蓝桥杯软件大赛题目集锦之编程大题
1、分红酒
有4个红酒瓶子,它们的容量分别是:9升, 7升, 4升, 2升开始的状态是 [9,0,0,0],也就是说:第一个瓶子满着,其它的都空着。
允许把酒从一个瓶子倒入另一个瓶子,但只能把一个瓶子倒满或把一个瓶子倒空,不能有中间状态。这样的一次倒酒动作称为1次操作。
假设瓶子的容量和初始状态不变,对于给定的目标状态,至少需要多少次操作才能实现?
本题就是要求你编程实现最小操作次数的计算。
输入:最终状态(逗号分隔)
输出:最小操作次数(如无法实现,则输出-1)
例如:
输入:
9,0,0,0
应该输出:
0
输入:
6,0,0,3
应该输出:
-1
输入:
7,2,0,0
应该输出:
2
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
class State
{
int n[] = new int[4];
int step = 0;
public State(){}
public State(State state)
{
setVol(state.n);
step = state.step;
}
public void setVol(int N[])
{
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
n[i] = N[i];
}
}
public class Main
{
static int full[] = {9,7,4,2};
//static State state2 = new State();
static int vis[][][][] = new int[10][8][5][3];
public static boolean bfs(State state2, int start, int end)
{
//自己不能倒酒给自己
if(start == end) return false;
//start杯子为空不能倒酒
if(state2.n[start] == 0) return false;
//end杯子满了不能倒酒
if(state2.n[end] == full[end]) return false;
//将A中的酒倒入B中
if(state2.n[end] + state2.n[start] <= full[end])
{
state2.n[end] += state2.n[start];
state2.n[start] = 0;
}
//A中的酒没有完全倒干净
else
{
state2.n[start] = state2.n[start] - (full[end] - state2.n[end]);
state2.n[end] = full[end];
}
if(vis[state2.n[0]][state2.n[1]][state2.n[2]][state2.n[3]] == 1) return false;
else
vis[state2.n[0]][state2.n[1]][state2.n[2]][state2.n[3]] = 1;
state2.step++;
return true;
}
public static boolean isEnd(State state, int end[])
{
int flag = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if(state.n[i] != end[i])
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
if(flag == 1) return true;
else return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int end[] = new int[4];
Queueq = new LinkedList();
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
String s;
s = cin.nextLine();
String ss[] = s.split(",");
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
end[i] = Integer.parseInt(ss[i]);
//判断初始状态是否合法
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
if(end[i] > full[i])
{
System.out.println("-1");
return;
}
//初始起点入队列
State state = new State();
int start[] = {9,0,0,0};
state.setVol(start);
state.step = 0;
q.add(state);
//开始搜索
int flag = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
State temp1 = new State();
temp1 = q.remove();
if(isEnd(temp1, end))
{
flag = 1;
System.out.println(temp1.step);
break;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
State state2 = new State(temp1);
if(bfs(state2,i , j))
{
q.add(state2);
}
}//for j
}//for i
}//while
if(flag == 0) System.out.println("-1");
}//main()
}//class Main
2、制作表格
在中文Windows环境下,控制台窗口中也可以用特殊符号拼出漂亮的表格来。比如:
┌─┬─┐
│ │ │
├─┼─┤
│ │ │
└─┴─┘
其实,它是由如下的符号拼接的:
左上 = ┌
上 = ┬
右上 = ┐
左 = ├
中心 = ┼
右 = ┤
左下= └
下 = ┴
右下 = ┘
垂直 = │
水平 = ─
本题目要求编写一个程序,根据用户输入的行、列数画出相应的表格来。
例如用户输入:
3 2
则程序输出:
┌─┬─┐
│ │ │
├─┼─┤
│ │ │
├─┼─┤
│ │ │
└─┴─┘
用户输入:
2 3
则程序输出:
┌─┬─┬─┐
│ │ │ │
├─┼─┼─┤
│ │ │ │
└─┴─┴─┘
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s[] = {"┌","┬","┐","├","┼","┤","└","┴","┘","│","─"};
int x , y;
int i , j;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
x = cin.nextInt();
y = cin.nextInt();
//第一层部分
System.out.print(""+s[0]+s[10]);
for(i = 0; i < y - 1; i++)
System.out.print(""+s[1]+s[10]);
System.out.println(""+s[2]);
System.out.print(""+s[9]);
for(i = 0; i < y; i++)
System.out.print(" "+s[9]);
System.out.println();
//中间部分
for(i = 0; i < x - 1; i++)
{
System.out.print(""+s[3]+s[10]);
for(j = 0; j < y-1; j++)
System.out.print(""+s[4]+s[10]);
System.out.println(""+s[5]);
System.out.print(""+s[9]);
for(j = 0; j < y; j++)
System.out.print(" "+s[9]);
System.out.println();
}
//最后一层部分
System.out.print(""+s[6] + s[10]);
for(i = 0; i < y - 1; i++)
System.out.print(""+s[7] + s[10]);
System.out.println(""+s[8]);
}
}3、运动员分组
有N个人参加100米短跑比赛。跑道为8条。程序的任务是按照尽量使每组的人数相差最少的原则分组。例如:
N=8时,分成1组即可。
N=9时,分成2组:一组5人,一组4人。
N=25时,分4组:7、6、6、6。
请编程计算分组数字。
要求从标准输入获得一个正整数(1~100之间,不必考虑输入错误的情况),表示参赛的人数。
程序输出每个组的人数。从大到小顺序输出,每个数字一行。
比如,
用户输入:25
程序输出:
7
6
6
6
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n;
int i, j, k;
int count;
int num[] = new int[30];
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
n = cin.nextInt();
i = n / 8;
j = n % 8;
for(k = 0; k < i; k++)
num[k] = 8;
if(j == 0) count = i;
else
{
count = i+1;
num[i] = j;
}
while(true)
{
Arrays.sort(num, 0, count);
if(num[count-1] - num[0] > 1)
{
num[count-1]--;
num[0]++;
continue;
}
else break;
}
for(j = count-1; j >=0; j--)
System.out.println(""+num[j]);
}
}4、信用卡校验
当你输入信用卡号码的时候,有没有担心输错了而造成损失呢?其实可以不必这么担心,因为并不是一个随便的信用卡号码都是合法的,它必须通过Luhn算法来验证通过。该校验的过程:
1、从卡号最后一位数字开始,逆向将奇数位(1、3、5等等)相加。
2、从卡号最后一位数字开始,逆向将偶数位数字,先乘以2(如果乘积为两位数,则将其减去9),再求和。
3、将奇数位总和加上偶数位总和,结果应该可以被10整除。
例如,卡号是:5432123456788881
逆向奇数位为 4 2 2 4 6 8 8 1 和 = 35
逆向偶数位乘以2(有些要减去9)的结果:1 6 2 6 1 5 7 7,求和 = 35。
最后 35 + 35 = 70 可以被10整除,认定校验通过。
请编写一个程序,从标准输入获得卡号,然后判断是否校验通过。
通过显示:“成功”,否则显示“失败”。
比如,
输入:356827027232780
程序输出:成功
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s;
int i , j;
int a = 0 , b = 0;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
s = cin.next();
char ss[] = s.toCharArray();
for(i = s.length() - 1; i >=0; i--)
{
if((i + 1) % 2 == 1)
a = a + (ss[i] - '0');
else
{
int temp;
temp = (ss[i] - '0') * 2;
if(temp > 9) temp -= 9;
b = b + temp;
}
}
if((a+b) % 10 == 0)
System.out.println("成功");
else System.out.println("失败");
}
}5、取字符
从键盘读入一个由字母构成的串(不大于30个字符)。
从该串中取出3个不重复的字符,求所有的取法。
取出的字符,要求按字母升序排列成一个串。
不同的取法输出顺序可以不考虑。
例如:
输入:
abc
则输出:
abc
输入:
abcd
则输出:
abc
abd
acd
bcd
输入:
abcaa
则输出:
abc
要求考生把所有类写在一个文件中。
调试好后,存入与考生文件夹下对应题号的“解答.txt”中即可。
相关的工程文件不要拷入。请不要使用package语句。
另外,源程序中只能出现JDK1.5中允许的语法或调用。不能使用1.6或更高版本。
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str;
String temp;
int i , j , k;
int len;
List list = new ArrayList();
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
str = cin.next();
