Android语言切换原理
Android语言切换原理
前言
之前因为系统有些国家使用的字体乱码的原因,研究了下Android系统字体加载相关的知识,写了一篇Android系统字体加载流程的总结,浅析Android字体加载原理,然而系统的字体与系统当前的语言有密切的关系,因此抽空了解了下Android系统语言切换的流程,写下总结,加深印象。
Android语言切换流程分析
概述
有过Android开发经验的人,应该都知道Android有一套成熟的国际化机制,通常应用或系统要走出海外,都要进行国际化适配,而Android语言切换依赖于国际化适配,但这里,我们不深入了解Android国际化的原理,有兴趣的读者可以自行Google或者百度,下面对Android语言切换流程进行分析。
Android多语言描述
有关Android系统本地化的介绍,请查看官网,本地化。
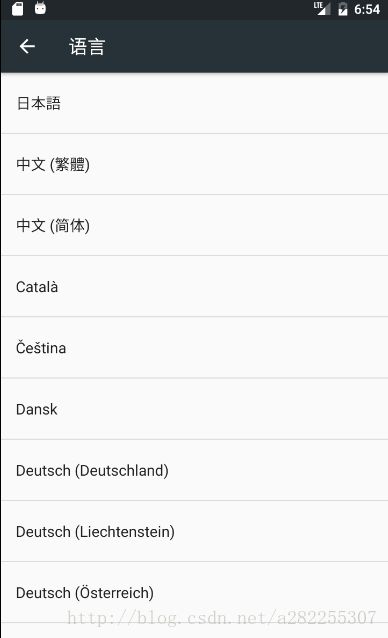
对于Android语言切换接口,在Android 6.0及以前的语言设置都是单一的语言,只能选一种语言,见下图。
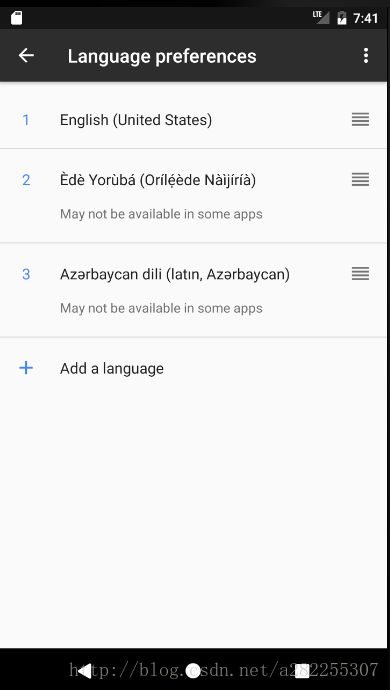
Android7.0系统以上,则是更人性化了,允许用户在设置中选择多个语言,如下图,用户可以根据自己的喜好选择语言列表,并将默认的语言拖拽到首项,设为系统默认语言。
这么做的目的是为了一些国家使用多种语言,比如印度,印度语是第一母语,英语则为其第二母语,这样的话,在系统捏添加这两个语言后,会加载相应的语言资源,当第一语言没有相应资源时,会去第二语言中查找,而7.0以下的系统就只能加载一种语言下的资源文件,存在很大的限制,这里就不做扩展,有兴趣的读者可以自行了解。
Android多语言切换
如上所述,Android在不同的系统版本为用户提供不同的语言切换功能,因此在切换流程过中,调用的接口也不同,如Android6.0及以下,设置切换语言的接口调用的是updateLocale(Locale locale),如Android7.0以上,设置切换语言的接口调用的是updateLocales(LocaleList locales),但是大致的流程还是保持一致,多的只是文件存放位置的变化,下面笔者将以Android7.0的流程进行分析,7.0以下的,读者可自行分析。
注:从上面的两个接口,也可以看出,高版本系统与低版本系统加载语言的区别,前者是加载多个语言的列表,后者是加载一个语言。
如上所述,当用户在设置中选择对应的语言后,Android会首先调frameworks/base/com/android/internal/app/LocalePicker.java中的updateLocales(LocaleList locales)方法。
注:如果你不想用Android7.0以上的语言切换功能,可以考虑自己实现updateLocale(Locale locale)方法。
/**
* Requests the system to update the list of system locales.
* Note that the system looks halted for a while during the Locale migration,
* so the caller need to take care of it.
*/
public static void updateLocales(LocaleList locales) {
try {
//获取am
final IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
//获取am配置对象
final Configuration config = am.getConfiguration();
//为配置对象重新设置语言
config.setLocales(locales);
//重置标志位
config.userSetLocale = true;
am.updatePersistentConfiguration(config);
// Trigger the dirty bit for the Settings Provider.
