JDBC连接数据库第二步:与数据交互 Statement 和 PreparedStatement
当获得了与数据库的连接后,就可以与数据库进行交互了。 获取数据库连接,参考上一篇文章。
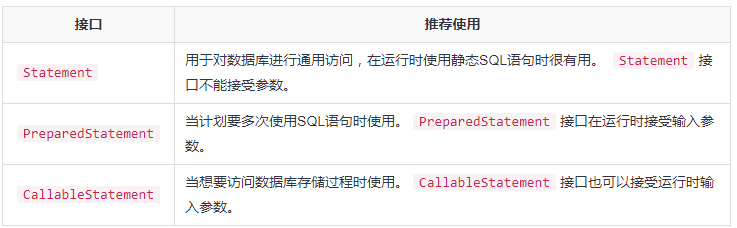
JDBC中Statement,PreparedStatement和CallableStatement接口定义了可用于发送SQL或PL/SQL命令,并从数据库接收数据的方法和属性。
下表提供了每个接口定义,以及使用这些接口的目的的总结。
表格来源:https://www.yiibai.com/jdbc/jdbc-statements.html
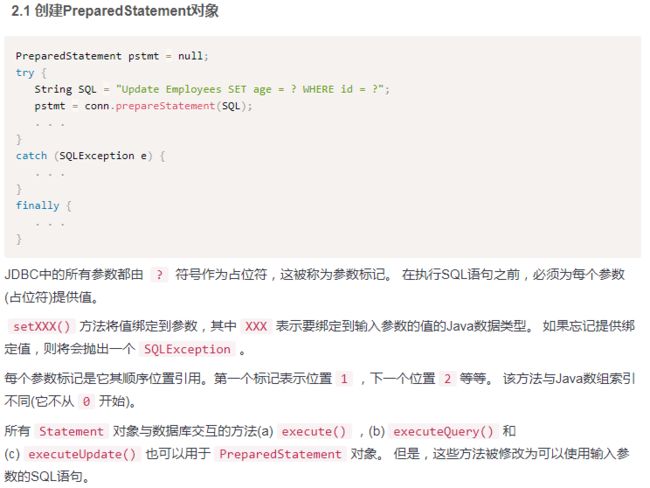
1.PreparedStatement对象
图片来源:https://www.yiibai.com/jdbc/jdbc-statements.html
1.2. 使用PreparedStatement对象进行数据库操作
1.2.1 获取数据库连接
/**
* 获取数据库连接
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection = null;
Properties info = new Properties();
try {
//***********代码缺陷:每次获取数据库连接时都要读配置文件**************************
info.load(JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().
getResourceAsStream("com/conf/properties/jdbc-conf.properties"));
String driverClass = info.getProperty("driverClass");
String jdbcUrl = info.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String user = info.getProperty("user");
String password = info.getProperty("password");
//*****************************************************************************
Class.forName(driverClass);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl,user,password);
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
//log.error("Not found properties file.");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//log.error("Not found driver class, load driver failed.");
} catch (SQLException e) {
//log.error("Get connection error.");
}
return connection;
}
1.2.2 preparedStatement执行 Query 操作
/**
* preparedStatement执行 Query 操作
* PreparedStatement接口扩展了Statement接口,它添加了比Statement对象更好一些优点的功能。此语句可以动态地提供/接受参数。
* JDBC中的所有参数都由 ? 符号作为占位符,这被称为参数标记。
* 在执行SQL语句之前,必须为每个参数(占位符)提供值。setXxx()方法将值绑定到参数,其中XXX表示要绑定到输入参数的值的Java数据类型。
* 如果忘记提供绑定值,则将会抛出一个SQLException。每个参数标记是它其顺序位置引用,第一个标记表示位置1,下一个位置2等等。
* 该方法与Java数组索引不同(它不从0开始)。
* 所有Statement对象与数据库交互的方法(a)execute(),(b)executeQuery()和(c)executeUpdate()也可以用于PreparedStatement对象。
* 但是,这些方法被修改为可以使用输入参数的SQL语句。
* @param sql
* @param args
* @return
*/
public static List preparedStatementExecuteSelect(final String sql,Object ...args){
Connection connection = getConnection();
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return null;
}
List users = new ArrayList<>();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0, length = args.length; i < length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,args[i]);
}
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
//使用构造函数创建user实例对象
// User user = new User(resultSet.getInt(1),resultSet.getString(2),
// resultSet.getString(3),resultSet.getDate(5),resultSet.getString(4));
User user = new User(resultSet.getInt("id"),resultSet.getString("userName"),
resultSet.getString("password"),resultSet.getDate("date"),
resultSet.getString("address"));
users.add(user);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(connection,null,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
return users;
}
/**
* preparedStatement查询一个User
* @param sql
* @return
*/
public static User preparedStatementExecuteQueryUser(final String sql,Object ...args){
List users = preparedStatementExecuteSelect(sql,args);
if (null != users && 0 != users.size()){
return users.get(0);
}
return null;
}
1.2.3 preparedStatement执行 update 操作
/**
* preparedStatement执行 update 操作
* @param sql
* @param args
*/
public static void preparedStatementExecuteUpdate(final String sql,Object ... args){
Connection connection = getConnection();
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return;
}
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0,length = args.length; i < length; i++){
//setObject的序号是从1开始的。
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,args[i]);
}
boolean flag = preparedStatement.execute();
//preparedStatement.execute()执行的是update、delete或insert语句的时候,返回的是false;
//执行的是select语句的时候,返回的true。
//参考地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mahuangping/p/6252887.html
System.out.println("preparedStatementExecuteUpdate:" + flag);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(connection,null,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
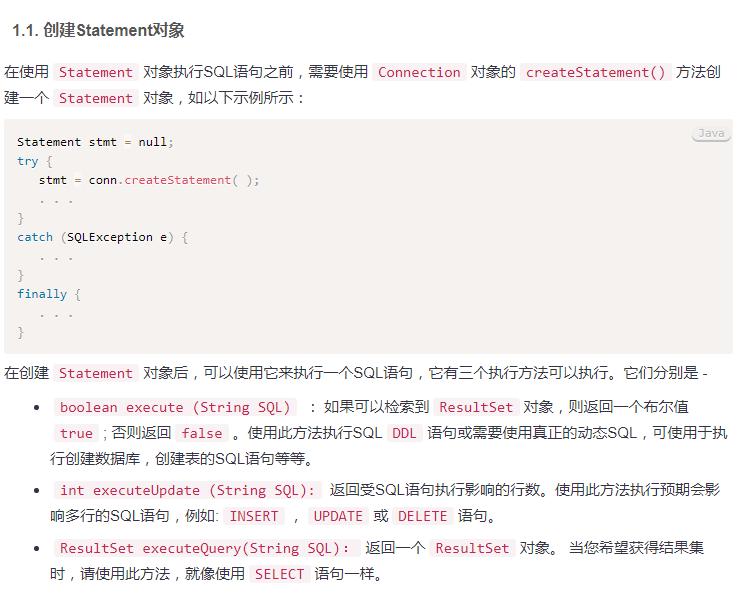
2. Statement对象
图片来源:https://www.yiibai.com/jdbc/jdbc-statements.html
2.2. 使用Statement对象进行数据库操作
2.2.1 获取数据库连接
/**
* 获取数据库连接
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection = null;
Properties info = new Properties();
try {
//***********代码缺陷:每次获取数据库连接时都要读配置文件**************************
info.load(JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().
