Java获取函数参数名称的几种方法
Java获取函数参数名称的几种方法
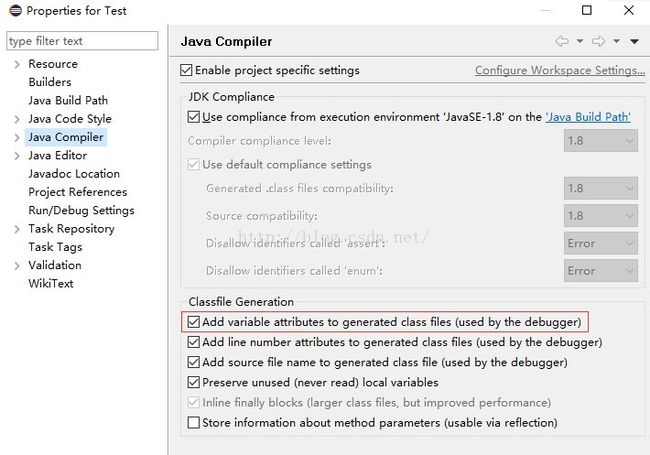
JDK1.7及以下版本的API并不能获取到函数的参数名称,需要使用字节码处理框架,如ASM、javassist等来实现,且需要编译器开启输出调试符号信息的参数的-g,在Eclipse中就是要勾选下面的选项:
1、下面给出一个使用ASM获取函数参数名称的例子:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassReader;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
import org.objectweb.asm.Type;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class clazz = TestMain.class;
try {
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test", String.class,
int.class);
String[] pns = getParameterNamesByAsm5(clazz, method);
System.out.print(method.getName() + " : ");
for (String parameterName : pns) {
System.out.print(parameterName + ' ');
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void test(String param1, int param2) {
System.out.println(param1 + param2);
}
public static String[] getParameterNamesByAsm5(Class clazz,
final Method method) {
final Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes == null || parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return null;
}
final Type[] types = new Type[parameterTypes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
types[i] = Type.getType(parameterTypes[i]);
}
final String[] parameterNames = new String[parameterTypes.length];
String className = clazz.getName();
int lastDotIndex = className.lastIndexOf(".");
className = className.substring(lastDotIndex + 1) + ".class";
InputStream is = clazz.getResourceAsStream(className);
try {
ClassReader classReader = new ClassReader(is);
classReader.accept(new ClassVisitor(Opcodes.ASM5) {
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name,
String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
// 只处理指定的方法
Type[] argumentTypes = Type.getArgumentTypes(desc);
if (!method.getName().equals(name)
|| !Arrays.equals(argumentTypes, types)) {
return super.visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature,
exceptions);
}
return new MethodVisitor(Opcodes.ASM5) {
@Override
public void visitLocalVariable(String name, String desc,
String signature, org.objectweb.asm.Label start,
org.objectweb.asm.Label end, int index) {
// 非静态成员方法的第一个参数是this
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
parameterNames[index] = name;
} else if (index > 0) {
parameterNames[index - 1] = name;
}
}
};
}
}, 0);
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
return parameterNames;
}
}2、使用javassist获取函数参数名称的例子:
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javassist.CtMethod;
import javassist.Modifier;
import javassist.NotFoundException;
import javassist.bytecode.CodeAttribute;
import javassist.bytecode.LocalVariableAttribute;
import javassist.bytecode.MethodInfo;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class clazz = TestMain.class;
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
try {
CtClass ctClass = pool.get(clazz.getName());
CtMethod ctMethod = ctClass.getDeclaredMethod("test");
// 使用javassist的反射方法的参数名
MethodInfo methodInfo = ctMethod.getMethodInfo();
CodeAttribute codeAttribute = methodInfo.getCodeAttribute();