BackupManager.dataChanged("com.android.providers.settings");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Intentionally left blank
}
}
Google对该方法的介绍是,当更新系统语言列表的时候,就会调用这个方法。从上方展示的源码来看,该方法首先会调用ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()来获取ActivityManagerServices(以下简称AMS)在本地的代理,从而调用AMS中的updatePersistentConfiguration()并传入创建好的配置对象(Configuration)。
注:这里是ActivityManagerNative使用远程代理通过Binder条用AMS的同名方法,由于Android的代理机制十分复杂,这里不继续介绍Android代理机制。
@Override
public void updatePersistentConfiguration(Configuration values) {
//强制权限校验
enforceCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION,
"updateConfiguration()");
//强制写入设置权限
enforceWriteSettingsPermission("updateConfiguration()");
if (values == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Configuration must not be null");
}
//获取调用用户的ID
int userId = UserHandle.getCallingUserId();
synchronized(this) {
//调用方法
updatePersistentConfigurationLocked(values, userId);
}
}
可以看出,该方法首先进行了权限校验,权限赋予,然后调用updatePersistentConfigurationLocked()方法,继续看下这个方法。
private void updatePersistentConfigurationLocked(Configuration values, @UserIdInt int userId) {
//清除Binder调用标识
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
//重要方法
updateConfigurationLocked(values, null, false, true, userId, false /* deferResume */);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
这个方法只是清除了Binder标识,并调用了updateConfigurationLocked()方法,该方法非常重要,注意这里的传参,继续往下看。
/**
* Do either or both things: (1) change the current configuration, and (2)
* make sure the given activity is running with the (now) current
* configuration. Returns true if the activity has been left running, or
* false if starting is being destroyed to match the new
* configuration.
*
* @param userId is only used when persistent parameter is set to true to persist configuration
* for that particular user
*/
private boolean updateConfigurationLocked(Configuration values, ActivityRecord starting,
boolean initLocale, boolean persistent, int userId, boolean deferResume) {
int changes = 0;
...
if (values != null) {
Configuration newConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
changes = newConfig.updateFrom(values);
if (changes != 0) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.i(TAG_CONFIGURATION,
"Updating configuration to: " + values);
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, changes);
if (!initLocale && !values.getLocales().isEmpty() && values.userSetLocale) {
//得到选择的国家语言列表
final LocaleList locales = values.getLocales();
int bestLocaleIndex = 0;
if (locales.size() > 1) {
if (mSupportedSystemLocales == null) {
//获取系统支持国家语言列表
mSupportedSystemLocales =
Resources.getSystem().getAssets().getLocales();
}
//匹配国家,获取选择默认国家语言下标
bestLocaleIndex = Math.max(0,
locales.getFirstMatchIndex(mSupportedSystemLocales));
}
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale",
locales.get(bestLocaleIndex).toLanguageTag());
//设置为选择的国家语言为默认国家语言
LocaleList.setDefault(locales, bestLocaleIndex);
//发送消息通知挂载守护进程国家语言变更
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(SEND_LOCALE_TO_MOUNT_DAEMON_MSG,
locales.get(bestLocaleIndex)));
}
...
// Make sure all resources in our process are updated
// right now, so that anyone who is going to retrieve
// resource values after we return will be sure to get
// the new ones. This is especially important during
// boot, where the first config change needs to guarantee
// all resources have that config before following boot
// code is executed.
//更新资源配置
mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy);
//如果有配置改动,就发送该消息通知配置改动
if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG);
msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
msg.arg1 = userId;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
...
for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION, "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
...
}
从Google给的注释说明可以看到,这个方法的最重要的作用如下:
- 更新当前系统的配置到最新的配置;
- 保证所有的Activity都能更新到改变后的配置。
注:在更新或者清除configuration时,是通过changes位标记法来确认是configuration中的哪一项。
继续来看Android是如何进行配置更新的。首先调用updateFrom(),方法来更新配置,我们先看看这个方法。
/**
* Copies the fields from delta into this Configuration object, keeping
* track of which ones have changed. Any undefined fields in {@code delta}
* are ignored and not copied in to the current Configuration.
*
* @return a bit mask of the changed fields, as per {@link #diff}
*/
public @Config int updateFrom(@NonNull Configuration delta) {
//变化项
int changed = 0;
...
