Android数据适配-ExpandableListView
Android中ListView的用法基本上学的时候都会使用,其中可以使用ArrayAdapter,SimpleAdapter,BaseAdapter去实现,这次主要使用的ExpandableListView展示一种两层的效果,ExpandableListView是android中可以实现下拉list的一个控件类似于QQ那种我好友之后就是一排自己的好友,就是两层效果,实现的话使用SimpleExpandableListAdapter即可。
布局文件
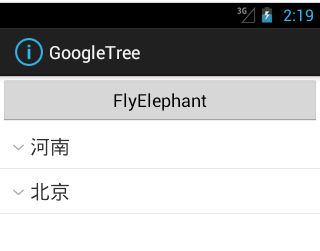
先看下效果:
main中xml代码:
<Button
android:onClick="test"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="FlyElephant" />
<ExpandableListView
android:id="@id/android:list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" />
定义一个省份的province.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/list_provinceText"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:paddingBottom="8px"
android:paddingLeft="30px"
android:paddingRight="5px"
android:paddingTop="8px"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
定义了一个地区的child.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/child_text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:paddingBottom="8px"
android:paddingLeft="30px"
android:paddingRight="5px"
android:paddingTop="8px"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
Demo实现
主要实现代码,代码中都已经注释,其中最主要的SimpleExpandableListAdapter中的参数,这个参数太多,很容易弄错,可以看下注释或者API文档:
// 创建一级条目
List<Map<String, String>> provinces = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
//创建两个省份一级条目
Map<String, String> firstProvince= new HashMap<String, String>();
firstProvince.put("province", "河南");
Map<String, String> secondProvince= new HashMap<String, String>();
secondProvince.put("province", "北京");
provinces.add(firstProvince);
provinces.add(secondProvince);
// 创建一级条目下的的二级地区条目
List<Map<String, String>> childList1= new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
//同样是在一级条目目录下创建两个对应的二级条目目录
Map<String, String> child1= new HashMap<String, String>();
child1.put("child", "郑州");
Map<String, String> child2 = new HashMap<String, String>();
child2.put("child", "开封");
childList1.add(child1);
childList1.add(child2);
//同上
List<Map<String, String>> childList2 = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
Map<String, String> child3 = new HashMap<String, String>();
child3.put("child", "海淀");
Map<String, String> child4 = new HashMap<String, String>();
child4.put("child", "昌平");
childList2.add(child3);
childList2.add(child4);
// 将二级条目放在一个集合里,供显示时使用
List<List<Map<String, String>>> childs = new ArrayList<List<Map<String, String>>>();
childs.add(childList1);
childs.add(childList2);
/**
* 使用SimpleExpandableListAdapter显示ExpandableListView
* 参数1.上下文对象Context
* 参数2.一级条目目录集合
* 参数3.一级条目对应的布局文件
* 参数4.fromto,就是map中的key,指定要显示的对象
* 参数5.与参数4对应,指定要显示在groups中的id
* 参数6.二级条目目录集合
* 参数7.二级条目对应的布局文件
* 参数8.fromto,就是map中的key,指定要显示的对象
* 参数9.与参数8对应,指定要显示在childs中的id
*/
SimpleExpandableListAdapter adapter = new SimpleExpandableListAdapter(
this, provinces, R.layout.list_group, new String[] { "province" },
new int[] { R.id.list_groupText }, childs, R.layout.child,
new String[] { "child" }, new int[] { R.id.child_text });
setListAdapter(adapter);
这个mainActivity需要继承ExpandableListActivity,当然你可以设置其中的点击事件,只要重写一下方法即可:
/**
* 设置哪个二级目录被默认选中
*/
@Override
public boolean setSelectedChild(int groupPosition, int childPosition,
boolean shouldExpandGroup) {
//do something
return super.setSelectedChild(groupPosition, childPosition,
shouldExpandGroup);
}
/**
* 设置哪个一级目录被默认选中
*/
@Override
public void setSelectedGroup(int groupPosition) {
//do something
super.setSelectedGroup(groupPosition);
}
/**
* 当二级条目被点击时响应
*/
@Override
public boolean onChildClick(ExpandableListView parent, View v,
int groupPosition, int childPosition, long id) {
//do something
return super.onChildClick(parent, v, groupPosition, childPosition, id);
}
效果如下:

上面这个例子写的有点单调,其实第二个你子的布局直接是空的也行,例如定义一个images.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageView
android:src="@drawable/open"
android:layout_width="20dp"
android:layout_height="20dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtName"
android:paddingLeft="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
然后定义一个items.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/items"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
</TextView>
代码调用:
public class MyExpandleActivity extends Activity {
/**
* 实现可扩展展开列ExpandableListView的三种方式
* 一是使用SimpleExpandableListAdpater将两个List集合包装成ExpandableListView 二是
* 扩展BaseExpandableListAdpter
* 三是使用simpleCursorTreeAdapter将Cursor中的数据包装成SimpleCuroTreeAdapter
*/
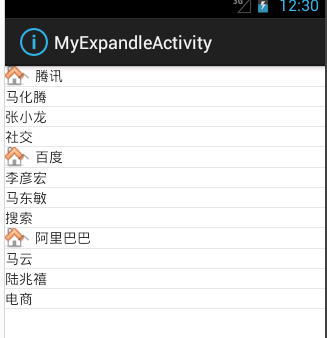
private String[] names = { "腾讯", "百度", "阿里巴巴" };
private String[][] childnames = { { "马化腾", "张小龙","社交"},
{ "李彦宏", "马东敏","搜索" }, { "马云", "陆兆禧","电商" } };
private ExpandableListView ep;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_my_expandle);
// 定义父列表项List数据集合
List<Map<String, String>> group = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
// 定义子列表项List数据集合
List<List<Map<String, String>>> ss = new ArrayList<List<Map<String, String>>>();
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
// 提供父列表的数据
Map<String, String> maps = new HashMap<String, String>();
maps.put("names", names[i]);
group.add(maps);
// 提供当前父列的子列数据
List<Map<String, String>> child = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) {
Map<String, String> mapsj = new HashMap<String, String>();
mapsj.put("map", childnames[i][j]);
child.add(mapsj);
}
ss.add(child);
}
/**
* 第一个参数 应用程序接口 this 第二个父列List<?extends Map<String,Object>>集合 为父列提供数据
* 第三个参数 父列显示的组件资源文件 第四个参数 键值列表 父列Map字典的key 第五个要显示的父列组件id 第六个 子列的显示资源文件
* 第七个参数 键值列表的子列Map字典的key 第八个要显示子列的组件id
*/
SimpleExpandableListAdapter expand = new SimpleExpandableListAdapter(
this, group, R.layout.images, new String[] { "names" },
new int[] { R.id.txtName }, ss, R.layout.items,
new String[] { "map" }, new int[] { R.id.items });
ep = (ExpandableListView) findViewById(R.id.expanable_mylist);
ep.setAdapter(expand);
}
}
效果跟上面相同: