新年新气象,也希望新年可以挣大钱。不管今年年底会不会跟去年一样,满怀抱负却又壮志未酬。(不过没事,我已为各位卜上一卦,卦象显示各位都能挣钱...)。已经上班两天了,公司大部分人还在休假,而我早已上班,估计今年我就是加班狗的命。(不说了,要坚强...)
以上扯淡已毕,下面言归正传。
这次的.NET加密解析系列中,前面已经讲解了散列加密、对称加密、数字签名三种加密方式,在这篇博文种,将会主要讲解非对称加密的原理,以及非对称加密在.NET种的应用。
一.非对称加密概述:
前面讲解过对称加密,对称加密中加密和解密的密钥是相同的,但是正因为如此,这会给协商过程带来潜在的危险。所以产生了非对称加密方式。
1.非对称加密原理概述:
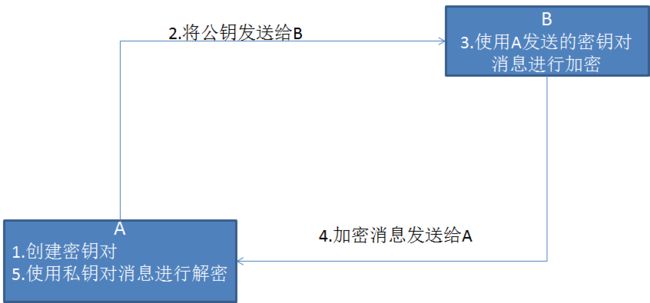
非对称加密算法需要两个密钥,分别是公钥和私钥。公钥和私钥是一对,如果公钥对数据进行加密,只有使用私钥才可以进行解密,反之亦然。对于非对称加密的原理有如下图:
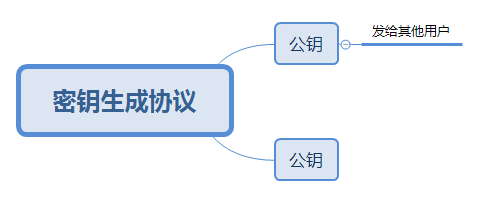
以上是大致说明了消息利用非对称加密和解密的方式,解析来我们再来看一下如果生成密钥对。非对称加密算法包含一个“密钥生成”协议,用户可以使用该协议生成密钥对。有如下图:
在非对称加密算法中,使用两个有关的函数,一个是加密函数,使用一个公钥加密消息,加密函数只能加密数据;一个时解密函数,使用一个私钥来解密被响应公钥加密的消息。
2.非对称加密特点概述:
非对称加密算法中,采用加密函数和解密函数,加密函数只能加密函数,解密函数只能解密函数。加密函数的单向性意味着一个发送者创建的消息不能被另一个发送者阅读。非对称加密相对于对称加密来说,非对称加密的速度非常慢,而且不适用于加密大量数据,公钥加密(非对称加密)是用来为对称加密算法解决密钥协商的问题而产生的。RSA算法中指定密钥长度为最小的位数,这些位的个数使用二进制数表示密钥系数N的值。
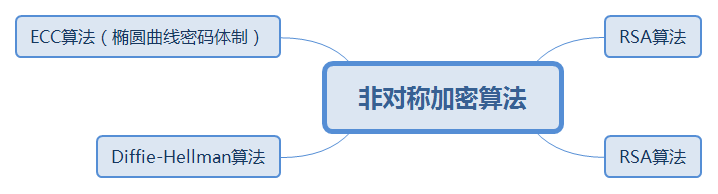
3.非对称加密算法分类概述:
对于非对称加密算法的种类,有如下图:
RSA算法:此算法是基于数论的非对称密码体制,采用分组加密方式。安全性是基于大整数因子分解的困难性,RSA算法是第一个既能用于数据加密也能用与数字签名的算法。
DSA算法(数字签名算法):次算法是基于证书有限域离散对数难题。
ECC算法(椭圆曲线密码体制):椭圆曲线指的是由维尔斯特拉斯方程所确定的平面曲线。
Diffie-Hellman算法:该算法本身限于密钥交换的用途,目的在于使得两个用户安全地交换一个秘密密钥以便用与以后的报文加密。该算法依赖于计算离散对数的难度。
以上是简单介绍了一些算法,没有更加深入的介绍其算法原理,由于涉及的知识面比较广,分析起来比较的繁琐,在这里就不做讲解,如果有兴趣可以自行学习和了解。
二.DotNet非对称加密核心对象解析:
上面简单叙述了非对称加密的原理,在这里主要介绍非对称加密算法在.NET种的应用,以及实现该算法所创建的对象。在这里主要介绍RSA算法的核心对象。
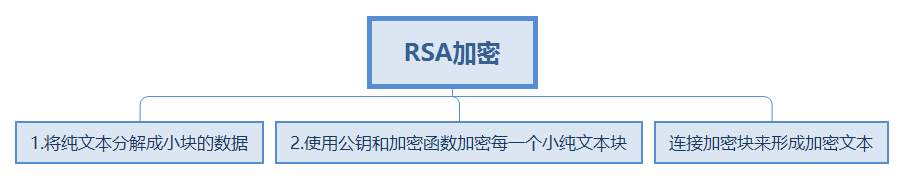
1.RSA加密和解密的方式:
2.DotNet种RSA算法核心对象概述:
在.NET种对于非对称加密算法的结构体系有如下图:
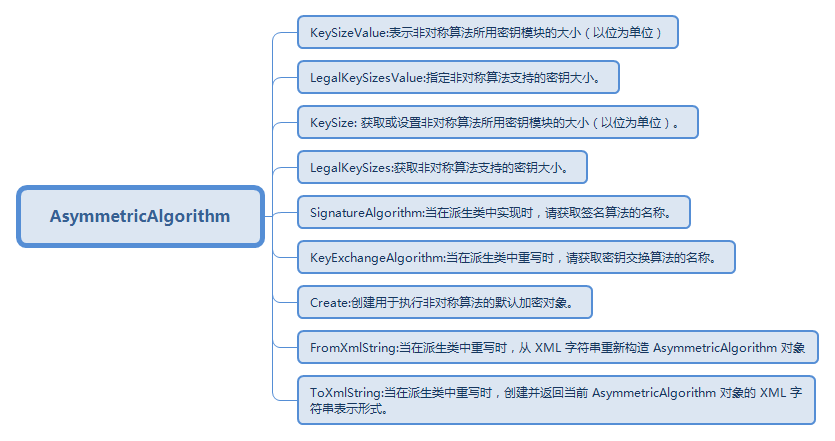
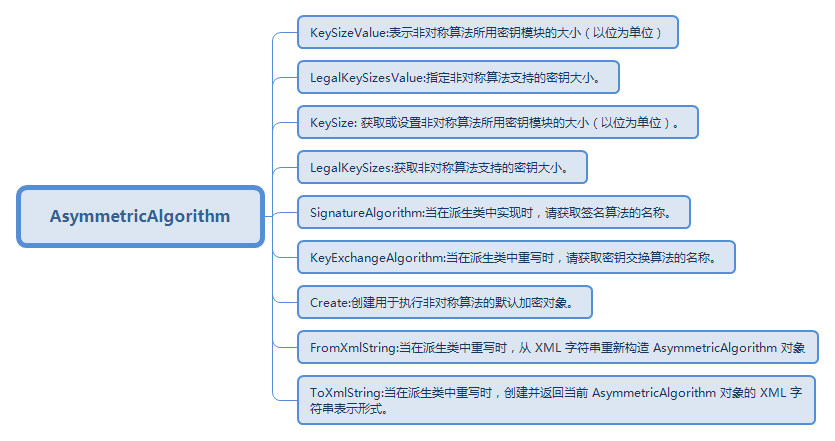
3.AsymmetricAlgorithm类解析:
(1).Create():创建用于执行非对称算法的默认加密对象。
public static AsymmetricAlgorithm Create() { return AsymmetricAlgorithm.Create("System.Security.Cryptography.AsymmetricAlgorithm"); }
该方法返回新的 RSACryptoServiceProvider 实例,除非已使用 <cryptoClass> 元素更改默认设置。
public static AsymmetricAlgorithm Create(string algName) { return (AsymmetricAlgorithm) CryptoConfig.CreateFromName(algName); }
该方法返回所指定的非对称算法实现的新实例。接收参数为要使用的非对称算法实现。CryptoConfig.CreateFromName()该方法在前面的加密方式中已经做过解析,这里就不做介绍了。
(2).KeySize:获取或设置非对称算法所用密钥模块的大小(以位为单位)。
public virtual int KeySize { get { return this.KeySizeValue; } set { for (int index = 0; index < this.LegalKeySizesValue.Length; ++index) { if (this.LegalKeySizesValue[index].SkipSize == 0) { if (this.LegalKeySizesValue[index].MinSize == value) { this.KeySizeValue = value; return; } } else { int minSize = this.LegalKeySizesValue[index].MinSize; while (minSize <= this.LegalKeySizesValue[index].MaxSize) { if (minSize == value) { this.KeySizeValue = value; return; } minSize += this.LegalKeySizesValue[index].SkipSize; } } } throw new CryptographicException(Environment.GetResourceString("Cryptography_InvalidKeySize")); } }
由以上代码可以发现,该属性具有get和set两个构造器,说明该属性是可读可写的。该属性返回非对称算法所用密钥模块的大小(以位为单位)。
4.RSA类解析:
(1).FromXmlString():通过 XML 字符串中的密钥信息初始化Cryptography.RSA对象。
public override void FromXmlString(string xmlString) { if (xmlString == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("xmlString"); RSAParameters parameters = new RSAParameters(); SecurityElement topElement = new Parser(xmlString).GetTopElement(); string inputBuffer1 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("Modulus"); if (inputBuffer1 == null) { string key = "Cryptography_InvalidFromXmlString"; object[] objArray = new object[2]; int index1 = 0; string str1 = "RSA"; objArray[index1] = (object) str1; int index2 = 1; string str2 = "Modulus"; objArray[index2] = (object) str2; throw new CryptographicException(Environment.GetResourceString(key, objArray)); } parameters.Modulus = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer1)); string inputBuffer2 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("Exponent"); if (inputBuffer2 == null) { string key = "Cryptography_InvalidFromXmlString"; object[] objArray = new object[2]; int index1 = 0; string str1 = "RSA"; objArray[index1] = (object) str1; int index2 = 1; string str2 = "Exponent"; objArray[index2] = (object) str2; throw new CryptographicException(Environment.GetResourceString(key, objArray)); } parameters.Exponent = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer2)); string inputBuffer3 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("P"); if (inputBuffer3 != null) parameters.P = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer3)); string inputBuffer4 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("Q"); if (inputBuffer4 != null) parameters.Q = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer4)); string inputBuffer5 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("DP"); if (inputBuffer5 != null) parameters.DP = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer5)); string inputBuffer6 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("DQ"); if (inputBuffer6 != null) parameters.DQ = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer6)); string inputBuffer7 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("InverseQ"); if (inputBuffer7 != null) parameters.InverseQ = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer7)); string inputBuffer8 = topElement.SearchForTextOfLocalName("D"); if (inputBuffer8 != null) parameters.D = Convert.FromBase64String(Utils.DiscardWhiteSpaces(inputBuffer8)); this.ImportParameters(parameters); }
该方法是继承自AsymmetricAlgorithm类,在RSA类种被重写,该方法接收参数包含 RSA 密钥信息的 XML 字符串。SecurityElement类表示用于编码安全对象的XML对象模型。
(2).ToXmlString():创建并返回包含当前 RSA 对象的密钥的 XML 字符串。
public override string ToXmlString(bool includePrivateParameters) { RSAParameters rsaParameters = this.ExportParameters(includePrivateParameters); StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.Append(""); stringBuilder.Append(" " + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.Modulus) + ""); stringBuilder.Append(" " + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.Exponent) + ""); if (includePrivateParameters) { stringBuilder.Append("" + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.P) + ""); stringBuilder.Append("" + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.Q) + ""); stringBuilder.Append(" " + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.DP) + ""); stringBuilder.Append(" " + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.DQ) + ""); stringBuilder.Append(" " + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.InverseQ) + ""); stringBuilder.Append(" " + Convert.ToBase64String(rsaParameters.D) + ""); } stringBuilder.Append(""); return stringBuilder.ToString(); }
该方法同样继承自AsymmetricAlgorithm类,该方法接收一个布尔型的参数,true 表示同时包含 RSA 公钥和私钥;false 表示仅包含公钥。该方法返回包含当前 RSA 对象的密钥的 XML 字符串。RSAParameters为一个结构,表示System.Security.Cryptography.RSA算法的标准参数。
5.RSACryptoServiceProvider类解析:
(1).Encrypt():使用 RSA算法对数据进行加密。
[SecuritySafeCritical] public byte[] Encrypt(byte[] rgb, bool fOAEP) { if (rgb == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("rgb"); this.GetKeyPair(); byte[] o = (byte[]) null; RSACryptoServiceProvider.EncryptKey(this._safeKeyHandle, rgb, rgb.Length, fOAEP, JitHelpers.GetObjectHandleOnStack<byte[]>(ref o)); return o; }
该方法接受两个参数,要加密的数据。fOAEP如果为 true,则使用 OAEP 填充(仅在运行 Microsoft Windows XP 或更高版本的计算机上可用)执行直接的 RSA 加密;否则,如果为 false,则使用 PKCS#1 1.5 版填充。该方法返回一个已加密的数据,为一个字节数组。
(2).Decrypt():使用 RSA算法对数据进行解密。
[SecuritySafeCritical] public byte[] Decrypt(byte[] rgb, bool fOAEP) { if (rgb == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("rgb"); this.GetKeyPair(); if (rgb.Length > this.KeySize / 8) { string key = "Cryptography_Padding_DecDataTooBig"; object[] objArray = new object[1]; int index = 0; // ISSUE: variable of a boxed type __Boxed<int> local = (ValueType) (this.KeySize / 8); objArray[index] = (object) local; throw new CryptographicException(Environment.GetResourceString(key, objArray)); } if (!this.CspKeyContainerInfo.RandomlyGenerated && !CompatibilitySwitches.IsAppEarlierThanWindowsPhone8) { KeyContainerPermission containerPermission = new KeyContainerPermission(KeyContainerPermissionFlags.NoFlags); KeyContainerPermissionAccessEntry accessEntry = new KeyContainerPermissionAccessEntry(this._parameters, KeyContainerPermissionFlags.Decrypt); containerPermission.AccessEntries.Add(accessEntry); containerPermission.Demand(); } byte[] o = (byte[]) null; RSACryptoServiceProvider.DecryptKey(this._safeKeyHandle, rgb, rgb.Length, fOAEP, JitHelpers.GetObjectHandleOnStack<byte[]>(ref o)); return o; }
该方法接受两个参数,rgb要解密的数据。fOAEP如果为 true,则使用 OAEP 填充(仅在运行 Microsoft Windows XP 或更高版本的计算机上可用)执行直接的
三.应用实例:
1.RsaHelper类:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Text; namespace BasicMmethodExtensionClass.EncryptHelper { ////// 非对称RSA加密类 /// 需要BigInteger类来辅助 /// public static class RsaHelper { /// /// RSA的容器 可以解密的源字符串长度为 DWKEYSIZE/8-11 /// public const int Dwkeysize = 1024; /// /// RSA加密的密匙结构 公钥和私匙 /// public struct RsaKey { public string PublicKey { get; set; } public string PrivateKey { get; set; } } /// /// 得到RSA的解谜的密匙对 /// /// public static RsaKey GetRasKey() { RSACryptoServiceProvider.UseMachineKeyStore = true; //声明一个指定大小的RSA容器 RSACryptoServiceProvider rsaProvider = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(Dwkeysize); //取得RSA容易里的各种参数 RSAParameters p = rsaProvider.ExportParameters(true); return new RsaKey { PublicKey = ComponentKey(p.Exponent, p.Modulus), PrivateKey = ComponentKey(p.D, p.Modulus) }; } /// /// 检查明文的有效性 DWKEYSIZE/8-11 长度之内为有效 中英文都算一个字符 /// /// /// public static bool CheckSourceValidate(string source) { return (Dwkeysize / 8 - 11) >= source.Length; } /// /// 组合成密匙字符串 /// /// /// /// private static string ComponentKey(byte[] b1, byte[] b2) { var list = new List<byte> { (byte) b1.Length }; list.AddRange(b1); list.AddRange(b2); var b = list.ToArray<byte>(); return Convert.ToBase64String(b); } /// /// 解析密匙 /// /// 密匙 /// RSA的相应参数1 /// RSA的相应参数2 private static void ResolveKey(string key, out byte[] b1, out byte[] b2) { //从base64字符串 解析成原来的字节数组 byte[] b = Convert.FromBase64String(key); //初始化参数的数组长度 b1 = new byte[b[0]]; b2 = new byte[b.Length - b[0] - 1]; //将相应位置是值放进相应的数组 for (int n = 1, i = 0, j = 0; n < b.Length; n++) { if (n <= b[0]) { b1[i++] = b[n]; } else { b2[j++] = b[n]; } } } /// /// 字符串加密 /// /// 源字符串 明文 /// 密匙 /// 加密遇到错误将会返回原字符串 public static string EncryptString(string source, string key) { string encryptString; try { if (!CheckSourceValidate(source)) { throw new Exception("明文太长"); } //解析这个密钥 byte[] d; byte[] n; ResolveKey(key, out d, out n); var biN = new BigInteger(n); var biD = new BigInteger(d); encryptString = EncryptString(source, biD, biN); } catch { encryptString = source; } return encryptString; } /// /// 字符串解密 /// /// 密文 /// 密钥 /// 遇到解密失败将会返回原字符串 public static string DecryptString(string encryptString, string key) { string source; try { //解析这个密钥 byte[] e; byte[] n; ResolveKey(key, out e, out n); var biE = new BigInteger(e); var biN = new BigInteger(n); source = DecryptString(encryptString, biE, biN); } catch { source = encryptString; } return source; } /// /// 用指定的密匙加密 /// /// 明文 /// 可以是RSACryptoServiceProvider生成的D /// 可以是RSACryptoServiceProvider生成的Modulus /// 返回密文 private static string EncryptString(string source, BigInteger d, BigInteger n) { var len = source.Length; int len1; if ((len % 128) == 0) len1 = len / 128; else len1 = len / 128 + 1; var result = new StringBuilder(); for (var i = 0; i < len1; i++) { var blockLen = len >= 128 ? 