//当有语言列表变化时,走这
if (!delta.mLocaleList.isEmpty() && !mLocaleList.equals(delta.mLocaleList)) {
changed |= ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE;
mLocaleList = delta.mLocaleList;
// delta.locale can't be null, since delta.mLocaleList is not empty.
if (!delta.locale.equals(locale)) {
locale = (Locale) delta.locale.clone();
// If locale has changed, then layout direction is also changed ...
changed |= ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LAYOUT_DIRECTION;
// ... and we need to update the layout direction (represented by the first
// 2 most significant bits in screenLayout).
setLayoutDirection(locale);
}
}
...
if (delta.userSetLocale && (!userSetLocale || ((changed & ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE) != 0)))
{
changed |= ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE;
userSetLocale = true;
}
return changed;
}
从以上可以看到,当我们修改了语言列表,那么返回的变化项change一定大于0。继续回到updateConfigurationLocked()方法中,由于change不为0,并且根据前面的传参,updateConfigurationLocked()方法将从变更的国家语言列表中获取默认国家语言下标,然后设置默认国家语言以及默认国家列表,并发送消息通知挂载守护进程国家语言的变化,其中设置默认情况的代码如下。
//设置默认国家语言以及国家语言列表
/**
* This may be used directly by system processes to set the default locale list for apps. For
* such uses, the default locale list would always come from the user preferences, but the
* default locale may have been chosen to be a locale other than the first locale in the locale
* list (based on the locales the app supports).
*
* {@hide}
*/
public static void setDefault(@NonNull @Size(min=1) LocaleList locales, int localeIndex) {
if (locales == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("locales is null");
}
if (locales.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("locales is empty");
}
synchronized (sLock) {
sLastDefaultLocale = locales.get(localeIndex);
Locale.setDefault(sLastDefaultLocale);
sLastExplicitlySetLocaleList = locales;
sDefaultLocaleList = locales;
if (localeIndex == 0) {
sDefaultAdjustedLocaleList = sDefaultLocaleList;
} else {
sDefaultAdjustedLocaleList = new LocaleList(
sLastDefaultLocale, sDefaultLocaleList);
}
}
}
再此之后,系统进程会首先通知Configuration改变,所以mSystemThread即系统的ActivityThread类对象调用applyConfigurationToResources()确保自己所在的进程资源更新到最新(主要指framework-res.apk中的资源,也就是上面所说的updateConfigurationLocked()方法的第一个重要作用),以便任何人检索资源的时候拿到的都是最新的资源,然后发送通知更新用户配置。
注:这里是系统更新配置资源,后面将对pplyConfigurationToResources()方法进行描述。
// Make sure all resources in our process are updated
// right now, so that anyone who is going to retrieve
// resource values after we return will be sure to get
// the new ones. This is especially important during
// boot, where the first config change needs to guarantee
// all resources have that config before following boot
// code is executed.
//更新资源配置
mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy);
//如果有配置改动,就发送该消息通知配置改动
if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG);
msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
msg.arg1 = userId;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
继续往下看,以下是遍历每个应用,通知其配置的改变。
//保存所有应用的进程
final ArrayList mLruProcesses = new ArrayList();
for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION, "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
public final void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config)
throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
config.writeToParcel(data, 0);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
可以看到,mLruProcesses中保存的是所有运行的进程,Android中,每个应用运行时都对应于一个进程,因此这里包含了所有运行的应用。我们注意到这里循环调用了app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy),app.thread对应于每个应用的线程,其作用是通知各个应用进程Configuration改变。跳转后会发现,这里其实又是通过binder调用跨进程方法,在这里是调用ActivityThread.java中私有ApplicationThread的方法,查看该方法。
注:ApplicationThread是ActivityThread的内部类,也是一个Binder对象,这边用以等待AMS发送消息。
public void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config) {
updatePendingConfiguration(config);
//发送消息给对应的主线程
sendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, config);
}
...
case CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "configChanged");
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = ((Configuration)msg.obj).densityDpi;
mUpdatingSystemConfig = true;
//接收到AMS发来的数据
handleConfigurationChanged((Configuration)msg.obj, null);
mUpdatingSystemConfig = false;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
这里ApplicationThread接收到AMS的信息后,会发送消息CONFIGURATION_CHANGED给对应应用的ActivityThread。ActivityThread收到CONFIGURATION_CHANGED消息后,其会调用handleConfigurationChanged()方法。
final void handleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compat) {
int configDiff = 0;
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
...
//将资源配置修改应用到资源中
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(config, compat);
//更新语言列表
updateLocaleListFromAppContext(mInitialApplication.getApplicationContext(),
mResourcesManager.getConfiguration().getLocales());
...
