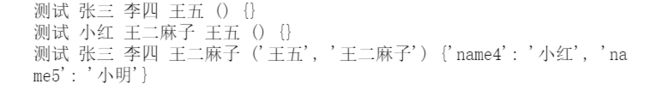python实训记录 One day
One day 打基础
python变量
作用:在内存中开辟空间,存储各种人类感知的数据,定义别名,用于引用
操作:创建文件,文件名称引用,文件内容存储数据
数据类型
- 数值: number
- 字符串: str
- 布尔: bool
- 序列:有多个元素组成
- 列表: list
- 元组: tuple
- 字典: dict key:value(类似于map)
a = 521
b = 5.21
c = "你是谁"
d = True
list1=[]
tuple1=()
dict1={}
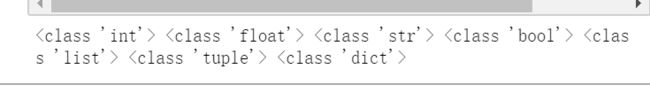
print(type(a), type(b), type(c),type(d), type(list1), type(tuple1),type(dict1))
动态数据类型
python变量类型决定是由=赋值决定,动态变化数据类型
(变量数据类型由等号右侧类型决定,同样随时因右侧数据类型的变化而变化,因此是动态的,不像java、c++等需要类型转换)
one = "一起去爬山吗?"
two = "我还有机会吗?"
print("动态数据",type(one))
one = 5.21
print("动态数据",type(one))
转换类型
把数据类型转换成其他类型
- int()
- float()
- str()
- list()
- tuple()
- dict()
print('521.1314',int(521.1314))
print('521',float(521))
print('521',type(str(521)))
print('一起去爬山',list('一起去爬山'))
print('我还有机会吗',tuple('我还有机会吗'))
# zip 压缩序列
# zip(key=[len],value=[len]) 1,2,3 4,5,6 = ((1,4),(2,5),(5,6))
# dict key:value ((1,4),(2,5),(5,6)) = {1:2,3:4,5:6}
print("KEY:VALUE",dict(zip([1,2,3],[4,5,6])))
序列
列表、元组、字典,字符串,学习序列对象的属性、函数
字符串
由若干个字符元素组成的特殊序列,只能保存字符类型
- 长度 len|len()
- 索引 str[index]
- 切片 str[start:last] 0:len-1
spe = "你是谁我是谁"
print("str-len长度",spe.__len__(),len(spe))
print("str-index索引",spe[0],spe[len(spe)-1])
print("str-index切片索引",spe[0:8],spe[:8],spe[0:],spe[:])
print("拼接",spe + "!!!!!")
print("多倍输出",spe * 5)
# 内置函数
c = spe.count(",")
print("统计",c)
stp = spe.strip("你是谁")
print("剔除",stp)
rep = spe.replace("你是谁","我是你")
print("替换",rep)
jo = "".join("521")
print("关联字符",jo)
列表
若干不同数据类型的元素组成,可以对数据进行增删改查
spe = "你是谁我是谁"
spe_list = list(spe)
print("list-len长度",spe_list.__len__(),len(spe_list))
print("list-index索引",spe_list[0],spe_list[len(spe_list)-1])
print("list-index切片索引",spe_list[0:8],spe_list[:8],spe_list[0:],spe_list[:])
print("拼接",spe_list+[1,2,3,4,5])
print("多倍输出",spe_list*5)
# 内置函数
c = spe_list.count("s")
print("统计",c)
spe_list=[1,12,14,4,2,5,7,8,9]
print("max",max(spe_list))
print("min",min(spe_list))
spe_list.sort()
print("排序",spe_list)
spe_list.reverse()
print("反转",spe_list)
# 修改
spe_list[0] = 20
# 添加和插入
spe_list.append(200)
spe_list.insert(0,100)
print(spe_list)
# 移除和清空
spe_list.remove(20)
print("移除",spe_list)
print("清空",spe_list.clear())
元组
由多个不同数据元素组成的序列,对初始数据有一个保护,所以不能修改、删除、添加数据
tuple1 = ("一","二","三","四","五")
print("tuple-len长度",tuple1.__len__(),len(tuple1))
print("tuple-index索引",tuple1[0],tuple1[len(tuple1)-1])
print("tuple-index切片索引",tuple1[0:3],tuple1[:3],tuple1[0:],tuple1[:])
print("拼接",tuple1+(1,2,3,4,5))
print("多倍输出",tuple1*5)
字典
保存数据结构 key:value,key是自定义索引(唯一),推荐str、int,value保存的值
star_dict = {"name":"张杰","sex":"男","age":18}
print("dict-len长度",len(star_dict))
print("dict-key索引",star_dict["name"],star_dict["sex"])
# 添加新集合
star_dict["tag"] = "偶像"
print(star_dict)
# 修改
star_dict["tag"] = "歌手"
print(star_dict)
# 删除
del star_dict["tag"]
print(star_dict)
# 内置函数
print("keys()",star_dict.keys())
print("values()",star_dict.values())
print("items()",star_dict.items())
star_dict.clear()
print(star_dict)
迭代器 for in 循环 while 循环
用于快速迭代序列,遍历
# /n 跨行 结束 “ ”空白符号 空格 间隔,模块范围 4个
i = 0
while i<5:
i+=1
print("i-",i)
else:
print("end")
条件关键字
- in 判断是否包裹,包裹返回true,不包裹false
- not 取非,相反值
- or 或
- and 与
for item in range(0,10):
print("item-",item)
#for char in "wuyifan":
# print("char-",char)
#for li in [1,2,3,4]:
# print("list-",li)
star_dict = {"name":"张杰","sex":"男","age":18}
for key in star_dict.keys():
print("key-",key)
for value in star_dict.values():
print("value-",value)
for key,value in star_dict.items():
print("key,value-",key,value)
Python函数 方法
可以定义执行某一段业务的代码块,模块化,阅读性提高,复用性,二次重构方便迭代,方便维护
声明 def name 函数引用 (自定义参数:可用于接受外部数据):
- 函数体
- 具体执行的业务模块
局部变量只能在其生命周期内使用,变量改变只引起当前变量改变,无法影响全局变量
def count(n:int) -> list:
"""
文档描述:该函数count用于计算斐波那契数列
keywork:1
n:int类型的值
return:result[] list类型
"""
result = []
a,b = 0,1
while a<n:
print(a,end=" ")
a,b = b,a+b
result.append(a)
return result # 返回调用位置
count(200)
# 函数重命名
f = count
r = f(200)
print(r)
# 函数文档和标注
print(count.__doc__)
print(count.__annotations__)
# lamda表达式 创建匿名函数关键字
x = 50
test = lambda y:x+y
test(100)
# 内嵌入的lamda表达式
def counts(x):
# x = 400
return lambda y:x+y
r1 = counts(400)
r1(100)
# 全局变量和局部变量
def test():
# 局部变量不是对全局的引用,所以不能修改全局的值
global x
x += 100
print(x)
test()
print(x)
参数多种形态
- 必备参数:必须传递的参数
- 命名参数:通过参数的名称直接赋值,可以不用参考顺序
- 缺省参数:参数设置默认值,可以不用传递数据
- 不定长度参数
4.1 元组参数 *tup
4.2 字典参数 **dict
def running(name1,name2,name3="王五",*tup,**dic):
print("测试",name1,name2,name3,tup,dic)
running("张三","李四")
running(name2="王二麻子",name1="小红")
running("张三","李四","王二麻子","王五","王二麻子",name4="小红",name5="小明")