getResourceAsStream("com/conf/properties/jdbc-conf.properties"));
String driverClass = info.getProperty("driverClass");
String jdbcUrl = info.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String user = info.getProperty("user");
String password = info.getProperty("password");
//*****************************************************************************
Class.forName(driverClass);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl,user,password);
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
//log.error("Not found properties file.");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//log.error("Not found driver class, load driver failed.");
} catch (SQLException e) {
//log.error("Get connection error.");
}
return connection;
}2.2.2 statement执行 Query 操作
/**
* statement查询一个User
* @param sql
* @return
*/
public static User statementExecuteQueryUser(final String sql){
List users = statementExecuteQuery(sql);
if (null != users && 0 != users.size()){
return users.get(0);
}
return null;
}
/**
* statement执行 Query 操作
* ResultSet:结果集,封装了查询的结果。
* 1、调用Statement对象的 executeQuery(sql) 方法进行查询结果集;
* 2、返回的 ResultSet 实际上是一张数据表,有一个指针指向数据表的第一行的前面;
* 可以调用 nest() 方法检测下一行是否有效,若有效返回true,且指针下移。相当于Iterator 对象的 hasNext() 和 next() 方法的结合体。
* 3、当指针移到某一行时,可以调用getXxx(index) 或 getXxx(columnName) 获取每一列的值。例如:getInt(1), getString("name")。
* 4、ResultSet 也需要进行关闭。
* @param sql
* @return
*/
public static List statementExecuteQuery(final String sql){
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
List userList = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = getConnection();
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return null;
}
try {
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if (null == resultSet){
//log.error("Get resultSet is null.");
return userList;
}
while (resultSet.next()){
User user = new User();
user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user.setUserName(resultSet.getNString("userName"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
user.setDate(resultSet.getDate("date"));
user.setAddress(resultSet.getString("address"));
userList.add(user);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
//log.error("execute operation failed.sql:" + sql);
} finally {
closeResource(connection,statement,null,resultSet);
}
return userList;
} 2.2.3 statement执行 Insert or Delete 操作
//1.获取数据库连接
//2.准备SQL语句
//3.执行SQL语句
//4.关闭Statement对象:如果关闭了connection,也会关闭statement. 关闭资源:注意关闭顺序:先关闭后获取的资源
//5.关闭connection连接
/**
* statement执行 Insert or Delete 操作
* 要提前将sql语句准备好
* @param sql
*/
public static boolean statementExecute(final String sql){
Connection connection = getConnection();
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
Statement statement = null;
try {
statement = connection.createStatement();
result =statement.execute(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
//log.error("execute operation failed.sql:" + sql);
result = false;
} finally {
closeResource(connection,statement,null,null);
}
return result;
}2.2.4 statement执行 Update 操作
/**
* statement执行 Update 操作
* @param sql
*/
public static void statementExecuteUpdate(final String sql){
Statement statement = null;
Connection connection = getConnection();
if (null == connection){
//log.error("Connection is null.");
return;
}
try {
statement = connection.createStatement();
int updateResult = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (0 == updateResult){
//log.error("execute update failed.");
}
System.out.println("update result: " + updateResult);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(connection,statement,null,null);
}
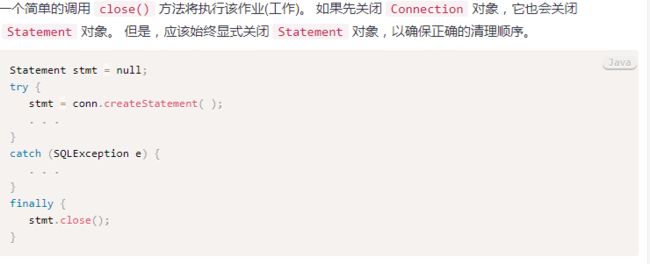
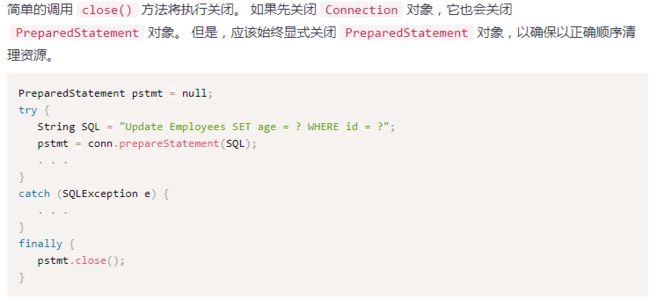
3. 关闭 Statement 和 PreparedStatement 对象
图片来源:https://www.yiibai.com/jdbc/jdbc-statements.html
关闭资源:
/**
* 关闭资源:注意关闭顺序:先关闭后获取的资源
* @param connection
* @param statement
* @param preparedStatement
* @param resultSet
*/
public static void closeResource(Connection connection, Statement statement,
PreparedStatement preparedStatement,ResultSet resultSet){
if (null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果先关闭Connection对象,它也会关闭Statement对象。
//但是,应该始终显式关闭Statement对象,以确保正确的清理顺序。
if (null != statement){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果先关闭Connection对象,它也会关闭PreparedStatement对象。
//但是,应该始终显式关闭PreparedStatement对象,以确保以正确顺序清理资源。
if (null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}更多连接: https://www.cnblogs.com/mahuangping/p/6252887.html 【preparedstatement execute()操作成功!但是返回false】