128 : len; var block = source.Substring(i * 128, blockLen); byte[] oText = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(block); var biText = new BigInteger(oText); var biEnText = biText.modPow(d, n); var temp = biEnText.ToHexString(); result.Append(temp).Append("@"); len -= blockLen; } return result.ToString().TrimEnd('@'); } /// /// 用指定的密匙加密 /// /// /// 可以是RSACryptoServiceProvider生成的Exponent /// 可以是RSACryptoServiceProvider生成的Modulus /// 返回明文 private static string DecryptString(string encryptString, BigInteger e, BigInteger n) { var result = new StringBuilder(); var strarr1 = encryptString.Split(new[] { '@' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); foreach (var block in strarr1) { var biText = new BigInteger(block, 16); var biEnText = biText.modPow(e, n); var temp = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(biEnText.getBytes()); result.Append(temp); } return result.ToString(); } } }
2.BigInteger类:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace BasicMmethodExtensionClass.EncryptHelper { public class BigInteger { // maximum length of the BigInteger in uint (4 bytes) // change this to suit the required level of precision. private const int maxLength = 70; // primes smaller than 2000 to test the generated prime number public static readonly int[] primesBelow2000 = { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293, 307, 311, 313, 317, 331, 337, 347, 349, 353, 359, 367, 373, 379, 383, 389, 397, 401, 409, 419, 421, 431, 433, 439, 443, 449, 457, 461, 463, 467, 479, 487, 491, 499, 503, 509, 521, 523, 541, 547, 557, 563, 569, 571, 577, 587, 593, 599, 601, 607, 613, 617, 619, 631, 641, 643, 647, 653, 659, 661, 673, 677, 683, 691, 701, 709, 719, 727, 733, 739, 743, 751, 757, 761, 769, 773, 787, 797, 809, 811, 821, 823, 827, 829, 839, 853, 857, 859, 863, 877, 881, 883, 887, 907, 911, 919, 929, 937, 941, 947, 953, 967, 971, 977, 983, 991, 997, 1009, 1013, 1019, 1021, 1031, 1033, 1039, 1049, 1051, 1061, 1063, 1069, 1087, 1091, 1093, 1097, 1103, 1109, 1117, 1123, 1129, 1151, 1153, 1163, 1171, 1181, 1187, 1193, 1201, 1213, 1217, 1223, 1229, 1231, 1237, 1249, 1259, 1277, 1279, 1283, 1289, 1291, 1297, 1301, 1303, 1307, 1319, 1321, 1327, 1361, 1367, 1373, 1381, 1399, 1409, 1423, 1427, 1429, 1433, 1439, 1447, 1451, 1453, 1459, 1471, 1481, 1483, 1487, 1489, 1493, 1499, 1511, 1523, 1531, 1543, 1549, 1553, 1559, 1567, 1571, 1579, 1583, 1597, 1601, 1607, 1609, 1613, 1619, 1621, 1627, 1637, 1657, 1663, 1667, 1669, 1693, 1697, 1699, 1709, 1721, 1723, 1733, 1741, 1747, 1753, 1759, 1777, 1783, 1787, 1789, 1801, 1811, 1823, 1831, 1847, 1861, 1867, 1871, 1873, 1877, 1879, 1889, 1901, 1907, 1913, 1931, 1933, 1949, 1951, 1973, 1979, 1987, 1993, 1997, 1999 }; private uint[] data; // stores bytes from the Big Integer public int DataLength; // number of actual chars used //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value for BigInteger is 0 //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger() { data = new uint[maxLength]; DataLength = 1; } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by long) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger(long value) { data = new uint[maxLength]; long tempVal = value; // copy bytes from long to BigInteger without any assumption of // the length of the long datatype DataLength = 0; while (value != 0 && DataLength < maxLength) { data[DataLength] = (uint)(value & 0xFFFFFFFF); value >>= 32; DataLength++; } if (tempVal > 0) // overflow check for +ve value { if (value != 0 || (data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) throw (new ArithmeticException("Positive overflow in constructor.")); } else if (tempVal < 0) // underflow check for -ve value { if (value != -1 || (data[DataLength - 1] & 0x80000000) == 0) throw (new ArithmeticException("Negative underflow in constructor.")); } if (DataLength == 0) DataLength = 1; } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by ulong) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger(ulong value) { data = new uint[maxLength]; // copy bytes from ulong to BigInteger without any assumption of // the length of the ulong datatype DataLength = 0; while (value != 0 && DataLength < maxLength) { data[DataLength] = (uint)(value & 0xFFFFFFFF); value >>= 32; DataLength++; } if (value != 0 || (data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) throw (new ArithmeticException("Positive overflow in constructor.")); if (DataLength == 0) DataLength = 1; } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by BigInteger) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger(BigInteger bi) { data = new uint[maxLength]; DataLength = bi.DataLength; for (int i = 0; i < DataLength; i++) data[i] = bi.data[i]; } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by a string of digits of the // specified base) // // Example (base 10) // ----------------- // To initialize "a" with the default value of 1234 in base 10 // BigInteger a = new BigInteger("1234", 10) // // To initialize "a" with the default value of -1234 // BigInteger a = new BigInteger("-1234", 10) // // Example (base 16) // ----------------- // To initialize "a" with the default value of 0x1D4F in base 16 // BigInteger a = new BigInteger("1D4F", 16) // // To initialize "a" with the default value of -0x1D4F // BigInteger a = new BigInteger("-1D4F", 16) // // Note that string values are specified in the// format. // //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger(string value, int radix) { BigInteger multiplier = new BigInteger(1); BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); value = (value.ToUpper()).Trim(); int limit = 0; if (value[0] == '-') limit = 1; for (int i = value.Length - 1; i >= limit; i--) { int posVal = (int)value[i]; if (posVal >= '0' && posVal <= '9') posVal -= '0'; else if (posVal >= 'A' && posVal <= 'Z') posVal = (posVal - 'A') + 10; else posVal = 9999999; // arbitrary large if (posVal >= radix) throw (new ArithmeticException("Invalid string in constructor.")); else { if (value[0] == '-') posVal = -posVal; result = result + (multiplier * posVal); if ((i - 1) >= limit) multiplier = multiplier * radix; } } if (value[0] == '-') // negative values { if ((result.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) == 0) throw (new ArithmeticException("Negative underflow in constructor.")); } else // positive values { if ((result.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) throw (new ArithmeticException("Positive overflow in constructor.")); } data = new uint[maxLength]; for (int i = 0; i < result.DataLength; i++) data[i] = result.data[i]; DataLength = result.DataLength; } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by an array of bytes) // // The lowest index of the input byte array (i.e [0]) should contain the // most significant byte of the number, and the highest index should // contain the least significant byte. // // E.g. // To initialize "a" with the default value of 0x1D4F in base 16 // byte[] temp = { 0x1D, 0x4F }; // BigInteger a = new BigInteger(temp) // // Note that this method of initialization does not allow the // sign to be specified. // //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger(byte[] inData) { DataLength = inData.Length >> 2; int leftOver = inData.Length & 0x3; if (leftOver != 0) // length not multiples of 4 DataLength++; if (DataLength > maxLength) throw (new ArithmeticException("Byte overflow in constructor.")); data = new uint[maxLength]; for (int i = inData.Length - 1, j = 0; i >= 3; i -= 4, j++) { data[j] = (uint)((inData[i - 3] << 24) + (inData[i - 2] << 16) + (inData[i - 1] << 8) + inData[i]); } if (leftOver == 1) data[DataLength - 1] = (uint)inData[0]; else if (leftOver == 2) data[DataLength - 1] = (uint)((inData[0] << 8) + inData[1]); else if (leftOver == 3) data[DataLength - 1] = (uint)((inData[0] << 16) + (inData[1] << 8) + inData[2]); while (DataLength > 1 && data[DataLength - 1] == 0) DataLength--; //Console.WriteLine("Len = " + dataLength); } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by an array of bytes of the // specified length.) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger(byte[] inData, int inLen) { DataLength = inLen >> 2; int leftOver = inLen & 0x3; if (leftOver != 0) // length not multiples of 4 DataLength++; if (DataLength > maxLength || inLen > inData.Length) throw (new ArithmeticException("Byte overflow in constructor.")); data = new uint[maxLength]; for (int i = inLen - 1, j = 0; i >= 3; i -= 4, j++) { data[j] = (uint)((inData[i - 3] << 24) + (inData[i - 2] << 16) + (inData[i - 1] << 8) + inData[i]); } if (leftOver == 1) data[DataLength - 1] = (uint)inData[0]; else if (leftOver == 2) data[DataLength - 1] = (uint)((inData[0] << 8) + inData[1]); else if (leftOver == 3) data[DataLength - 1] = (uint)((inData[0] << 16) + (inData[1] << 8) + inData[2]); if (DataLength == 0) DataLength = 1; while (DataLength > 1 && data[DataLength - 1] == 0) DataLength--; //Console.WriteLine("Len = " + dataLength); } //*********************************************************************** // Constructor (Default value provided by an array of unsigned integers) //********************************************************************* public BigInteger(uint[] inData) { DataLength = inData.Length; if (DataLength > maxLength) throw (new ArithmeticException("Byte overflow in constructor.")); data = new uint[maxLength]; for (int i = DataLength - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++) data[j] = inData[i]; while (DataLength > 1 && data[DataLength - 1] == 0) DataLength--; //Console.WriteLine("Len = " + dataLength); } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of the typecast operator. // For BigInteger bi = 10; //*********************************************************************** public static implicit operator BigInteger(long value) { return (new BigInteger(value)); } public static implicit operator BigInteger(ulong value) { return (new BigInteger(value)); } public static implicit operator BigInteger(int value) { return (new BigInteger((long)value)); } public static implicit operator BigInteger(uint value) { return (new BigInteger((ulong)value)); } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of addition operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator +(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); result.DataLength = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; long carry = 0; for (int i = 0; i < result.DataLength; i++) { long sum = (long)bi1.data[i] + (long)bi2.data[i] + carry; carry = sum >> 32; result.data[i] = (uint)(sum & 0xFFFFFFFF); } if (carry != 0 && result.DataLength < maxLength) { result.data[result.DataLength] = (uint)(carry); result.DataLength++; } while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; // overflow check int lastPos = maxLength - 1; if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) == (bi2.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) && (result.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != (bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000)) { throw (new ArithmeticException()); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of the unary ++ operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator ++(BigInteger bi1) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(bi1); long val, carry = 1; int index = 0; while (carry != 0 && index < maxLength) { val = (long)(result.data[index]); val++; result.data[index] = (uint)(val & 0xFFFFFFFF); carry = val >> 32; index++; } if (index > result.DataLength) result.DataLength = index; else { while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; } // overflow check int lastPos = maxLength - 1; // overflow if initial value was +ve but ++ caused a sign // change to negative. if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) == 0 && (result.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != (bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000)) { throw (new ArithmeticException("Overflow in ++.")); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of subtraction operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator -(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); result.DataLength = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; long carryIn = 0; for (int i = 0; i < result.DataLength; i++) { long diff; diff = (long)bi1.data[i] - (long)bi2.data[i] - carryIn; result.data[i] = (uint)(diff & 0xFFFFFFFF); if (diff < 0) carryIn = 1; else carryIn = 0; } // roll over to negative if (carryIn != 0) { for (int i = result.DataLength; i < maxLength; i++) result.data[i] = 0xFFFFFFFF; result.DataLength = maxLength; } // fixed in v1.03 to give correct datalength for a - (-b) while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; // overflow check int lastPos = maxLength - 1; if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != (bi2.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) && (result.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != (bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000)) { throw (new ArithmeticException()); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of the unary -- operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator --(BigInteger bi1) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(bi1); long val; bool carryIn = true; int index = 0; while (carryIn && index < maxLength) { val = (long)(result.data[index]); val--; result.data[index] = (uint)(val & 0xFFFFFFFF); if (val >= 0) carryIn = false; index++; } if (index > result.DataLength) result.DataLength = index; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; // overflow check int lastPos = maxLength - 1; // overflow if initial value was -ve but -- caused a sign // change to positive. if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0 && (result.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != (bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000)) { throw (new ArithmeticException("Underflow in --.")); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of multiplication operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator *(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { int lastPos = maxLength - 1; bool bi1Neg = false, bi2Neg = false; // take the absolute value of the inputs try { if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) // bi1 negative { bi1Neg = true; bi1 = -bi1; } if ((bi2.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) // bi2 negative { bi2Neg = true; bi2 = -bi2; } } catch (Exception) { } BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); // multiply the absolute values try { for (int i = 0; i < bi1.DataLength; i++) { if (bi1.data[i] == 0) continue; ulong mcarry = 0; for (int j = 0, k = i; j < bi2.DataLength; j++, k++) { // k = i + j ulong val = ((ulong)bi1.data[i] * (ulong)bi2.data[j]) + (ulong)result.data[k] + mcarry; result.data[k] = (uint)(val & 0xFFFFFFFF); mcarry = (val >> 32); } if (mcarry != 0) result.data[i + bi2.DataLength] = (uint)mcarry; } } catch (Exception) { throw (new ArithmeticException("Multiplication overflow.")); } result.DataLength = bi1.DataLength + bi2.DataLength; if (result.DataLength > maxLength) result.DataLength = maxLength; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; // overflow check (result is -ve) if ((result.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) { if (bi1Neg != bi2Neg && result.data[lastPos] == 0x80000000) // different sign { // handle the special case where multiplication produces // a max negative number in 2's complement. if (result.DataLength == 1) return result; else { bool isMaxNeg = true; for (int i = 0; i < result.DataLength - 1 && isMaxNeg; i++) { if (result.data[i] != 0) isMaxNeg = false; } if (isMaxNeg) return result; } } throw (new ArithmeticException("Multiplication overflow.")); } // if input has different signs, then result is -ve if (bi1Neg != bi2Neg) return -result; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of unary << operators //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator <<(BigInteger bi1, int shiftVal) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(bi1); result.DataLength = shiftLeft(result.data, shiftVal); return result; } // least significant bits at lower part of buffer private static int shiftLeft(uint[] buffer, int shiftVal) { int shiftAmount = 32; int bufLen = buffer.Length; while (bufLen > 1 && buffer[bufLen - 1] == 0) bufLen--; for (int count = shiftVal; count > 0;) { if (count < shiftAmount) shiftAmount = count; //Console.WriteLine("shiftAmount = {0}", shiftAmount); ulong carry = 0; for (int i = 0; i < bufLen; i++) { ulong val = ((ulong)buffer[i]) << shiftAmount; val |= carry; buffer[i] = (uint)(val & 0xFFFFFFFF); carry = val >> 32; } if (carry != 0) { if (bufLen + 1 <= buffer.Length) { buffer[bufLen] = (uint)carry; bufLen++; } } count -= shiftAmount; } return bufLen; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of unary >> operators //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator >>(BigInteger bi1, int shiftVal) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(bi1); result.DataLength = shiftRight(result.data, shiftVal); if ((bi1.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative { for (int i = maxLength - 1; i >= result.DataLength; i--) result.data[i] = 0xFFFFFFFF; uint mask = 0x80000000; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if ((result.data[result.DataLength - 1] & mask) != 0) break; result.data[result.DataLength - 1] |= mask; mask >>= 1; } result.DataLength = maxLength; } return result; } private static int shiftRight(uint[] buffer, int shiftVal) { int shiftAmount = 32; int invShift = 0; int bufLen = buffer.Length; while (bufLen > 1 && buffer[bufLen - 1] == 0) bufLen--; //Console.WriteLine("bufLen = " + bufLen + " buffer.Length = " + buffer.Length); for (int count = shiftVal; count > 0;) { if (count < shiftAmount) { shiftAmount = count; invShift = 32 - shiftAmount; } //Console.WriteLine("shiftAmount = {0}", shiftAmount); ulong carry = 0; for (int i = bufLen - 1; i >= 0; i--) { ulong val = ((ulong)buffer[i]) >> shiftAmount; val |= carry; carry = ((ulong)buffer[i]) << invShift; buffer[i] = (uint)(val); } count -= shiftAmount; } while (bufLen > 1 && buffer[bufLen - 1] == 0) bufLen--; return bufLen; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of the NOT operator (1's complement) //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator ~(BigInteger bi1) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(bi1); for (int i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) result.data[i] = (uint)(~(bi1.data[i])); result.DataLength = maxLength; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of the NEGATE operator (2's complement) //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator -(BigInteger bi1) { // handle neg of zero separately since it'll cause an overflow // if we proceed. if (bi1.DataLength == 1 && bi1.data[0] == 0) return (new BigInteger()); BigInteger result = new BigInteger(bi1); // 1's complement for (int i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) result.data[i] = (uint)(~(bi1.data[i])); // add one to result of 1's complement long val, carry = 1; int index = 0; while (carry != 0 && index < maxLength) { val = (long)(result.data[index]); val++; result.data[index] = (uint)(val & 0xFFFFFFFF); carry = val >> 32; index++; } if ((bi1.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) == (result.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000)) throw (new ArithmeticException("Overflow in negation.\n")); result.DataLength = maxLength; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of equality operator //*********************************************************************** public static bool operator ==(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { return bi1.Equals(bi2); } public static bool operator !=(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { return !