char s[] = str.toCharArray();
len = str.length();
for(i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < len; j++)
{
for(k = 0; k < len; k++)
{
if(i==j || i==k || j==k) continue;
if(s[i]==s[j] || s[i]==s[k] || s[j]==s[k]) continue;
temp = "" + s[i] + s[j] + s[k];
if(justice(list,temp) || list.size() == 0)
{
list.add(temp);
}
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
System.out.println(""+list.get(i));
}
public static boolean justice(List list, String str)
{
int i;
char s1[] = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(s1);
String temp1 = new String(s1);
for(i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
{
str = list.get(i);
s1 = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(s1);
String temp2 = new String(s1);
if(temp2.equals(temp1)) return false;
}
return true;
}
} 6、核桃的数量
小张是软件项目经理,他带领3个开发组。工期紧,今天都在加班呢。为鼓舞士气,小张打算给每个组发一袋核桃(据传言能补脑)。他的要求是:
1. 各组的核桃数量必须相同
2. 各组内必须能平分核桃(当然是不能打碎的)
3. 尽量提供满足1,2条件的最小数量(节约闹革命嘛)
程序从标准输入读入:
a b c
a,b,c都是正整数,表示每个组正在加班的人数,用空格分开(a,b,c<30)
程序输出:
一个正整数,表示每袋核桃的数量。
例如:
用户输入:
2 4 5
程序输出:
20
再例如:
用户输入:
3 1 1
程序输出:
3
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a , b , c, MAX;
int i = 1, j;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
a = cin.nextInt();
b = cin.nextInt();
c = cin.nextInt();
MAX = max(a,b,c);
while(true)
{
j = MAX * i;
if(j%a==0 && j%b==0 && j%c==0) break;
i++;
}
System.out.println(""+j);
}
public static int max(int a , int b, int c)
{
if(a > b)
{
if(a > c) return a;
else return c;
}
else
{
if(b > c) return b;
else return c;
}
}
}
7、第39级台阶
小明刚刚看完电影《第39级台阶》,离开电影院的时候,他数了数礼堂前的台阶数,恰好是39级!
站在台阶前,他突然又想着一个问题:
如果我每一步只能迈上1个或2个台阶。先迈左脚,然后左右交替,最后一步是迈右脚,也就是说一共要走偶数步。那么,上完39级台阶,有多少种不同的上法呢?
请你利用计算机的优势,帮助小明寻找答案。
要求提交的是一个整数。
注意:不要提交解答过程,或其它的辅助说明文字。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int count = 0;
void dfs(int sum , int step)
{
if(sum == 39)
{
if(step % 2 == 0)
{
count++;
return;
}
else return;
}
else if(sum > 39) return;
else
{
dfs(sum+1, step+1);
dfs(sum+2, step+1);
}
}
int main()
{
dfs(0 , 0);
cout< 8、打印十字图
小明为某机构设计了一个十字型的徽标(并非红十字会啊),如下所示(可参见p1.jpg)
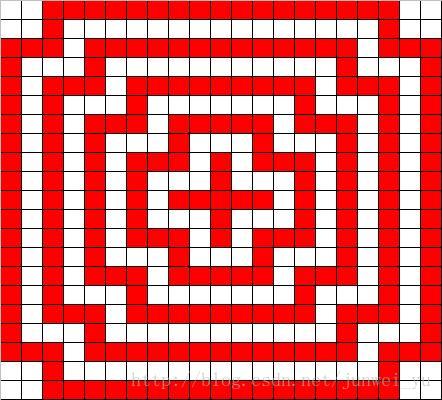
$$$$$$$$$$$$$
$ $
$$$ $$$$$$$$$ $$$
$ $ $ $
$ $$$ $$$$$ $$$ $
$ $ $ $ $ $
$ $ $$$ $ $$$ $ $
$ $ $ $ $ $ $
$ $ $ $$$$$ $ $ $
$ $ $ $ $ $ $
$ $ $$$ $ $$$ $ $
$ $ $ $ $ $
$ $$$ $$$$$ $$$ $
$ $ $ $
$$$ $$$$$$$$$ $$$
$ $
$$$$$$$$$$$$$
对方同时也需要在电脑dos窗口中以字符的形式输出该标志,并能任意控制层数。
为了能准确比对空白的数量,程序要求对行中的空白以句点(.)代替。
输入格式:
一个正整数 n (n<30) 表示要求打印图形的层数
输出:
对应包围层数的该标志。
例如:
用户输入:
1
程序应该输出:
..$$$$$..
..$...$..
$$$.$.$$$
$...$...$
$.$$$$$.$
$...$...$
$$$.$.$$$
..$...$..
..$$$$$..
再例如:
用户输入:
3
程序应该输出:
..$$$$$$$$$$$$$..
..$...........$..
$$$.$$$$$$$$$.$$$
$...$.......$...$
$.$$$.$$$$$.$$$.$
$.$...$...$...$.$
$.$.$$$.$.$$$.$.$
$.$.$...$...$.$.$
$.$.$.$$$$$.$.$.$
$.$.$...$...$.$.$
$.$.$$$.$.$$$.$.$
$.$...$...$...$.$
$.$$$.$$$$$.$$$.$
$...$.......$...$
$$$.$$$$$$$$$.$$$
..$...........$..
..$$$$$$$$$$$$$..
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
char map[130][130]; //储存需要打印的图形
int num[31]; //储存n对应图形的边长
void init()
{
int i , j;
for(i = 0; i < 30; i++)
num[i] = 5 + i * 4;
for(i = 0; i < 130; i++)
for(j = 0; j < 130; j++)
map[i][j] = '.';
}
int main()
{
int n;
int i, j;
init();
cin>>n;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < num[n-i-1]; j++) //打印第一行
map[i * 2][(i + 1) * 2 + j] = '$';
map[(i+1)*2-1][(i+1)*2] = '$'; //打印第二行,的单个$
map[(i+1)*2-1][(i+1)*2 + num[n-i-1] - 1] = '$';
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) //打印上拐角的三个字符
{
map[(i+1)*2][i*2 + j] = '$';
map[(i+1)*2][num[n-1]+1-(i*2) + j] = '$';
}
for(j = 0; j < num[n-i-1]; j++) //打印竖直的n个字符
{
map[(i+1)*2 + j][i*2] = '$';
map[(i+1)*2 + j][num[n-1]+4-1 - i*2] = '$';
}
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) //打印下拐角的三个字符
{
map[num[n-1]+4-1 - (i+1)*2][i*2 + j] = '$';
map[num[n-1]+4-1 - (i+1)*2][num[n-1]+1-(i*2) + j] = '$';
}
map[num[n-1]+4-1-((i+1)*2-1)][(i+1)*2] = '$'; //打印倒数第二行,的单个$
map[num[n-1]+4-1-((i+1)*2-1)][(i+1)*2 + num[n-i-1] - 1] = '$';
for(j = 0; j < num[n-i-1]; j++) //打印最后一行
map[num[n-1]+4-1 -i*2][(i + 1) * 2 + j] = '$';
}
//打印中间十字形状
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
map[2*(n+1)][2*n + i] = '$'; //heng
map[n*2 + i][2*(n+1)] = '$'; //shu
}
for(i = 0; i < num[n-1]+4; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < num[n-1]+4; j++)
cout< 9、颠倒的价牌
小李的店里专卖其它店中下架的样品电视机,可称为:样品电视专卖店。
其标价都是4位数字(即千元不等)。
小李为了标价清晰、方便,使用了预制的类似数码管的标价签,只要用颜色笔涂数字就可以了(参见p1.jpg)。
这种价牌有个特点,对一些数字,倒过来看也是合理的数字。如:1 2 5 6 8 9 0 都可以。这样一来,如果牌子挂倒了,有可能完全变成了另一个价格,比如:1958 倒着挂就是:8561,差了几千元啊!!
当然,多数情况不能倒读,比如,1110 就不能倒过来,因为0不能作为开始数字。
有一天,悲剧终于发生了。某个店员不小心把店里的某两个价格牌给挂倒了。并且这两个价格牌的电视机都卖出去了!
庆幸的是价格出入不大,其中一个价牌赔了2百多,另一个价牌却赚了8百多,综合起来,反而多赚了558元。
请根据这些信息计算:赔钱的那个价牌正确的价格应该是多少?
答案是一个4位的整数,请通过浏览器直接提交该数字。
注意:不要提交解答过程,或其它辅助说明类的内容。
9088
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef struct
{
int s_true;
int s_false;
int chajia;
}Stor;
int main()
{
int num1[7] = {0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 9};
int num2[7] = {0, 1, 2, 5, 9, 8, 6};
Stor stor1[2500]; //赚钱
int s1 = 0;
Stor stor2[2500]; //赔钱
int s2 = 0;
int a1, a2, a3, a4;
int i , j;
for(a1 = 1; a1 < 7; a1++)
{
for(a2 = 0; a2 < 7; a2++)
{
for(a3 = 0; a3 < 7; a3++)
{
for(a4 = 1; a4 < 7; a4++)
{
int temp1 = 0, temp2 = 0;
temp1 = num1[a1]*1000 + num1[a2]*100 + num1[a3]*10 + num1[a4];
temp2 = num2[a1] + num2[a2]*10 + num2[a3]*100 + num2[a4]*1000;
if(temp2-temp1 >= 800 && temp2 - temp1 < 900)
{
stor1[s1].s_false = temp2;
stor1[s1].s_true = temp1;
stor1[s1].chajia = temp2 - temp1;
s1++;
}
if(temp1 - temp2 >= 200 && temp1 - temp2 < 300)
{
stor2[s2].s_false = temp2;
stor2[s2].s_true = temp1;
stor2[s2].chajia = temp2 - temp1;
s2++;
}
}//FOR A4
}//for a3
}//for a2
}//for a1
for(i = 0; i < s1; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < s2; j++)
{
if(stor1[i].chajia + stor2[j].chajia == 558)
{
cout< 10、幻方填空
幻方是把一些数字填写在方阵中,使得行、列、两条对角线的数字之和都相等。
欧洲最著名的幻方是德国数学家、画家迪勒创作的版画《忧郁》中给出的一个4阶幻方。
他把1,2,3,...16 这16个数字填写在4 x 4的方格中。
如图p1.jpg所示,即:
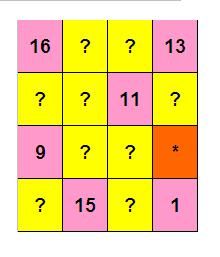
16 ? ? 13
? ? 11 ?
