Android高级-View是如何被添加到屏幕窗口上
View被添加到屏幕上分为以下几个步骤:
1 创建 顶层布局容器DecorView
新建一个extends的Activty 类,从onCreate方法的setContentView方法进入源码开始分析
setContentView(R.layout.activity_s_econd);
/** * Set the activity content from a layout resource. The resource will be * inflated, adding all top-level views to the activity. * * @param layoutResID Resource ID to be inflated. * * @see #setContentView(android.view.View) * @see #setContentView(android.view.View, android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams) */ public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) { getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID); initWindowDecorActionBar(); }
其中getWindow()返回的是Window对象,/** * Retrieve the current {@link android.view.Window} for the activity. * This can be used to directly access parts of the Window API that * are not available through Activity/Screen. * * @return Window The current window, or null if the activity is not * visual. */ public Window getWindow() { return mWindow; }
因 Winow是抽象类,所以我们需要找到它的实现类,红字部分提示,PhoneWindow是Window的唯一实现类,所以我们继续进入PhoneWindow的源码查看setContentView()方法
/** * Abstract base class for a top-level window look and behavior policy. An * instance of this class should be used as the top-level view added to the * window manager. It provides standard UI policies such as a background, title * area, default key processing, etc. * *The only existing implementation of this abstract class is * android.view.PhoneWindow, which you should instantiate when needing a * Window. */ public abstract class Window {
PhoneWindow的setContentView()
@Override public void setContentView(int layoutResID) { // Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window // decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature // before this happens. if (mContentParent == null) { installDecor(); 重点 } else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { mContentParent.removeAllViews(); } if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID, getContext()); transitionTo(newScene); } else { mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent); } //省略... }
接上文的installDecor()方法
private void installDecor() { mForceDecorInstall = false; if (mDecor == null) { mDecor = generateDecor(-1); mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS); mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true); if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) { mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable); } } else { mDecor.setWindow(this); } if (mContentParent == null) { mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor); // Set up decor part of UI to ignore fitsSystemWindows if appropriate. mDecor.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows(); final DecorContentParent decorContentParent = (DecorContentParent) mDecor.findViewById( R.id.decor_content_parent); //省略.... } }
从上面可以看到当mDecor (private DecorView mDecor) 为空时候,调用generateDecor方法创建了一个新的,
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) { // System process doesn't have application context and in that case we need to directly use // the context we have. Otherwise we want the application context, so we don't cling to the // activity. Context context; if (mUseDecorContext) { Context applicationContext = getContext().getApplicationContext(); if (applicationContext == null) { context = getContext(); } else { context = new DecorContext(applicationContext, getContext().getResources()); if (mTheme != -1) { context.setTheme(mTheme); } } } else { context = getContext(); } return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes()); }
中间一大段都是在初始化不同的上下文对象,而方法最终返回的是 new DecorView();
2 在顶层布局中加载基础布局ViewGroup
拿到DecorView 以后,,,继续看的installDecor()方法中的 mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor); 方法 其中这个
很长的一段
