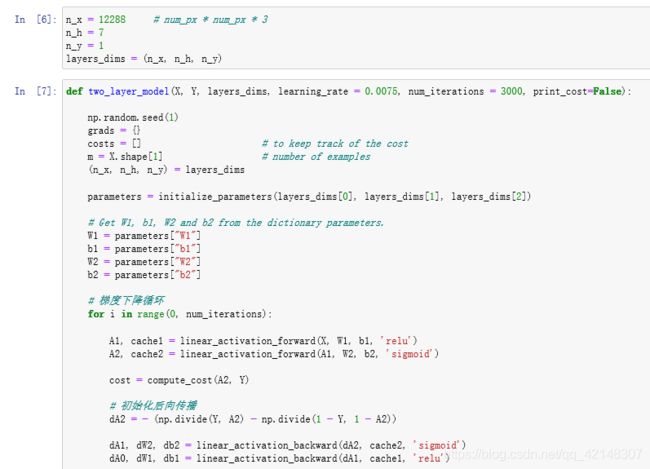
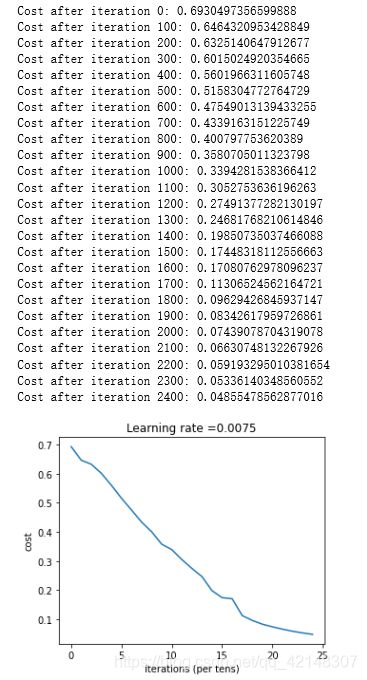
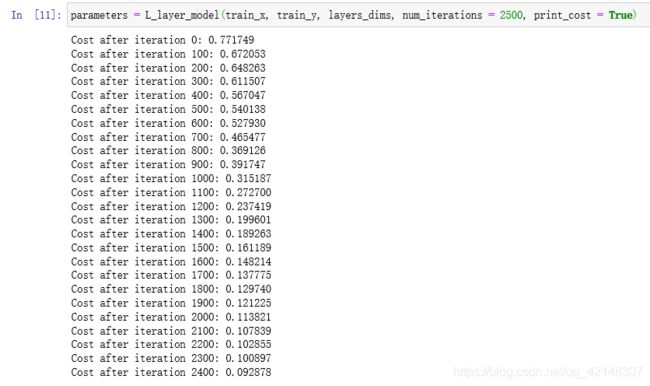
深度学习吴恩达作业题(4)
2、深度神经网络用于图片识别应用
2.1包
dnn_app_utils提供了在此笔记本的“构建深度神经网络:逐步”中实现的功能。
np.random.seed(1)用于使所有随机函数调用保持一致。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
def sigmoid(Z):
A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
cache = Z
return A, cache
def relu(Z):
A = np.maximum(0,Z)
assert(A.shape == Z.shape)
cache = Z
return A, cache
def relu_backward(dA, cache):
Z = cache
dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.
# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well.
dZ[Z <= 0] = 0
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache):
Z = cache
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
dZ = dA * s * (1-s)
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
def load_data():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
.random.seed(1)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x)*0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h)*0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
assert(W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert(b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert(W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert(b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
np.random.seed(1)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) / np.sqrt(layer_dims[l-1]) #*0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))
assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))
return parameters
def linear_forward(A, W, b):
Z = W.dot(A) + b
assert(Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
cache = (A, W, b)
return Z, cache
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
activation == "sigmoid":
# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
elif activation == "relu":
# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return A, cache
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
es = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], activation = "relu")
caches.append(cache)
# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], activation = "sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))
return AL, caches
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
m = Y.shape[1]
# Compute loss from aL and y.
cost = (1./m) * (-np.dot(Y,np.log(AL).T) - np.dot(1-Y, np.log(1-AL).T))
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17).
assert(cost.shape == ())
return cost
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):
rev, W, b = cache
m = A_prev.shape[1]
dW = 1./m * np.dot(dZ,A_prev.T)
db = 1./m * np.sum(dZ, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dA_prev = np.dot(W.T,dZ)
assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)
assert (dW.shape == W.shape)
assert (db.shape == b.shape)
return dA_prev, dW, db
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):
ar_cache, activation_cache = cache
if activation == "relu":
dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
elif activation == "sigmoid":
dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
return dA_prev, dW, db
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
{}
L = len(caches) # the number of layers
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL
# Initializing the backpropagation
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
# Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]
current_cache = caches[L-1]
grads["dA" + str(L)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, activation = "sigmoid")
for l in reversed(range(L-1)):
# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.
current_cache = caches[l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], current_cache, activation = "relu")
grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
return grads
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop.
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l+1)]
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l+1)]
return parameters
def predict(X, y, parameters):
= X.shape[1]
n = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
p = np.zeros((1,m))
# Forward propagation
probas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
# convert probas to 0/1 predictions
for i in range(0, probas.shape[1]):
if probas[0,i] > 0.5:
p[0,i] = 1
else:
p[0,i] = 0
#print results
#print ("predictions: " + str(p))
#print ("true labels: " + str(y))
print("Accuracy: " + str(np.sum((p == y)/m)))
return p
def print_mislabeled_images(classes, X, y, p):
a = p + y
mislabeled_indices = np.asarray(np.where(a == 1))
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (40.0, 40.0) # set default size of plots
num_images = len(mislabeled_indices[0])
for i in range(num_images):
index = mislabeled_indices[1][i]
plt.subplot(2, num_images, i + 1)
plt.imshow(X[:,index].reshape(64,64,3), interpolation='nearest')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title("Prediction: " + classes[int(p[0,index])].decode("utf-8") + " \n Class: " + classes[y[0,index]].decode("utf-8")2.2数据集
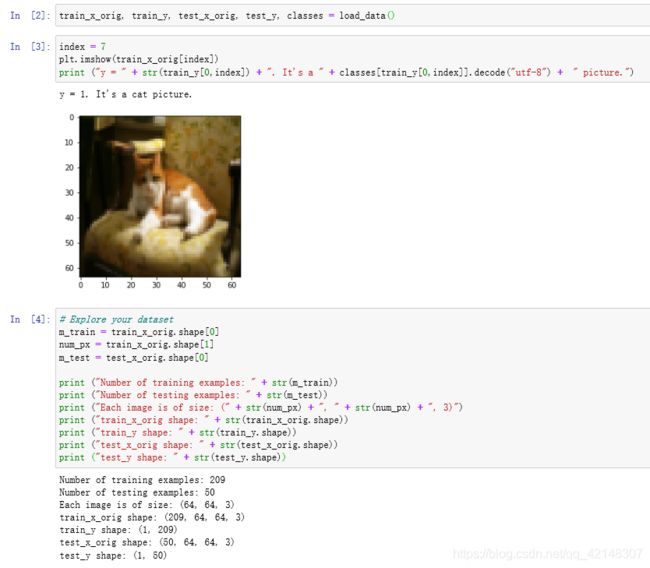
您将使用与“逻辑回归作为神经网络”(分配2)中相同的“猫与非猫”数据集。 您建立的模型在对猫和非猫图像进行分类时具有70%的测试准确性。 希望您的新模型性能更好!
问题陈述:您将获得一个包含以下内容的数据集(“ data.h5”):
-标记为cat(1)或非cat(0)的m_train图像的训练集
-标记为cat和non-cat的m_test图像的测试集
-每个图像的形状(num_px,num_px,3),其中3表示3个通道(RGB)。

2.3构建你的模型
与往常一样,您将遵循深度学习方法来构建模型:
1.初始化参数/定义超参数
2.循环执行num_iterations:
正向传播
计算成本函数
向后传播
更新参数(使用参数和反向传播的渐变)
4.使用训练有素的参数来预测标签