(bi1.Equals(bi2)); } public override bool Equals(object o) { BigInteger bi = (BigInteger)o; if (this.DataLength != bi.DataLength) return false; for (int i = 0; i < this.DataLength; i++) { if (this.data[i] != bi.data[i]) return false; } return true; } public override int GetHashCode() { return this.ToString().GetHashCode(); } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of inequality operator //*********************************************************************** public static bool operator >(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { int pos = maxLength - 1; // bi1 is negative, bi2 is positive if ((bi1.data[pos] & 0x80000000) != 0 && (bi2.data[pos] & 0x80000000) == 0) return false; // bi1 is positive, bi2 is negative else if ((bi1.data[pos] & 0x80000000) == 0 && (bi2.data[pos] & 0x80000000) != 0) return true; // same sign int len = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; for (pos = len - 1; pos >= 0 && bi1.data[pos] == bi2.data[pos]; pos--) ; if (pos >= 0) { if (bi1.data[pos] > bi2.data[pos]) return true; return false; } return false; } public static bool operator <(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { int pos = maxLength - 1; // bi1 is negative, bi2 is positive if ((bi1.data[pos] & 0x80000000) != 0 && (bi2.data[pos] & 0x80000000) == 0) return true; // bi1 is positive, bi2 is negative else if ((bi1.data[pos] & 0x80000000) == 0 && (bi2.data[pos] & 0x80000000) != 0) return false; // same sign int len = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; for (pos = len - 1; pos >= 0 && bi1.data[pos] == bi2.data[pos]; pos--) ; if (pos >= 0) { if (bi1.data[pos] < bi2.data[pos]) return true; return false; } return false; } public static bool operator >=(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { return (bi1 == bi2 || bi1 > bi2); } public static bool operator <=(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { return (bi1 == bi2 || bi1 < bi2); } //*********************************************************************** // Private function that supports the division of two numbers with // a divisor that has more than 1 digit. // // Algorithm taken from [1] //*********************************************************************** private static void multiByteDivide(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2, BigInteger outQuotient, BigInteger outRemainder) { uint[] result = new uint[maxLength]; int remainderLen = bi1.DataLength + 1; uint[] remainder = new uint[remainderLen]; uint mask = 0x80000000; uint val = bi2.data[bi2.DataLength - 1]; int shift = 0, resultPos = 0; while (mask != 0 && (val & mask) == 0) { shift++; mask >>= 1; } //Console.WriteLine("shift = {0}", shift); //Console.WriteLine("Before bi1 Len = {0}, bi2 Len = {1}", bi1.dataLength, bi2.dataLength); for (int i = 0; i < bi1.DataLength; i++) remainder[i] = bi1.data[i]; shiftLeft(remainder, shift); bi2 = bi2 << shift; /* Console.WriteLine("bi1 Len = {0}, bi2 Len = {1}", bi1.dataLength, bi2.dataLength); Console.WriteLine("dividend = " + bi1 + "\ndivisor = " + bi2); for(int q = remainderLen - 1; q >= 0; q--) Console.Write("{0:x2}", remainder[q]); Console.WriteLine(); */ int j = remainderLen - bi2.DataLength; int pos = remainderLen - 1; ulong firstDivisorByte = bi2.data[bi2.DataLength - 1]; ulong secondDivisorByte = bi2.data[bi2.DataLength - 2]; int divisorLen = bi2.DataLength + 1; uint[] dividendPart = new uint[divisorLen]; while (j > 0) { ulong dividend = ((ulong)remainder[pos] << 32) + (ulong)remainder[pos - 1]; //Console.WriteLine("dividend = {0}", dividend); ulong q_hat = dividend / firstDivisorByte; ulong r_hat = dividend % firstDivisorByte; //Console.WriteLine("q_hat = {0:X}, r_hat = {1:X}", q_hat, r_hat); bool done = false; while (!done) { done = true; if (q_hat == 0x100000000 || (q_hat * secondDivisorByte) > ((r_hat << 32) + remainder[pos - 2])) { q_hat--; r_hat += firstDivisorByte; if (r_hat < 0x100000000) done = false; } } for (int h = 0; h < divisorLen; h++) dividendPart[h] = remainder[pos - h]; BigInteger kk = new BigInteger(dividendPart); BigInteger ss = bi2 * (long)q_hat; //Console.WriteLine("ss before = " + ss); while (ss > kk) { q_hat--; ss -= bi2; //Console.WriteLine(ss); } BigInteger yy = kk - ss; //Console.WriteLine("ss = " + ss); //Console.WriteLine("kk = " + kk); //Console.WriteLine("yy = " + yy); for (int h = 0; h < divisorLen; h++) remainder[pos - h] = yy.data[bi2.DataLength - h]; /* Console.WriteLine("dividend = "); for(int q = remainderLen - 1; q >= 0; q--) Console.Write("{0:x2}", remainder[q]); Console.WriteLine("\n************ q_hat = {0:X}\n", q_hat); */ result[resultPos++] = (uint)q_hat; pos--; j--; } outQuotient.DataLength = resultPos; int y = 0; for (int x = outQuotient.DataLength - 1; x >= 0; x--, y++) outQuotient.data[y] = result[x]; for (; y < maxLength; y++) outQuotient.data[y] = 0; while (outQuotient.DataLength > 1 && outQuotient.data[outQuotient.DataLength - 1] == 0) outQuotient.DataLength--; if (outQuotient.DataLength == 0) outQuotient.DataLength = 1; outRemainder.DataLength = shiftRight(remainder, shift); for (y = 0; y < outRemainder.DataLength; y++) outRemainder.data[y] = remainder[y]; for (; y < maxLength; y++) outRemainder.data[y] = 0; } //*********************************************************************** // Private function that supports the division of two numbers with // a divisor that has only 1 digit. //*********************************************************************** private static void singleByteDivide(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2, BigInteger outQuotient, BigInteger outRemainder) { uint[] result = new uint[maxLength]; int resultPos = 0; // copy dividend to reminder for (int i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) outRemainder.data[i] = bi1.data[i]; outRemainder.DataLength = bi1.DataLength; while (outRemainder.DataLength > 1 && outRemainder.data[outRemainder.DataLength - 1] == 0) outRemainder.DataLength--; ulong divisor = (ulong)bi2.data[0]; int pos = outRemainder.DataLength - 1; ulong dividend = (ulong)outRemainder.data[pos]; //Console.WriteLine("divisor = " + divisor + " dividend = " + dividend); //Console.WriteLine("divisor = " + bi2 + "\ndividend = " + bi1); if (dividend >= divisor) { ulong quotient = dividend / divisor; result[resultPos++] = (uint)quotient; outRemainder.data[pos] = (uint)(dividend % divisor); } pos--; while (pos >= 0) { //Console.WriteLine(pos); dividend = ((ulong)outRemainder.data[pos + 1] << 32) + (ulong)outRemainder.data[pos]; ulong quotient = dividend / divisor; result[resultPos++] = (uint)quotient; outRemainder.data[pos + 1] = 0; outRemainder.data[pos--] = (uint)(dividend % divisor); //Console.WriteLine(">>>> " + bi1); } outQuotient.DataLength = resultPos; int j = 0; for (int i = outQuotient.DataLength - 1; i >= 0; i--, j++) outQuotient.data[j] = result[i]; for (; j < maxLength; j++) outQuotient.data[j] = 0; while (outQuotient.DataLength > 1 && outQuotient.data[outQuotient.DataLength - 1] == 0) outQuotient.DataLength--; if (outQuotient.DataLength == 0) outQuotient.DataLength = 1; while (outRemainder.DataLength > 1 && outRemainder.data[outRemainder.DataLength - 1] == 0) outRemainder.DataLength--; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of division operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator /(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger quotient = new BigInteger(); BigInteger remainder = new BigInteger(); int lastPos = maxLength - 1; bool divisorNeg = false, dividendNeg = false; if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) // bi1 negative { bi1 = -bi1; dividendNeg = true; } if ((bi2.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) // bi2 negative { bi2 = -bi2; divisorNeg = true; } if (bi1 < bi2) { return quotient; } else { if (bi2.DataLength == 1) singleByteDivide(bi1, bi2, quotient, remainder); else multiByteDivide(bi1, bi2, quotient, remainder); if (dividendNeg != divisorNeg) return -quotient; return quotient; } } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of modulus operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator %(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger quotient = new BigInteger(); BigInteger remainder = new BigInteger(bi1); int lastPos = maxLength - 1; bool dividendNeg = false; if ((bi1.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) // bi1 negative { bi1 = -bi1; dividendNeg = true; } if ((bi2.data[lastPos] & 0x80000000) != 0) // bi2 negative bi2 = -bi2; if (bi1 < bi2) { return remainder; } else { if (bi2.DataLength == 1) singleByteDivide(bi1, bi2, quotient, remainder); else multiByteDivide(bi1, bi2, quotient, remainder); if (dividendNeg) return -remainder; return remainder; } } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of bitwise AND operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator &(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); int len = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { uint sum = (uint)(bi1.data[i] & bi2.data[i]); result.data[i] = sum; } result.DataLength = maxLength; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of bitwise OR operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator |(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); int len = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { uint sum = (uint)(bi1.data[i] | bi2.data[i]); result.data[i] = sum; } result.DataLength = maxLength; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Overloading of bitwise XOR operator //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger operator ^(BigInteger bi1, BigInteger bi2) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); int len = (bi1.DataLength > bi2.DataLength) ? bi1.DataLength : bi2.DataLength; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { uint sum = (uint)(bi1.data[i] ^ bi2.data[i]); result.data[i] = sum; } result.DataLength = maxLength; while (result.DataLength > 1 && result.data[result.DataLength - 1] == 0) result.DataLength--; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns max(this, bi) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger max(BigInteger bi) { if (this > bi) return (new BigInteger(this)); else return (new BigInteger(bi)); } //*********************************************************************** // Returns min(this, bi) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger min(BigInteger bi) { if (this < bi) return (new BigInteger(this)); else return (new BigInteger(bi)); } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the absolute value //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger abs() { if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) return (-this); else return (new BigInteger(this)); } //*********************************************************************** // Returns a string representing the BigInteger in base 10. //*********************************************************************** public override string ToString() { return ToString(10); } //*********************************************************************** // Returns a string representing the BigInteger in sign-and-magnitude // format in the specified radix. // // Example // ------- // If the value of BigInteger is -255 in base 10, then // ToString(16) returns "-FF" // //*********************************************************************** public string ToString(int radix) { if (radix < 2 || radix > 36) throw (new ArgumentException("Radix must be >= 2 and <= 36")); string charSet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; string result = ""; BigInteger a = this; bool negative = false; if ((a.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) { negative = true; try { a = -a; } catch (Exception) { } } BigInteger quotient = new BigInteger(); BigInteger remainder = new BigInteger(); BigInteger biRadix = new BigInteger(radix); if (a.DataLength == 1 && a.data[0] == 0) result = "0"; else { while (a.DataLength > 1 || (a.DataLength == 1 && a.data[0] != 0)) { singleByteDivide(a, biRadix, quotient, remainder); if (remainder.data[0] < 10) result = remainder.data[0] + result; else result = charSet[(int)remainder.data[0] - 10] + result; a = quotient; } if (negative) result = "-" + result; } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns a hex string showing the contains of the BigInteger // // Examples // ------- // 1) If the value of BigInteger is 255 in base 10, then // ToHexString() returns "FF" // // 2) If the value of BigInteger is -255 in base 10, then // ToHexString() returns ".....FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF01", // which is the 2's complement representation of -255. // //*********************************************************************** public string ToHexString() { string result = data[DataLength - 1].ToString("X"); for (int i = DataLength - 2; i >= 0; i--) { result += data[i].ToString("X8"); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Modulo Exponentiation //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger modPow(BigInteger exp, BigInteger n) { if ((exp.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) throw (new ArithmeticException("Positive exponents only.")); BigInteger resultNum = 1; BigInteger tempNum; bool thisNegative = false; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative this { tempNum = -this % n; thisNegative = true; } else tempNum = this % n; // ensures (tempNum * tempNum) < b^(2k) if ((n.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative n n = -n; // calculate constant = b^(2k) / m BigInteger constant = new BigInteger(); int i = n.DataLength << 1; constant.data[i] = 0x00000001; constant.DataLength = i + 1; constant = constant / n; int totalBits = exp.bitCount(); int count = 0; // perform squaring and multiply exponentiation for (int pos = 0; pos < exp.DataLength; pos++) { uint mask = 0x01; //Console.WriteLine("pos = " + pos); for (int index = 0; index < 32; index++) { if ((exp.data[pos] & mask) != 0) resultNum = BarrettReduction(resultNum * tempNum, n, constant); mask <<= 1; tempNum = BarrettReduction(tempNum * tempNum, n, constant); if (tempNum.DataLength == 1 && tempNum.data[0] == 1) { if (thisNegative && (exp.data[0] & 0x1) != 0) //odd exp return -resultNum; return resultNum; } count++; if (count == totalBits) break; } } if (thisNegative && (exp.data[0] & 0x1) != 0) //odd exp return -resultNum; return resultNum; } //*********************************************************************** // Fast calculation of modular reduction using Barrett's reduction. // Requires x < b^(2k), where b is the base. In this case, base is // 2^32 (uint). // // Reference [4] //*********************************************************************** private BigInteger BarrettReduction(BigInteger x, BigInteger n, BigInteger constant) { int k = n.DataLength, kPlusOne = k + 1, kMinusOne = k - 1; BigInteger q1 = new BigInteger(); // q1 = x / b^(k-1) for (int i = kMinusOne, j = 0; i < x.DataLength; i++, j++) q1.data[j] = x.data[i]; q1.DataLength = x.DataLength - kMinusOne; if (q1.DataLength <= 0) q1.DataLength = 1; BigInteger q2 = q1 * constant; BigInteger q3 = new BigInteger(); // q3 = q2 / b^(k+1) for (int i = kPlusOne, j = 0; i < q2.DataLength; i++, j++) q3.data[j] = q2.data[i]; q3.DataLength = q2.DataLength - kPlusOne; if (q3.DataLength <= 0) q3.DataLength = 1; // r1 = x mod b^(k+1) // i.e. keep the lowest (k+1) words BigInteger r1 = new BigInteger(); int lengthToCopy = (x.DataLength > kPlusOne) ? kPlusOne : x.DataLength; for (int i = 0; i < lengthToCopy; i++) r1.data[i] = x.data[i]; r1.DataLength = lengthToCopy; // r2 = (q3 * n) mod b^(k+1) // partial multiplication of q3 and n BigInteger r2 = new BigInteger(); for (int i = 0; i < q3.DataLength; i++) { if (q3.data[i] == 0) continue; ulong mcarry = 0; int t = i; for (int j = 0; j < n.DataLength && t < kPlusOne; j++, t++) { // t = i + j ulong val = ((ulong)q3.data[i] * (ulong)n.data[j]) + (ulong)r2.data[t] + mcarry; r2.data[t] = (uint)(val & 0xFFFFFFFF); mcarry = (val >> 32); } if (t < kPlusOne) r2.data[t] = (uint)mcarry; } r2.DataLength = kPlusOne; while (r2.DataLength > 1 && r2.data[r2.DataLength - 1] == 0) r2.DataLength--; r1 -= r2; if ((r1.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative { BigInteger val = new BigInteger(); val.data[kPlusOne] = 0x00000001; val.DataLength = kPlusOne + 1; r1 += val; } while (r1 >= n) r1 -= n; return r1; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns gcd(this, bi) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger gcd(BigInteger bi) { BigInteger x; BigInteger y; if ((data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative x = -this; else x = this; if ((bi.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative y = -bi; else y = bi; BigInteger g = y; while (x.DataLength > 1 || (x.DataLength == 1 && x.data[0] != 0)) { g = x; x = y % x; y = g; } return g; } //*********************************************************************** // Populates "this" with the specified amount of random bits //*********************************************************************** public void genRandomBits(int bits, Random rand) { int dwords = bits >> 5; int remBits = bits & 0x1F; if (remBits != 0) dwords++; if (dwords > maxLength) throw (new ArithmeticException("Number of required bits > maxLength.")); for (int i = 0; i < dwords; i++) data[i] = (uint)(rand.NextDouble() * 0x100000000); for (int i = dwords; i < maxLength; i++) data[i] = 0; if (remBits != 0) { uint mask = (uint)(0x01 << (remBits - 1)); data[dwords - 1] |= mask; mask = (uint)(0xFFFFFFFF >> (32 - remBits)); data[dwords - 1] &= mask; } else data[dwords - 1] |= 0x80000000; DataLength = dwords; if (DataLength == 0) DataLength = 1; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the position of the most significant bit in the BigInteger. // // Eg. The result is 0, if the value of BigInteger is 0...0000 0000 // The result is 1, if the value of BigInteger is 0...0000 0001 // The result is 2, if the value of BigInteger is 0...0000 0010 // The result is 2, if the value of BigInteger is 0...0000 0011 // //*********************************************************************** public int bitCount() { while (DataLength > 1 && data[DataLength - 1] == 0) DataLength--; uint value = data[DataLength - 1]; uint mask = 0x80000000; int bits = 32; while (bits > 0 && (value & mask) == 0) { bits--; mask >>= 1; } bits += ((DataLength - 1) << 5); return bits; } //*********************************************************************** // Probabilistic prime test based on Fermat's little theorem // // for any a < p (p does not divide a) if // a^(p-1) mod p != 1 then p is not prime. // // Otherwise, p is probably prime (pseudoprime to the chosen base). // // Returns // ------- // True if "this" is a pseudoprime to randomly chosen // bases. The number of chosen bases is given by the "confidence" // parameter. // // False if "this" is definitely NOT prime. // // Note - this method is fast but fails for Carmichael numbers except // when the randomly chosen base is a factor of the number. // //*********************************************************************** public bool FermatLittleTest(int confidence) { BigInteger thisVal; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative thisVal = -this; else thisVal = this; if (thisVal.DataLength == 1) { // test small numbers if (thisVal.data[0] == 0 || thisVal.data[0] == 1) return false; else if (thisVal.data[0] == 2 || thisVal.data[0] == 3) return true; } if ((thisVal.data[0] & 0x1) == 0) // even numbers return false; int bits = thisVal.bitCount(); BigInteger a = new BigInteger(); BigInteger p_sub1 = thisVal - (new BigInteger(1)); Random rand = new Random(); for (int round = 0; round < confidence; round++) { bool done = false; while (!done) // generate a < n { int testBits = 0; // make sure "a" has at least 2 bits while (testBits < 2) testBits = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * bits); a.genRandomBits(testBits, rand); int byteLen = a.DataLength; // make sure "a" is not 0 if (byteLen > 1 || (byteLen == 1 && a.data[0] != 1)) done = true; } // check whether a factor exists (fix for version 1.03) BigInteger gcdTest = a.gcd(thisVal); if (gcdTest.DataLength == 1 && gcdTest.data[0] != 1) return false; // calculate a^(p-1) mod p BigInteger expResult = a.modPow(p_sub1, thisVal); int resultLen = expResult.DataLength; // is NOT prime is a^(p-1) mod p != 1 if (resultLen > 1 || (resultLen == 1 && expResult.data[0] != 1)) { //Console.WriteLine("a = " + a.ToString()); return false; } } return true; } //*********************************************************************** // Probabilistic prime test based on Rabin-Miller's // // for any p > 0 with p - 1 = 2^s * t // // p is probably prime (strong pseudoprime) if for any a < p, // 1) a^t mod p = 1 or // 2) a^((2^j)*t) mod p = p-1 for some 0 <= j <= s-1 // // Otherwise, p is composite. // // Returns // ------- // True if "this" is a strong pseudoprime to randomly chosen // bases. The number of chosen bases is given by the "confidence" // parameter. // // False if "this" is definitely NOT prime. // //*********************************************************************** public bool RabinMillerTest(int confidence) { BigInteger thisVal; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative thisVal = -this; else thisVal = this; if (thisVal.DataLength == 1) { // test small numbers if (thisVal.data[0] == 0 || thisVal.data[0] == 1) return false; else if (thisVal.data[0] == 2 || thisVal.data[0] == 3) return true; } if ((thisVal.data[0] & 0x1) == 0) // even numbers return false; // calculate values of s and t BigInteger p_sub1 = thisVal - (new BigInteger(1)); int s = 0; for (int index = 0; index < p_sub1.DataLength; index++) { uint mask = 0x01; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if ((p_sub1.data[index] & mask) != 0) { index = p_sub1.DataLength; // to break the outer loop break; } mask <<= 1; s++; } } BigInteger t = p_sub1 >> s; int bits = thisVal.bitCount(); BigInteger a = new BigInteger(); Random rand = new Random(); for (int round = 0; round < confidence; round++) { bool done = false; while (!done) // generate a < n { int testBits = 0; // make sure "a" has at least 2 bits while (testBits < 2) testBits = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * bits); a.genRandomBits(testBits, rand); int byteLen = a.DataLength; // make sure "a" is not 0 if (byteLen > 1 || (byteLen == 1 && a.data[0] != 1)) done = true; } // check whether a factor exists (fix for version 1.03) BigInteger gcdTest = a.gcd(thisVal); if (gcdTest.DataLength == 1 && gcdTest.data[0] != 1) return false; BigInteger b = a.modPow(t, thisVal); /* Console.WriteLine("a = " + a.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("b = " + b.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("t = " + t.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("s = " + s); */ bool result = false; if (b.DataLength == 1 && b.data[0] == 1) // a^t mod p = 1 result = true; for (int j = 0; result == false && j < s; j++) { if (b == p_sub1) // a^((2^j)*t) mod p = p-1 for some 0 <= j <= s-1 { result = true; break; } b = (b * b) % thisVal; } if (result == false) return false; } return true; } //*********************************************************************** // Probabilistic prime test based on Solovay-Strassen (Euler Criterion) // // p is probably prime if for any a < p (a is not multiple of p), // a^((p-1)/2) mod p = J(a, p) // // where J is the Jacobi symbol. // // Otherwise, p is composite. // // Returns // ------- // True if "this" is a Euler pseudoprime to randomly chosen // bases. The number of chosen bases is given by the "confidence" // parameter. // // False if "this" is definitely NOT prime. // //*********************************************************************** public bool SolovayStrassenTest(int confidence) { BigInteger thisVal; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative thisVal = -this; else thisVal = this; if (thisVal.DataLength == 1) { // test small numbers if (thisVal.data[0] == 0 || thisVal.data[0] == 1) return false; else if (thisVal.data[0] == 2 || thisVal.data[0] == 3) return true; } if ((thisVal.data[0] & 0x1) == 0) // even numbers return false; int bits = thisVal.bitCount(); BigInteger a = new BigInteger(); BigInteger p_sub1 = thisVal - 1; BigInteger p_sub1_shift = p_sub1 >> 1; Random rand = new Random(); for (int round = 0; round < confidence; round++) { bool done = false; while (!done) // generate a < n { int testBits = 0; // make sure "a" has at least 2 bits while (testBits < 2) testBits = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * bits); a.genRandomBits(testBits, rand); int byteLen = a.DataLength; // make sure "a" is not 0 if (byteLen > 1 || (byteLen == 1 && a.data[0] != 1)) done = true; } // check whether a factor exists (fix for version 1.03) BigInteger gcdTest = a.gcd(thisVal); if (gcdTest.DataLength == 1 && gcdTest.data[0] != 1) return false; // calculate a^((p-1)/2) mod p BigInteger expResult = a.modPow(p_sub1_shift, thisVal); if (expResult == p_sub1) expResult = -1; // calculate Jacobi symbol BigInteger jacob = Jacobi(a, thisVal); //Console.WriteLine("a = " + a.ToString(10) + " b = " + thisVal.ToString(10)); //Console.WriteLine("expResult = " + expResult.ToString(10) + " Jacob = " + jacob.ToString(10)); // if they are different then it is not prime if (expResult != jacob) return false; } return true; } //*********************************************************************** // Implementation of the Lucas Strong Pseudo Prime test. // // Let n be an odd number with gcd(n,D) = 1, and n - J(D, n) = 2^s * d // with d odd and s >= 0. // // If Ud mod n = 0 or V2^r*d mod n = 0 for some 0 <= r < s, then n // is a strong Lucas pseudoprime with parameters (P, Q). We select // P and Q based on Selfridge. // // Returns True if number is a strong Lucus pseudo prime. // Otherwise, returns False indicating that number is composite. //*********************************************************************** public bool LucasStrongTest() { BigInteger thisVal; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative thisVal = -this; else thisVal = this; if (thisVal.DataLength == 1) { // test small numbers if (thisVal.data[0] == 0 || thisVal.data[0] == 1) return false; else if (thisVal.data[0] == 2 || thisVal.data[0] == 3) return true; } if ((thisVal.data[0] & 0x1) == 0) // even numbers return false; return LucasStrongTestHelper(thisVal); } private bool LucasStrongTestHelper(BigInteger thisVal) { // Do the test (selects D based on Selfridge) // Let D be the first element of the sequence // 5, -7, 9, -11, 13, ... for which J(D,n) = -1 // Let P = 1, Q = (1-D) / 4 long D = 5, sign = -1, dCount = 0; bool done = false; while (!done) { int Jresult = BigInteger.Jacobi(D, thisVal); if (Jresult == -1) done = true; // J(D, this) = 1 else { if (Jresult == 0 && Math.Abs(D) < thisVal) // divisor found return false; if (dCount == 20) { // check for square BigInteger root = thisVal.sqrt(); if (root * root == thisVal) return false; } //Console.WriteLine(D); D = (Math.Abs(D) + 2) * sign; sign = -sign; } dCount++; } long Q = (1 - D) >> 2; /* Console.WriteLine("D = " + D); Console.WriteLine("Q = " + Q); Console.WriteLine("(n,D) = " + thisVal.gcd(D)); Console.WriteLine("(n,Q) = " + thisVal.gcd(Q)); Console.WriteLine("J(D|n) = " + BigInteger.Jacobi(D, thisVal)); */ BigInteger p_add1 = thisVal + 1; int s = 0; for (int index = 0; index < p_add1.DataLength; index++) { uint mask = 0x01; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if ((p_add1.data[index] & mask) != 0) { index = p_add1.DataLength; // to break the outer loop break; } mask <<= 1; s++; } } BigInteger t = p_add1 >> s; // calculate constant = b^(2k) / m // for Barrett Reduction BigInteger constant = new BigInteger(); int nLen = thisVal.DataLength << 1; constant.data[nLen] = 0x00000001; constant.DataLength = nLen + 1; constant = constant / thisVal; BigInteger[] lucas = LucasSequenceHelper(1, Q, t, thisVal, constant, 0); bool isPrime = false; if ((lucas[0].DataLength == 1 && lucas[0].data[0] == 0) || (lucas[1].DataLength == 1 && lucas[1].data[0] == 0)) { // u(t) = 0 or V(t) = 0 isPrime = true; } for (int i = 1; i < s; i++) { if (!isPrime) { // doubling of index lucas[1] = thisVal.BarrettReduction(lucas[1] * lucas[1], thisVal, constant); lucas[1] = (lucas[1] - (lucas[2] << 1)) % thisVal; //lucas[1] = ((lucas[1] * lucas[1]) - (lucas[2] << 1)) % thisVal; if ((lucas[1].DataLength == 1 && lucas[1].data[0] == 0)) isPrime = true; } lucas[2] = thisVal.BarrettReduction(lucas[2] * lucas[2], thisVal, constant); //Q^k } if (isPrime) // additional checks for composite numbers { // If n is prime and gcd(n, Q) == 1, then // Q^((n+1)/2) = Q * Q^((n-1)/2) is congruent to (Q * J(Q, n)) mod n BigInteger g = thisVal.gcd(Q); if (g.DataLength == 1 && g.data[0] == 1) // gcd(this, Q) == 1 { if ((lucas[2].data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) lucas[2] += thisVal; BigInteger temp = (Q * BigInteger.Jacobi(Q, thisVal)) % thisVal; if ((temp.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) temp += thisVal; if (lucas[2] != temp) isPrime = false; } } return isPrime; } //*********************************************************************** // Determines whether a number is probably prime, using the Rabin-Miller's // test. Before applying the test, the number is tested for divisibility // by primes < 2000 // // Returns true if number is probably prime. //*********************************************************************** public bool isProbablePrime(int confidence) { BigInteger thisVal; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative thisVal = -this; else thisVal = this; // test for divisibility by primes < 2000 for (int p = 0; p < primesBelow2000.Length; p++) { BigInteger divisor = primesBelow2000[p]; if (divisor >= thisVal) break; BigInteger resultNum = thisVal % divisor; if (resultNum.IntValue() == 0) { /* Console.WriteLine("Not prime! Divisible by {0}\n", primesBelow2000[p]); */ return false; } } if (thisVal.RabinMillerTest(confidence)) return true; else { //Console.WriteLine("Not prime! Failed primality test\n"); return false; } } //*********************************************************************** // Determines whether this BigInteger is probably prime using a // combination of base 2 strong pseudoprime test and Lucas strong // pseudoprime test. // // The sequence of the primality test is as follows, // // 1) Trial divisions are carried out using prime numbers below 2000. // if any of the primes divides this BigInteger, then it is not prime. // // 2) Perform base 2 strong pseudoprime test. If this BigInteger is a // base 2 strong pseudoprime, proceed on to the next step. // // 3) Perform strong Lucas pseudoprime test. // // Returns True if this BigInteger is both a base 2 strong pseudoprime // and a strong Lucas pseudoprime. // // For a detailed discussion of this primality test, see [6]. // //*********************************************************************** public bool isProbablePrime() { BigInteger thisVal; if ((this.