}
//组件修改回调对象
ArrayList callbacks = collectComponentCallbacks(false, config);
freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(configDiff);
if (callbacks != null) {framework-res.apk
final int N = callbacks.size();
for (int i=0; iif (cb instanceof Activity) {
// If callback is an Activity - call corresponding method to consider override
// config and avoid onConfigurationChanged if it hasn't changed.
Activity a = (Activity) cb;
//Activity回调响应
performConfigurationChangedForActivity(mActivities.get(a.getActivityToken()),
config, REPORT_TO_ACTIVITY);
} else {
//其他回调响应
performConfigurationChanged(cb, null, config, null, REPORT_TO_ACTIVITY);
}
}
}
}
在handleConfigurationChanged()方法中,也会调用applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked()方法,去更新每个应用的配置资源(也就是上述updateConfigurationLocked()方法的第二个重要作用)。
也就是说,不管是系统资源还是应用资源的更新都要调用applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked()方法。按字面意思,大概的作用就是将资源配置修改应用到资源中,而资源文件就包含语言资源文件、图片资源、布局资源等,查看其代码。
public final boolean applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(@NonNull Configuration config,
@Nullable CompatibilityInfo compat) {
private final ArrayMap> mResourceImpls =
new ArrayMap<>();
try {
...
//获取更新项
int changes = mResConfiguration.updateFrom(config);
// Things might have changed in display manager, so clear the cached displays.
mDisplays.clear();
...
//更新系统资源配置
Resources.updateSystemConfiguration(config, defaultDisplayMetrics, compat);
//通知配置文件修改,清理缓存,如Icon和String
ApplicationPackageManager.configurationChanged();
//Slog.i(TAG, "Configuration changed in " + currentPackageName());
Configuration tmpConfig = null;
for (int i = mResourceImpls.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ResourcesKey key = mResourceImpls.keyAt(i);
ResourcesImpl r = mResourceImpls.valueAt(i).get();
if (r != null) {
...
r.updateConfiguration(tmpConfig, dm, compat);
} else {
r.updateConfiguration(config, dm, compat);
}
//Slog.i(TAG, "Updated app resources " + v.getKey()
// + " " + r + ": " + r.getConfiguration());
} else {
//Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old resources " + v.getKey());
mResourceImpls.removeAt(i);
}
}
return changes != 0;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES);
}
}
按照上面的说法,系统进程以及应用进程会分别调用applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked()方法来更新配置。
当系统进程执行该方法时,Resources.updateSystemConfiguration()会更新系统资源配置(frameworks-res.apk),在执行完ApplicationPackageManager.configurationChanged()方法后,会清除进程的资源缓存,如Icon与String,并移除其他旧的资源,最终加载新的系统资源。
注:这里并未对更新细节进行详细描述,如有兴趣可以自行研究下。
当应用进程执行该方法时,会通知应用进程更新资源配置,并且实现ComponentCallbacks2接口的组件,如Activity、Services、Application等会被记录,并在handleConfigurationChanged()中被遍历回调通知更新资源配置,因此我们再回到handleConfigurationChanged()方法中。
//组件修改回调对象
ArrayList callbacks = collectComponentCallbacks(false, config);
freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(configDiff);
if (callbacks != null) {
final int N = callbacks.size();
for (int i=0; iif (cb instanceof Activity) {
// If callback is an Activity - call corresponding method to consider override
// config and avoid onConfigurationChanged if it hasn't changed.
Activity a = (Activity) cb;
//Activity回调响应
performConfigurationChangedForActivity(mActivities.get(a.getActivityToken()),
config, REPORT_TO_ACTIVITY);
} else {
//其他回调响应
performConfigurationChanged(cb, null, config, null, REPORT_TO_ACTIVITY);
}
}
}
从上面可以看出,在回调中,如果是Activity,则回调performConfigurationChangedForActivity()方法,如果是Services、Application等,回调performConfigurationChanged()方法,按注释解释,这样做是为了Activity在更新配置时重写配置和避免没有修改时回调onConfigurationChanged()方法,但不管是什么组件,最终都是调用performConfigurationChanged()方法,我们来具体看下这个方法。
private void performConfigurationChanged(ComponentCallbacks2 cb,
IBinder activityToken,
Configuration newConfig,
Configuration amOverrideConfig,
boolean reportToActivity) {
// Only for Activity objects, check that they actually call up to their
// superclass implementation. ComponentCallbacks2 is an interface, so
// we check the runtime type and act accordingly.
