C++ sort排序函数的用法总结
标准模板库STL中的sort()函数,时间复杂度为n*log2(n),执行效率较高。
用法:
①、sort()函数可以三个参数也可以两个参数;
②、必须的头文件 #include < algorithm>和using namespace std。
③、它使用的排序方法类似于快排,时间复杂度为n*log2(n)
sort()函数有三个参数:(第三个参数可不写)
(1)第一个是要排序的数组的起始地址。
(2)第二个是最后一位要排序的元素的下一位的地址。
(3)第三个参数是排序的方法,可以是从大到小也可是从小到大,还可以不写第三个参数,此时默认的排序方法是从小到
大排序。
sort函数,左闭右开,即 int a[10]={2,4,1,23,5,76,0,43,24,65}。 sort(a,a+10)。
两个参数用法:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[10]={2,4,1,23,5,76,0,43,24,65};
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout< 输出结果是升序排列。(两个参数的sort默认升序排序)
结果:
三个参数:
①、加入一个比较函数 complare():
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool complare(int a,int b){
return a>b;
}
int main(){
int a[10]={2,4,1,23,5,76,0,43,24,65};
//打印原数组
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout< 结果:
②、使用 less<数据类型>(),或 greater<数据类型>():
less<数据类型>()//从小到大排序
greater<数据类型>()//从大到小排序
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[10]={2,4,1,23,5,76,0,43,24,65};
//打印原数组
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout<());
//打印排序后的数组
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout< 结果:
③、对向量vector排序:
1、使用 sort(vec.begin(),vec.end())排序;
2、使用sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),greater
())排序。
vector
vec(arr,arr+10); // 用数组元素初始化vector容器,左闭右开,即+元素数量 。
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),greater
()); // <>里面只需装容器所容纳的元素的类型
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int arr[10]={5,6,1,9,3,7,3,1,0,8};
//vector容器存放arr数组中的元素
vector vec(arr,arr+10); //经典!用数组元素初始化vector容器,左闭右开,即+元素数量
for(int i=0;i()规则:
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),greater()); //这就很神奇了!!!
cout<<"使用greater<>()规则: ";
for(int i=0;i 结果:
③、对字符数组进行排序:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
char arr[11]="asdfghjklk";
sort(arr,arr+10,greater());
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout< 结果:
④、对字符串排序:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
string arr="asdfghjklk";
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end(),less());
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout< 结果:
⑤、 对结构体排序:
1、自定义规则;
2、运算符重载。
1、自定义规则:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct student{
string name;
int age;
};
//自己定义的规则:按姓名从小到大排列,若姓名一样,按年龄从小到大排列
bool comp(student s1,student s2){
if(s1.name==s2.name){
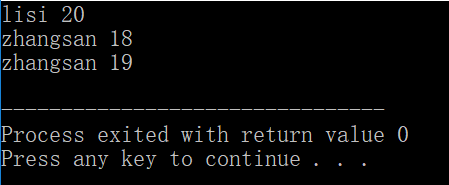
return s1.age 结果:
2、运算符重载:
bool operator < (const student &s) const
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct student{
string name;
int age;
bool operator < (const student &s)const{//符号重载
if(name==s.name){
return age 结果:
string 使用反向迭代器来完成逆序排列
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str("cvicses"); //用()对字符串赋值
string s(str.rbegin(),str.rend()); //反向迭代器,将字符串str翻转,赋值给字符串s
cout << s < 结果:
NOTICE:
数据量较大时,用sort不太好,比如,员工年龄那道题,这时就要自己写排序函数了。