MySQL InnoDB引擎的表通过拷贝物理文件来进行单表或指定表的复制,可以想到多种方式,今天测试其中2种:
- 将innodb引擎的表修改为Myisam引擎,然后拷贝物理文件
- 直接拷贝innodb的表空间文件(前提是独立表空间(默认,通过show variables like 'innodb_file_per_table' 查看))进行复制
一、修改引擎
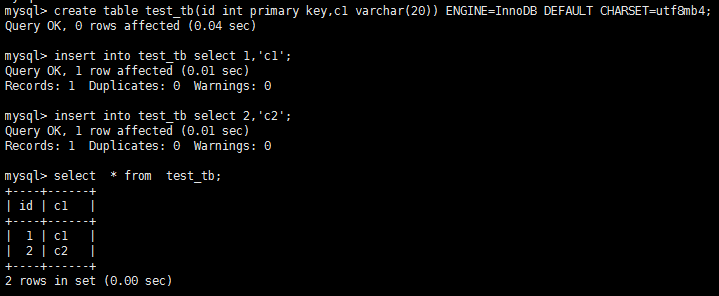
1.创建一张innodb引擎的表,并插入测试数据;
create table test_tb(id int primary key,c1 varchar(20)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; insert into test_tb select 1,'c1'; insert into test_tb select 2,'c2';
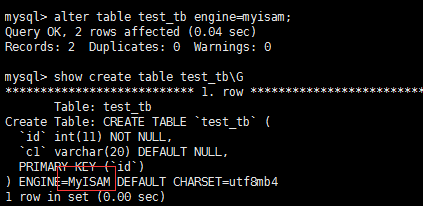
2. 修改引擎
alter table test_tb engine=myisam; show create table test_tb\G
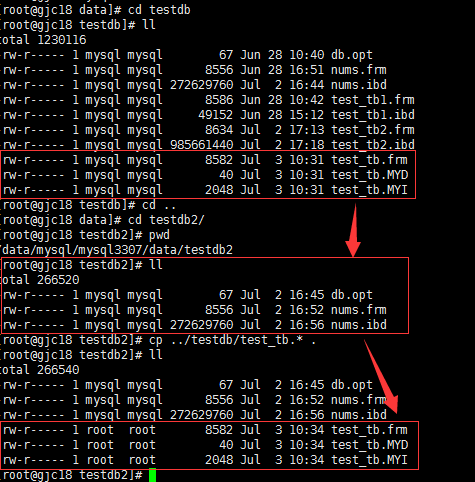
3. 将物理文件拷贝至目标库
cd /data/mysql/mysql3307/data/ cd testdb ll cd ../testdb2/ pwd ll cp ../testdb/test_tb.* . ll
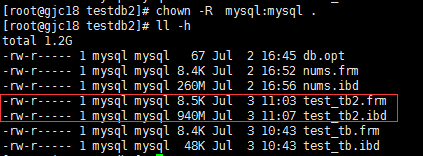
4.修改权限
chown -R mysql:mysql .
5. 查看结果
记录和源库一致。
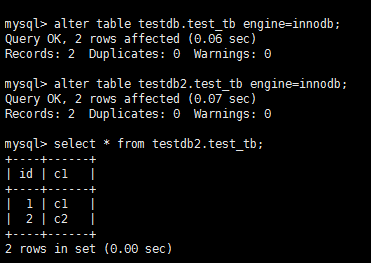
6. 将源库及目标库的表引擎修改为innodb
alter table testdb.test_tb engine=innodb; alter table testdb2.test_tb engine=innodb;
二、拷贝.idb物理表空间文件
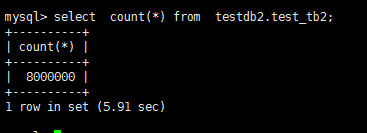
1. 创建一张innodb的表,为了测试大表的情况,我创建了一张800W记录的表,占用940M空间
/*先创建快速生成连续数的表及存储过程*/ -- 建表 CREATE TABLE `test_tb2` ( `id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `aa` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `bb` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `cc` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4; --创建过程 DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE `sp_test_tb2`(cnt INT ) BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1; TRUNCATE TABLE test_tb2; INSERT INTO test_tb2 SELECT concat(i,'a'),concat(i,'b'),concat(i,'c') ; WHILE i < cnt DO BEGIN INSERT INTO test_tb2 SELECT id + i,concat(id+i,'a'),concat(id+i,'b'),concat(id+i,'c') FROM test_tb2 WHERE id + i<=cnt; SET i = i*2; END; END WHILE; END$$ DELIMITER ; -- 生成8000000条记录 call sp_test_tb2(8000000); select count(*) from test_tb2;
2. 在目标库创建相同的表名
mysql> use testdb2; CREATE TABLE `test_tb2` ( `id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `aa` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `bb` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `cc` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
3. 删除目标表的表空间
alter table test_tb2 discard tablespace;
此时目标库的test_tb2表近剩下数据定义文件,表空间文件已删除
4. 拷贝源库的idb文件
5. 修改表空间文件权限
6. 目标表导入表空间数据(记录较多的时候需要一点时间)
alter table test_tb2 import tablespace;
7. 查看导入结果
结果与源表一致
Tips:
以上2种处理方式都需要源表无写入更新等操作下进行,且需要flush tables 将数据刷新到物理磁盘的文件上。所以建议先锁表或停止业务,待拷贝文件后再恢复写入等操作。