Activity activity = (cb instanceof Activity) ? (Activity) cb : null;
if (activity != null) {
activity.mCalled = false;
}
boolean shouldChangeConfig = false;
if ((activity == null) || (activity.mCurrentConfig == null)) {
shouldChangeConfig = true;
} else {
// If the new config is the same as the config this Activity is already
// running with and the override config also didn't change, then don't
// bother calling onConfigurationChanged.
int diff = activity.mCurrentConfig.diff(newConfig);
if (diff != 0 || !mResourcesManager.isSameResourcesOverrideConfig(activityToken,
amOverrideConfig)) {
// Always send the task-level config changes. For system-level configuration, if
// this activity doesn't handle any of the config changes, then don't bother
// calling onConfigurationChanged as we're going to destroy it.
if (!mUpdatingSystemConfig
|| (~activity.mActivityInfo.getRealConfigChanged() & diff) == 0
|| !reportToActivity) {
shouldChangeConfig = true;
}
}
}
if (shouldChangeConfig) {
// Propagate the configuration change to the Activity and ResourcesManager.
// ContextThemeWrappers may override the configuration for that context.
// We must check and apply any overrides defined.
Configuration contextThemeWrapperOverrideConfig = null;
if (cb instanceof ContextThemeWrapper) {
final ContextThemeWrapper contextThemeWrapper = (ContextThemeWrapper) cb;
contextThemeWrapperOverrideConfig = contextThemeWrapper.getOverrideConfiguration();
}
// We only update an Activity's configuration if this is not a global
// configuration change. This must also be done before the callback,
// or else we violate the contract that the new resources are available
// in {@link ComponentCallbacks2#onConfigurationChanged(Configuration)}.
if (activityToken != null) {
// Apply the ContextThemeWrapper override if necessary.
// NOTE: Make sure the configurations are not modified, as they are treated
// as immutable in many places.
final Configuration finalOverrideConfig = createNewConfigAndUpdateIfNotNull(
amOverrideConfig, contextThemeWrapperOverrideConfig);
mResourcesManager.updateResourcesForActivity(activityToken, finalOverrideConfig);
}
if (reportToActivity) {
// Apply the ContextThemeWrapper override if necessary.
// NOTE: Make sure the configurations are not modified, as they are treated
// as immutable in many places.
final Configuration configToReport = createNewConfigAndUpdateIfNotNull(
newConfig, contextThemeWrapperOverrideConfig);
cb.onConfigurationChanged(configToReport);
}
if (activity != null) {
if (reportToActivity && !activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + activity.getLocalClassName() +
" did not call through to super.onConfigurationChanged()");
}
activity.mConfigChangeFlags = 0;
activity.mCurrentConfig = new Configuration(newConfig);
}
}
}
从上面代码注释,可以看到,只有Activity组件才会实现这个方法,并且只有当配置修改不是全局时,Activity会在回调前调用updateResourcesForActivity()方法来更新配置资源,最后回调onConfigurationChanged()方法。
/**
* Called by the system when the device configuration changes while your
* activity is running. Note that this will only be called if
* you have selected configurations you would like to handle with the
* {@link android.R.attr#configChanges} attribute in your manifest. If
* any configuration change occurs that is not selected to be reported
* by that attribute, then instead of reporting it the system will stop
* and restart the activity (to have it launched with the new
* configuration).
*
*
At the time that this function has been called, your Resources
* object will have been updated to return resource values matching the
* new configuration.
*
* @param newConfig The new device configuration.
*/
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
if (DEBUG_LIFECYCLE) Slog.v(TAG, "onConfigurationChanged " + this + ": " + newConfig);
mCalled = true;
mFragments.dispatchConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
if (mWindow != null) {
// Pass the configuration changed event to the window
mWindow.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
}
if (mActionBar != null) {
// Do this last; the action bar will need to access
// view changes from above.
mActionBar.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
}
}
以上注释大概的意思是,当你的Activity在运行时,有设备配置发生了变化,系统就会调用这个方法。如果你在manifest中配置了configChanges属性,则表示由你自己处理配置修改,否则就会重启这个Activity,并且会加载新的资源,这样就让系统以及应用加载完新的资源,完成了语言的切换。
总结
从整个流程来看,Android字体切换的流程如下:
- 当切换或添加新的语言时,会生成新的Configuration来替换原来的Configuration,并且修改项是可追寻的;
- 根据最新的Configuration来更新系统资源以及应用资源;
- 重启所有的Activity并更新到最新的资源;
- 完成语言切换。
以下为语言切换流程大致的时序图。
注:由于个人能力有限以及时间关系,有遗漏或错误的地方,还请批评指出,谢谢。
参考博客
wqhjfree
七号大蒜