)
print("Accuracy = %f" % accurac_score)
return
else:
print("No checkpoint file found")
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("D:\data", one_hot = True)
train(mnist)
evaluate(mnist)