LocalVariableAttribute attr = (LocalVariableAttribute) codeAttribute
.getAttribute(LocalVariableAttribute.tag);
if (attr != null) {
int len = ctMethod.getParameterTypes().length;
// 非静态的成员函数的第一个参数是this
int pos = Modifier.isStatic(ctMethod.getModifiers()) ? 0 : 1;
System.out.print("test : ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.print(attr.variableName(i + pos) + ' ');
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (NotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void test(String param1, int param2) {
System.out.println(param1 + param2);
}
}
可以看见直接使用ASM和javassist来获取函数参数名称都还是比较麻烦的
3、使用spring-core中的LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer来获取函数参数名称,它对ASM进行了封装:
import org.springframework.core.LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterNameDiscoverer;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer =
new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer();
try {
String[] parameterNames = parameterNameDiscoverer
.getParameterNames(TestMain.class.getDeclaredMethod("test",
String.class, int.class));
System.out.print("test : ");
for (String parameterName : parameterNames) {
System.out.print(parameterName + ' ');
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void test(String param1, int param2) {
System.out.println(param1 + param2);
}
}
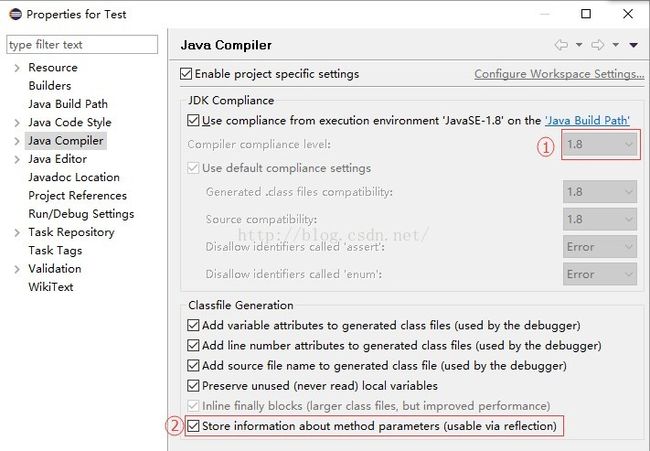
4、在Java1.8之后,可以通过反射API java.lang.reflect.Executable.getParameters来获取到方法参数的元信息。这要求在使用编译器时加上-parameters参数,它会在生成的.class文件中额外存储参数的元信息,这会增加class文件的大小。在Eclipse下默认没有使用该编译参数,需要设置:
下面给出一个使用Java8反射函数参数名称的例子:
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(final String[] arguments) throws Exception {
Class clazz = TestMain.class;
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test", String.class, int.class);
System.out.print("test : ");
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (final Parameter parameter : parameters) {
if (parameter.isNamePresent()) {
System.out.print(parameter.getName() + ' ');
}
}
}
public void test(String param1, int param2) {
System.out.println(param1 + param2);
}
}5、使用注解。
上面介绍的几种方法都需要依赖编译器附加一定的编译参数,才能获取到。如果程序编译不想保留这些调试信息和附加的元数据,或者你开发一个了框架提供给别人使用,可是该框架想要获取用户代码的函数参数名,因为你并不能控制别人怎么编译Java代码,这时怎么提供一种不受编译器影响的途径来确保获取到函数参数名呐?看看spring mvc是怎么做的——使用函数参数注解。下面使用注解来获取参数名的例子:
定义函数参数注解:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
public @interface Parameter {
String value();
}使用该注解,并反射函数参数名:
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Method method = TestMain.class.getMethod("test", String.class, int.class);
System.out.print("test : ");
Annotation parameterAnnotations[][] = method.getParameterAnnotations();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterAnnotations.length; i++) {
for (Annotation annotation : parameterAnnotations[i]) {
if (Parameter.class.equals(annotation.annotationType())) {
System.out.print(((Parameter) annotation).value() + ' ');
}
}
}
}
public void test(@Parameter("param1") String param1,
@Parameter("param2") int param2) {
System.out.println(param1 + param2);
}
}