9 ? ? *
? 15 ? 1
表中有些数字已经显露出来,还有些用?和*代替。
请你计算出? 和 * 所代表的数字。并把 * 所代表的数字作为本题答案提交。
答案是一个整数,请通过浏览器直接提交该数字。
注意:不要提交解答过程,或其它辅助说明类的内容。
12
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//16 [0] [1] 13
//[2] [3] 11 [4]
//9 [5] [6] [7]
//[8] 15 [9] 1
int Num[10] = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,10,12,14};
int num[10];
int SUM;
int vis[10];
int check()
{
if(SUM != 16+num[0]+num[1]+13) return 0;
if(SUM != num[2]+num[3]+11+num[4])return 0;
if(SUM != 9+num[5]+num[6]+num[7])return 0;
if(SUM != num[8]+15+num[9]+1)return 0;
if(SUM != 16+num[2]+9+num[8])return 0;
if(SUM != num[0]+num[3]+num[5]+15)return 0;
if(SUM != num[1]+11+num[6]+num[9])return 0;
if(SUM != 13+num[4]+num[7]+1)return 0;
if(SUM != 16+num[3]+num[6]+1)return 0;
if(SUM != 13+11+num[5]+num[8])return 0;
cout< 11、机器人行走
某少年宫引进了一批机器人小车。可以接受预先输入的指令,按指令行动。小车的基本动作很简单,只有3种:左转(记为L),右转(记为R),向前走若干厘米(直接记数字)。例如,我们可以对小车输入如下的指令:
15L10R5LRR10R20
则,小车先直行15厘米,左转,再走10厘米,再右转,...
不难看出,对于此指令串,小车又回到了出发地。
你的任务是:编写程序,由用户输入指令,程序输出每条指令执行后小车位置与指令执行前小车位置的直线距离。
【输入、输出格式要求】
用户先输入一个整数n(n<100),表示接下来将有n条指令。
接下来输入n条指令。每条指令只由L、R和数字组成(数字是0~100之间的整数)
每条指令的长度不超过256个字符。
程序则输出n行结果。
每条结果表示小车执行相应的指令前后位置的直线距离。要求四舍五入到小数后2位。
例如:用户输入:
5
L100R50R10
3LLL5RR4L12
LL
100R
5L5L5L5
则程序输出:
102.96
9.06
0.00
100.00
0.00
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main
{
static int dir_x[] = {0,1,0,-1};
static int dir_y[] = {1,0,-1,0};
static int dir = 0;
static int x = 0 , y = 0;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n;
String s;
char ss[] = new char[260];
int i , j , k;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
n = cin.nextInt();
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
x = 0; y = 0; dir = 0;
s = cin.next();
ss = s.toCharArray();
for(j = 0; j < ss.length;)
{
if(ss[j] == 'L')
{
j++;
dir = (dir - 1 + 4) % 4;
}
else if(ss[j] == 'R')
{
j++;
dir = (dir + 1) % 4;
}
else if(ss[j]>='0' && ss[j]<='9')
{
k = j;
while(k < ss.length && ss[k]>='0' && ss[k]<='9')
k++;
k--;
int len = 0, p = 1;
int temp = k+1;
while(j <= k)
{
len = len + (ss[k]-'0')*p;
p *= 10;
k--;
}
x = x + dir_x[dir]*len;
y = y + dir_y[dir]*len;
j = temp;
}//else if
}//for j
double len = Math.sqrt(x*x*1.0+y*y*1.0);
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",len);
}//for i
}//main()
}//class Main
12、立方和等式
考虑方程式:a^3 + b^3 = c^3 + d^3其中:“^”表示乘方。a、b、c、d是互不相同的小于30的正整数。
这个方程有很多解。比如:
a = 1,b=12,c=9,d=10 就是一个解。因为:1的立方加12的立方等于1729,而9的立方加10的立方也等于1729。
当然,a=12,b=1,c=9,d=10 显然也是解。
如果不计abcd交换次序的情况,这算同一个解。
你的任务是:找到所有小于30的不同的正整数解。把a b c d按从小到大排列,用逗号分隔,每个解占用1行。比如,刚才的解输出为:
1,9,10,12
不同解间的顺序可以不考虑。
import java.util.*;
class Num
{
int n[] = new int[4];
public Num(){}
public Num(int temp[])
{
n[0] = temp[0]; n[1]=temp[1]; n[2]=temp[2]; n[3]=temp[3];
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a , b , c , d;
Num num[] = new Num[100];
int count = 0;
int flag;
for(a = 1; a < 30; a++)
{
for(b = 1; b < 30; b++)
{
if(a == b) continue;
for(c = 1; c < 30; c++)
{
if(c == a || c == b) continue;
for(d = 1; d < 30; d ++)
{
if(d==a || d == c || d == b) continue;
if(a*a*a+b*b*b != c*c*c+d*d*d) continue;
flag = 1;
int temp[] = new int[4];
temp[0] = a; temp[1] = b; temp[2] = c; temp[3] = d;
Arrays.sort(temp);
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if(temp[0]==num[i].n[0] && temp[1]==num[i].n[1] && temp[2]==num[i].n[2] && temp[3]==num[i].n[3])
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
if(flag == 1)
{
num[count] = new Num(temp);
System.out.println(""+num[count].n[0]+","+num[count].n[1]+","+num[count].n[2]+","+num[count].n[3]);
count++;
}//if(flag == 1)
}//for(d = 0)
}//for(c == 0)
}//for(b == 0)
}//for(a==0)
}//main()
}//class Main13、匪警请拨110
匪警请拨110,即使手机欠费也可拨通!为了保障社会秩序,保护人民群众生命财产安全,警察叔叔需要与罪犯斗智斗勇,因而需要经常性地进行体力训练和智力训练!
某批警察叔叔正在进行智力训练:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 = 110;
请看上边的算式,为了使等式成立,需要在数字间填入加号或者减号(可以不填,但不能填入其它符号)。之间没有填入符号的数字组合成一个数,例如:12+34+56+7-8+9 就是一种合格的填法;123+4+5+67-89 是另一个可能的答案。
请你利用计算机的优势,帮助警察叔叔快速找到所有答案。
每个答案占一行。形如:
12+34+56+7-8+9
123+4+5+67-89
......
已知的两个答案可以输出,但不计分。
各个答案的前后顺序不重要。
123+4+5+67-89=110
123+4-5-6-7-8+9=110
123-4+5-6-7+8-9=110
123-4-5+6+7-8-9=110
12+34+56+7-8+9=110
12+3+45+67-8-9=110
12-3+4-5+6+7+89=110
1+234-56-78+9=110
1+2+34+5+67-8+9=110
1-2+3+45-6+78-9=110
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int ch[8];
//存储符号,0为空格,1为+, 2 为-
int Num[9] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
void check()
{
//检查式子是否满足条件
int fuhao[8];
int n1 = 0;
int num[9];
int n2 = 0;
int i , j;
int temp = 0; //界限标志
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if(ch[i] == 1 || ch[i] == 2)
{
int temp_num = 0;
int k = 1;
for(j = i; j >= temp; j--)
{
temp_num += Num[j] * k;
k *= 10;
}
num[n2++] = temp_num;
fuhao[n1++] = ch[i];
temp = i+1;
}
}
if(ch[7] == 1 || ch[7] == 2)
{
num[n2++] = 9;
}
else
{
int temp_num = 0;
int k = 1;
for(j = 8; j >= temp; j--)
{
temp_num += Num[j] * k;
k *= 10;
}
num[n2++] = temp_num;
}
//进行运算,判断是否满足条件
int sum = num[0];
for(i = 0; i < n1; i++)
{
if(fuhao[i] == 1)
sum += num[i+1];
else if(fuhao[i] == 2)
sum -= num[i+1];
}
if(sum == 110)
{
cout<