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) { // Apply data from current theme. TypedArray a = getWindowStyle(); //省略.... if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) { requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE); } else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) { // Don't allow an action bar if there is no title. requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR); } //省略很多类似于上文的requestFeature // Inflate the window decor. 加载dector的基础布局 int layoutResource; int features = getLocalFeatures(); // System.out.println("Features: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(features)); if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_SWIPE_TO_DISMISS)) != 0) { layoutResource = R.layout.screen_swipe_dismiss;//这是一个优化退出的布局 setCloseOnSwipeEnabled(true); }//省略很多..... layoutResource = else { // Embedded, so no decoration is needed. layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple; // System.out.println("Simple!"); } mDecor.startChanging(); mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource); ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT); if (contentParent == null) { throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view"); } // Remaining setup -- of background and title -- that only applies // to top-level windows. if (getContainer() == null) { final Drawable background; if (mBackgroundResource != 0) { background = getContext().getDrawable(mBackgroundResource); } else { background = mBackgroundDrawable; } mDecor.setWindowBackground(background); final Drawable frame; if (mFrameResource != 0) { frame = getContext().getDrawable(mFrameResource); } else { frame = null; } mDecor.setWindowFrame(frame); mDecor.setElevation(mElevation); mDecor.setClipToOutline(mClipToOutline); if (mTitle != null) { setTitle(mTitle); } if (mTitleColor == 0) { mTitleColor = mTextColor; } setTitleColor(mTitleColor); } mDecor.finishChanging(); return contentParent; }
通过解析基础布局,将View添加到DecorView上,这个onResourcesLoaded()方法是DecorView的
void onResourcesLoaded(LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutResource) { mStackId = getStackId(); //省略.... mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater); final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null); if (mDecorCaptionView != null) { if (mDecorCaptionView.getParent() == null) { addView(mDecorCaptionView, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT)); } mDecorCaptionView.addView(root, new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT)); } else { // Put it below the color views. addView(root, 0, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT)); } mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) root; initializeElevation(); }
解析完基础布局以后,我们接着看generateLayout()方法的
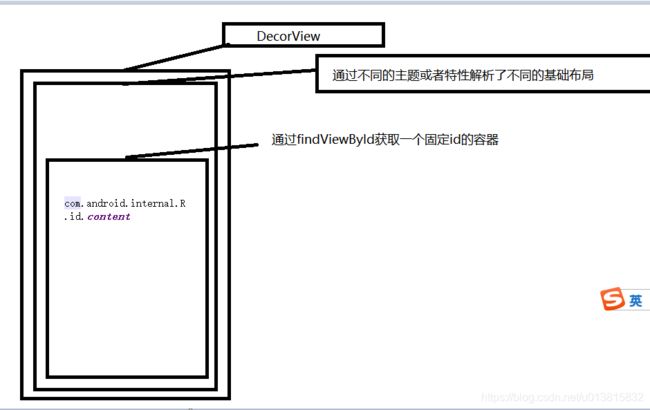
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
通过findViewById获取一个容器,这个容器的id是固定的值,通过注释可以看到,这个是主容器的id,而且是必须要存在的
/** * The ID that the main layout in the XML layout file should have. */ public static final int ID_ANDROID_CONTENT = com.android.internal.R.id.content;
然后将这个容器返回。
到此为止,我们的创建DecorView的操作就完成了。
总结关系图
1,Window是抽象类,提供了绘制窗口的一些列API
2,PhoneWindow是Window的具体继承实现类,而且该类包含了一个DecorView对象,这个对象是所有应用窗口(Activity界面)的根View
3,DecorView是PhoneWindow的内部类,是FrameLayout的子类,是对Framelayout功能的修饰。
补充:
DecorView:顶层视图,将要显示的具体内容呈现在PhoneWindow上. DecorView
是当前Activity所有View的祖先,它并不会向用户呈现任何东西,它主要有如下几个功能,可能不全
· A. Dispatch ViewRoot分发来的key、touch、trackball等外部事件;
· B. DecorView有一个直接的子View,我们称之为System Layout,这个View是从系统的Layout.xml中解析出的,它包含当前UI的风格,如是否带title、是否带process bar等。可以称这些属性为Window decorations。
· C. 作为PhoneWindow与ViewRoot之间的桥梁,ViewRoot通过DecorView设置窗口属性。//可以这样获取 View view = getWindow().getDecorView();· DecorView只有一个子元素为LinearLayout。代表整个Window界面,包含通知栏,标题栏,内容显示栏三块区域。DecorView里面TitleView:标题,可以设置requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE)取消掉ContentView:是一个id为content的FrameLayout。我们平常在Activity使用的setContentView就是设置在这里,也就是在FrameLayout上
3: 将ContentView添加到基础布局中去
分析完上面的,我们接着回到PhoneWindow的setContentView方法中
@Override public void setContentView(int layoutResID) { if (mContentParent == null) { installDecor(); } else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { mContentParent.removeAllViews(); } if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID, getContext()); transitionTo(newScene); } else { mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent); } //省略... }
分析完installDecor方法,创建了DecorView,根据不同的主题或者特性解析了不同的基础布局,并将基础布局加载到DecorView上,创建完成后,我们将主activity上
setContentView(R.layout.activity_s_econd);
set过来的R.layout.activity_s_econd 这个布局文件,添加到mContentParent中去,而mContentParent就是解析过的基础布局,
到此,只是完成了创建DecorView,以及将需要展示的view添加到基础布局上,真正的view并没有展示---接着看下面的文章