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative thisVal = -this; else thisVal = this; if (thisVal.DataLength == 1) { // test small numbers if (thisVal.data[0] == 0 || thisVal.data[0] == 1) return false; else if (thisVal.data[0] == 2 || thisVal.data[0] == 3) return true; } if ((thisVal.data[0] & 0x1) == 0) // even numbers return false; // test for divisibility by primes < 2000 for (int p = 0; p < primesBelow2000.Length; p++) { BigInteger divisor = primesBelow2000[p]; if (divisor >= thisVal) break; BigInteger resultNum = thisVal % divisor; if (resultNum.IntValue() == 0) { //Console.WriteLine("Not prime! Divisible by {0}\n", // primesBelow2000[p]); return false; } } // Perform BASE 2 Rabin-Miller Test // calculate values of s and t BigInteger p_sub1 = thisVal - (new BigInteger(1)); int s = 0; for (int index = 0; index < p_sub1.DataLength; index++) { uint mask = 0x01; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if ((p_sub1.data[index] & mask) != 0) { index = p_sub1.DataLength; // to break the outer loop break; } mask <<= 1; s++; } } BigInteger t = p_sub1 >> s; int bits = thisVal.bitCount(); BigInteger a = 2; // b = a^t mod p BigInteger b = a.modPow(t, thisVal); bool result = false; if (b.DataLength == 1 && b.data[0] == 1) // a^t mod p = 1 result = true; for (int j = 0; result == false && j < s; j++) { if (b == p_sub1) // a^((2^j)*t) mod p = p-1 for some 0 <= j <= s-1 { result = true; break; } b = (b * b) % thisVal; } // if number is strong pseudoprime to base 2, then do a strong lucas test if (result) result = LucasStrongTestHelper(thisVal); return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the lowest 4 bytes of the BigInteger as an int. //*********************************************************************** public int IntValue() { return (int)data[0]; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the lowest 8 bytes of the BigInteger as a long. //*********************************************************************** public long LongValue() { long val = 0; val = (long)data[0]; try { // exception if maxLength = 1 val |= (long)data[1] << 32; } catch (Exception) { if ((data[0] & 0x80000000) != 0) // negative val = (int)data[0]; } return val; } //*********************************************************************** // Computes the Jacobi Symbol for a and b. // Algorithm adapted from [3] and [4] with some optimizations //*********************************************************************** public static int Jacobi(BigInteger a, BigInteger b) { // Jacobi defined only for odd integers if ((b.data[0] & 0x1) == 0) throw (new ArgumentException("Jacobi defined only for odd integers.")); if (a >= b) a %= b; if (a.DataLength == 1 && a.data[0] == 0) return 0; // a == 0 if (a.DataLength == 1 && a.data[0] == 1) return 1; // a == 1 if (a < 0) { if ((((b - 1).data[0]) & 0x2) == 0) //if( (((b-1) >> 1).data[0] & 0x1) == 0) return Jacobi(-a, b); else return -Jacobi(-a, b); } int e = 0; for (int index = 0; index < a.DataLength; index++) { uint mask = 0x01; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if ((a.data[index] & mask) != 0) { index = a.DataLength; // to break the outer loop break; } mask <<= 1; e++; } } BigInteger a1 = a >> e; int s = 1; if ((e & 0x1) != 0 && ((b.data[0] & 0x7) == 3 || (b.data[0] & 0x7) == 5)) s = -1; if ((b.data[0] & 0x3) == 3 && (a1.data[0] & 0x3) == 3) s = -s; if (a1.DataLength == 1 && a1.data[0] == 1) return s; else return (s * Jacobi(b % a1, a1)); } //*********************************************************************** // Generates a positive BigInteger that is probably prime. //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger genPseudoPrime(int bits, int confidence, Random rand) { BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); bool done = false; while (!done) { result.genRandomBits(bits, rand); result.data[0] |= 0x01; // make it odd // prime test done = result.isProbablePrime(confidence); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Generates a random number with the specified number of bits such // that gcd(number, this) = 1 //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger genCoPrime(int bits, Random rand) { bool done = false; BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); while (!done) { result.genRandomBits(bits, rand); //Console.WriteLine(result.ToString(16)); // gcd test BigInteger g = result.gcd(this); if (g.DataLength == 1 && g.data[0] == 1) done = true; } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the modulo inverse of this. Throws ArithmeticException if // the inverse does not exist. (i.e. gcd(this, modulus) != 1) //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger modInverse(BigInteger modulus) { BigInteger[] p = { 0, 1 }; BigInteger[] q = new BigInteger[2]; // quotients BigInteger[] r = { 0, 0 }; // remainders int step = 0; BigInteger a = modulus; BigInteger b = this; while (b.DataLength > 1 || (b.DataLength == 1 && b.data[0] != 0)) { BigInteger quotient = new BigInteger(); BigInteger remainder = new BigInteger(); if (step > 1) { BigInteger pval = (p[0] - (p[1] * q[0])) % modulus; p[0] = p[1]; p[1] = pval; } if (b.DataLength == 1) singleByteDivide(a, b, quotient, remainder); else multiByteDivide(a, b, quotient, remainder); /* Console.WriteLine(quotient.dataLength); Console.WriteLine("{0} = {1}({2}) + {3} p = {4}", a.ToString(10), b.ToString(10), quotient.ToString(10), remainder.ToString(10), p[1].ToString(10)); */ q[0] = q[1]; r[0] = r[1]; q[1] = quotient; r[1] = remainder; a = b; b = remainder; step++; } if (r[0].DataLength > 1 || (r[0].DataLength == 1 && r[0].data[0] != 1)) throw (new ArithmeticException("No inverse!")); BigInteger result = ((p[0] - (p[1] * q[0])) % modulus); if ((result.data[maxLength - 1] & 0x80000000) != 0) result += modulus; // get the least positive modulus return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the value of the BigInteger as a byte array. The lowest // index contains the MSB. //*********************************************************************** public byte[] getBytes() { int numBits = bitCount(); int numBytes = numBits >> 3; if ((numBits & 0x7) != 0) numBytes++; byte[] result = new byte[numBytes]; //Console.WriteLine(result.Length); int pos = 0; uint tempVal, val = data[DataLength - 1]; if ((tempVal = (val >> 24 & 0xFF)) != 0) result[pos++] = (byte)tempVal; if ((tempVal = (val >> 16 & 0xFF)) != 0) result[pos++] = (byte)tempVal; if ((tempVal = (val >> 8 & 0xFF)) != 0) result[pos++] = (byte)tempVal; if ((tempVal = (val & 0xFF)) != 0) result[pos++] = (byte)tempVal; for (int i = DataLength - 2; i >= 0; i--, pos += 4) { val = data[i]; result[pos + 3] = (byte)(val & 0xFF); val >>= 8; result[pos + 2] = (byte)(val & 0xFF); val >>= 8; result[pos + 1] = (byte)(val & 0xFF); val >>= 8; result[pos] = (byte)(val & 0xFF); } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Sets the value of the specified bit to 1 // The Least Significant Bit position is 0. //*********************************************************************** public void setBit(uint bitNum) { uint bytePos = bitNum >> 5; // divide by 32 byte bitPos = (byte)(bitNum & 0x1F); // get the lowest 5 bits uint mask = (uint)1 << bitPos; this.data[bytePos] |= mask; if (bytePos >= this.DataLength) this.DataLength = (int)bytePos + 1; } //*********************************************************************** // Sets the value of the specified bit to 0 // The Least Significant Bit position is 0. //*********************************************************************** public void unsetBit(uint bitNum) { uint bytePos = bitNum >> 5; if (bytePos < this.DataLength) { byte bitPos = (byte)(bitNum & 0x1F); uint mask = (uint)1 << bitPos; uint mask2 = 0xFFFFFFFF ^ mask; this.data[bytePos] &= mask2; if (this.DataLength > 1 && this.data[this.DataLength - 1] == 0) this.DataLength--; } } //*********************************************************************** // Returns a value that is equivalent to the integer square root // of the BigInteger. // // The integer square root of "this" is defined as the largest integer n // such that (n * n) <= this // //*********************************************************************** public BigInteger sqrt() { uint numBits = (uint)this.bitCount(); if ((numBits & 0x1) != 0) // odd number of bits numBits = (numBits >> 1) + 1; else numBits = (numBits >> 1); uint bytePos = numBits >> 5; byte bitPos = (byte)(numBits & 0x1F); uint mask; BigInteger result = new BigInteger(); if (bitPos == 0) mask = 0x80000000; else { mask = (uint)1 << bitPos; bytePos++; } result.DataLength = (int)bytePos; for (int i = (int)bytePos - 1; i >= 0; i--) { while (mask != 0) { // guess result.data[i] ^= mask; // undo the guess if its square is larger than this if ((result * result) > this) result.data[i] ^= mask; mask >>= 1; } mask = 0x80000000; } return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Returns the k_th number in the Lucas Sequence reduced modulo n. // // Uses index doubling to speed up the process. For example, to calculate V(k), // we maintain two numbers in the sequence V(n) and V(n+1). // // To obtain V(2n), we use the identity // V(2n) = (V(n) * V(n)) - (2 * Q^n) // To obtain V(2n+1), we first write it as // V(2n+1) = V((n+1) + n) // and use the identity // V(m+n) = V(m) * V(n) - Q * V(m-n) // Hence, // V((n+1) + n) = V(n+1) * V(n) - Q^n * V((n+1) - n) // = V(n+1) * V(n) - Q^n * V(1) // = V(n+1) * V(n) - Q^n * P // // We use k in its binary expansion and perform index doubling for each // bit position. For each bit position that is set, we perform an // index doubling followed by an index addition. This means that for V(n), // we need to update it to V(2n+1). For V(n+1), we need to update it to // V((2n+1)+1) = V(2*(n+1)) // // This function returns // [0] = U(k) // [1] = V(k) // [2] = Q^n // // Where U(0) = 0 % n, U(1) = 1 % n // V(0) = 2 % n, V(1) = P % n //*********************************************************************** public static BigInteger[] LucasSequence(BigInteger P, BigInteger Q, BigInteger k, BigInteger n) { if (k.DataLength == 1 && k.data[0] == 0) { BigInteger[] result = new BigInteger[3]; result[0] = 0; result[1] = 2 % n; result[2] = 1 % n; return result; } // calculate constant = b^(2k) / m // for Barrett Reduction BigInteger constant = new BigInteger(); int nLen = n.DataLength << 1; constant.data[nLen] = 0x00000001; constant.DataLength = nLen + 1; constant = constant / n; // calculate values of s and t int s = 0; for (int index = 0; index < k.DataLength; index++) { uint mask = 0x01; for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { if ((k.data[index] & mask) != 0) { index = k.DataLength; // to break the outer loop break; } mask <<= 1; s++; } } BigInteger t = k >> s; //Console.WriteLine("s = " + s + " t = " + t); return LucasSequenceHelper(P, Q, t, n, constant, s); } //*********************************************************************** // Performs the calculation of the kth term in the Lucas Sequence. // For details of the algorithm, see reference [9]. // // k must be odd. i.e LSB == 1 //*********************************************************************** private static BigInteger[] LucasSequenceHelper(BigInteger P, BigInteger Q, BigInteger k, BigInteger n, BigInteger constant, int s) { BigInteger[] result = new BigInteger[3]; if ((k.data[0] & 0x00000001) == 0) throw (new ArgumentException("Argument k must be odd.")); int numbits = k.bitCount(); uint mask = (uint)0x1 << ((numbits & 0x1F) - 1); // v = v0, v1 = v1, u1 = u1, Q_k = Q^0 BigInteger v = 2 % n, Q_k = 1 % n, v1 = P % n, u1 = Q_k; bool flag = true; for (int i = k.DataLength - 1; i >= 0; i--) // iterate on the binary expansion of k { //Console.WriteLine("round"); while (mask != 0) { if (i == 0 && mask == 0x00000001) // last bit break; if ((k.data[i] & mask) != 0) // bit is set { // index doubling with addition u1 = (u1 * v1) % n; v = ((v * v1) - (P * Q_k)) % n; v1 = n.BarrettReduction(v1 * v1, n, constant); v1 = (v1 - ((Q_k * Q) << 1)) % n; if (flag) flag = false; else Q_k = n.BarrettReduction(Q_k * Q_k, n, constant); Q_k = (Q_k * Q) % n; } else { // index doubling u1 = ((u1 * v) - Q_k) % n; v1 = ((v * v1) - (P * Q_k)) % n; v = n.BarrettReduction(v * v, n, constant); v = (v - (Q_k << 1)) % n; if (flag) { Q_k = Q % n; flag = false; } else Q_k = n.BarrettReduction(Q_k * Q_k, n, constant); } mask >>= 1; } mask = 0x80000000; } // at this point u1 = u(n+1) and v = v(n) // since the last bit always 1, we need to transform u1 to u(2n+1) and v to v(2n+1) u1 = ((u1 * v) - Q_k) % n; v = ((v * v1) - (P * Q_k)) % n; if (flag) flag = false; else Q_k = n.BarrettReduction(Q_k * Q_k, n, constant); Q_k = (Q_k * Q) % n; for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) { // index doubling u1 = (u1 * v) % n; v = ((v * v) - (Q_k << 1)) % n; if (flag) { Q_k = Q % n; flag = false; } else Q_k = n.BarrettReduction(Q_k * Q_k, n, constant); } result[0] = u1; result[1] = v; result[2] = Q_k; return result; } //*********************************************************************** // Tests the correct implementation of the /, %, * and + operators //*********************************************************************** public static void MulDivTest(int rounds) { Random rand = new Random(); byte[] val = new byte[64]; byte[] val2 = new byte[64]; for (int count = 0; count < rounds; count++) { // generate 2 numbers of random length int t1 = 0; while (t1 == 0) t1 = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * 65); int t2 = 0; while (t2 == 0) t2 = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * 65); bool done = false; while (!done) { for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) { if (i < t1) val[i] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); else val[i] = 0; if (val[i] != 0) done = true; } } done = false; while (!done) { for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) { if (i < t2) val2[i] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); else val2[i] = 0; if (val2[i] != 0) done = true; } } while (val[0] == 0) val[0] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); while (val2[0] == 0) val2[0] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); Console.WriteLine(count); BigInteger bn1 = new BigInteger(val, t1); BigInteger bn2 = new BigInteger(val2, t2); // Determine the quotient and remainder by dividing // the first number by the second. BigInteger bn3 = bn1 / bn2; BigInteger bn4 = bn1 % bn2; // Recalculate the number BigInteger bn5 = (bn3 * bn2) + bn4; // Make sure they're the same if (bn5 != bn1) { Console.WriteLine("Error at " + count); Console.WriteLine(bn1 + "\n"); Console.WriteLine(bn2 + "\n"); Console.WriteLine(bn3 + "\n"); Console.WriteLine(bn4 + "\n"); Console.WriteLine(bn5 + "\n"); return; } } } //*********************************************************************** // Tests the correct implementation of the modulo exponential function // using RSA encryption and decryption (using pre-computed encryption and // decryption keys). //*********************************************************************** public static void RSATest(int rounds) { Random rand = new Random(1); byte[] val = new byte[64]; // private and public key BigInteger bi_e = new BigInteger("a932b948feed4fb2b692609bd22164fc9edb59fae7880cc1eaff7b3c9626b7e5b241c27a974833b2622ebe09beb451917663d47232488f23a117fc97720f1e7", 16); BigInteger bi_d = new BigInteger("4adf2f7a89da93248509347d2ae506d683dd3a16357e859a980c4f77a4e2f7a01fae289f13a851df6e9db5adaa60bfd2b162bbbe31f7c8f828261a6839311929d2cef4f864dde65e556ce43c89bbbf9f1ac5511315847ce9cc8dc92470a747b8792d6a83b0092d2e5ebaf852c85cacf34278efa99160f2f8aa7ee7214de07b7", 16); BigInteger bi_n = new BigInteger("e8e77781f36a7b3188d711c2190b560f205a52391b3479cdb99fa010745cbeba5f2adc08e1de6bf38398a0487c4a73610d94ec36f17f3f46ad75e17bc1adfec99839589f45f95ccc94cb2a5c500b477eb3323d8cfab0c8458c96f0147a45d27e45a4d11d54d77684f65d48f15fafcc1ba208e71e921b9bd9017c16a5231af7f", 16); Console.WriteLine("e =\n" + bi_e.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("\nd =\n" + bi_d.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("\nn =\n" + bi_n.ToString(10) + "\n"); for (int count = 0; count < rounds; count++) { // generate data of random length int t1 = 0; while (t1 == 0) t1 = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * 65); bool done = false; while (!done) { for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) { if (i < t1) val[i] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); else val[i] = 0; if (val[i] != 0) done = true; } } while (val[0] == 0) val[0] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); Console.Write("Round = " + count); // encrypt and decrypt data BigInteger bi_data = new BigInteger(val, t1); BigInteger bi_encrypted = bi_data.modPow(bi_e, bi_n); BigInteger bi_decrypted = bi_encrypted.modPow(bi_d, bi_n); // compare if (bi_decrypted != bi_data) { Console.WriteLine("\nError at round " + count); Console.WriteLine(bi_data + "\n"); return; } Console.WriteLine(" . "); } } //*********************************************************************** // Tests the correct implementation of the modulo exponential and // inverse modulo functions using RSA encryption and decryption. The two // pseudoprimes p and q are fixed, but the two RSA keys are generated // for each round of testing. //*********************************************************************** public static void RSATest2(int rounds) { Random rand = new Random(); byte[] val = new byte[64]; byte[] pseudoPrime1 = { (byte)0x85, (byte)0x84, (byte)0x64, (byte)0xFD, (byte)0x70, (byte)0x6A, (byte)0x9F, (byte)0xF0, (byte)0x94, (byte)0x0C, (byte)0x3E, (byte)0x2C, (byte)0x74, (byte)0x34, (byte)0x05, (byte)0xC9, (byte)0x55, (byte)0xB3, (byte)0x85, (byte)0x32, (byte)0x98, (byte)0x71, (byte)0xF9, (byte)0x41, (byte)0x21, (byte)0x5F, (byte)0x02, (byte)0x9E, (byte)0xEA, (byte)0x56, (byte)0x8D, (byte)0x8C, (byte)0x44, (byte)0xCC, (byte)0xEE, (byte)0xEE, (byte)0x3D, (byte)0x2C, (byte)0x9D, (byte)0x2C, (byte)0x12, (byte)0x41, (byte)0x1E, (byte)0xF1, (byte)0xC5, (byte)0x32, (byte)0xC3, (byte)0xAA, (byte)0x31, (byte)0x4A, (byte)0x52, (byte)0xD8, (byte)0xE8, (byte)0xAF, (byte)0x42, (byte)0xF4, (byte)0x72, (byte)0xA1, (byte)0x2A, (byte)0x0D, (byte)0x97, (byte)0xB1, (byte)0x31, (byte)0xB3, }; byte[] pseudoPrime2 = { (byte)0x99, (byte)0x98, (byte)0xCA, (byte)0xB8, (byte)0x5E, (byte)0xD7, (byte)0xE5, (byte)0xDC, (byte)0x28, (byte)0x5C, (byte)0x6F, (byte)0x0E, (byte)0x15, (byte)0x09, (byte)0x59, (byte)0x6E, (byte)0x84, (byte)0xF3, (byte)0x81, (byte)0xCD, (byte)0xDE, (byte)0x42, (byte)0xDC, (byte)0x93, (byte)0xC2, (byte)0x7A, (byte)0x62, (byte)0xAC, (byte)0x6C, (byte)0xAF, (byte)0xDE, (byte)0x74, (byte)0xE3, (byte)0xCB, (byte)0x60, (byte)0x20, (byte)0x38, (byte)0x9C, (byte)0x21, (byte)0xC3, (byte)0xDC, (byte)0xC8, (byte)0xA2, (byte)0x4D, (byte)0xC6, (byte)0x2A, (byte)0x35, (byte)0x7F, (byte)0xF3, (byte)0xA9, (byte)0xE8, (byte)0x1D, (byte)0x7B, (byte)0x2C, (byte)0x78, (byte)0xFA, (byte)0xB8, (byte)0x02, (byte)0x55, (byte)0x80, (byte)0x9B, (byte)0xC2, (byte)0xA5, (byte)0xCB, }; BigInteger bi_p = new BigInteger(pseudoPrime1); BigInteger bi_q = new BigInteger(pseudoPrime2); BigInteger bi_pq = (bi_p - 1) * (bi_q - 1); BigInteger bi_n = bi_p * bi_q; for (int count = 0; count < rounds; count++) { // generate private and public key BigInteger bi_e = bi_pq.genCoPrime(512, rand); BigInteger bi_d = bi_e.modInverse(bi_pq); Console.WriteLine("\ne =\n" + bi_e.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("\nd =\n" + bi_d.ToString(10)); Console.WriteLine("\nn =\n" + bi_n.ToString(10) + "\n"); // generate data of random length int t1 = 0; while (t1 == 0) t1 = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * 65); bool done = false; while (!done) { for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) { if (i < t1) val[i] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); else val[i] = 0; if (val[i] != 0) done = true; } } while (val[0] == 0) val[0] = (byte)(rand.NextDouble() * 256); Console.Write("Round = " + count); // encrypt and decrypt data BigInteger bi_data = new BigInteger(val, t1); BigInteger bi_encrypted = bi_data.modPow(bi_e, bi_n); BigInteger bi_decrypted = bi_encrypted.modPow(bi_d, bi_n); // compare if (bi_decrypted != bi_data) { Console.WriteLine("\nError at round " + count); Console.WriteLine(bi_data + "\n"); return; } Console.WriteLine(". "); } } //*********************************************************************** // Tests the correct implementation of sqrt() method. //*********************************************************************** public static void SqrtTest(int rounds) { Random rand = new Random(); for (int count = 0; count < rounds; count++) { // generate data of random length int t1 = 0; while (t1 == 0) t1 = (int)(rand.NextDouble() * 1024); Console.Write("Round = " + count); BigInteger a = new BigInteger(); a.genRandomBits(t1, rand); BigInteger b = a.sqrt(); BigInteger c = (b + 1) * (b + 1); // check that b is the largest integer such that b*b <= a if (c <= a) { Console.WriteLine("\nError at round " + count); Console.WriteLine(a + "\n"); return; } Console.WriteLine(". "); } } } }
四.总结:
上面主要讲解了非对称加密算法的原理和分类,以及非对称加密算法在.NET中的应用,也对非对称加密算法的.NET底层源码做了分析,希望可以帮助到大家。
加密算法系列:
DotNet加密方式解析--散列加密:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengze0902/p/6268700.html
DotNet加密方式解析--对称加密:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengze0902/p/6268702.html
DotNet加密方式解析--数字签名:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengze0902/p/6268709.html
DotNet加密方式解析--非对称加密:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengze0902/p/6268705.html