Elasticsearch+Spring Boot集成实践
ELK-技术栈
Elasticsearch
简介
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式、RESTful 风格的搜索和数据分析引擎,能够解决不断涌现出的各种用例。 作为 Elastic Stack 的核心,它集中存储您的数据,帮助您发现意料之中以及意料之外的情况。
Elasticsearch是当前比较流行的开源的分布式搜索和数据分析引擎,具备易使用、高性能、扩展性强等特点。是ElasticStack的核心组件,以其为核心构建的ELK,已经是日志分析领域的事实标准。
与ES有关的关键字如下所示:
-
实时
-
分布式
-
搜索
-
分析
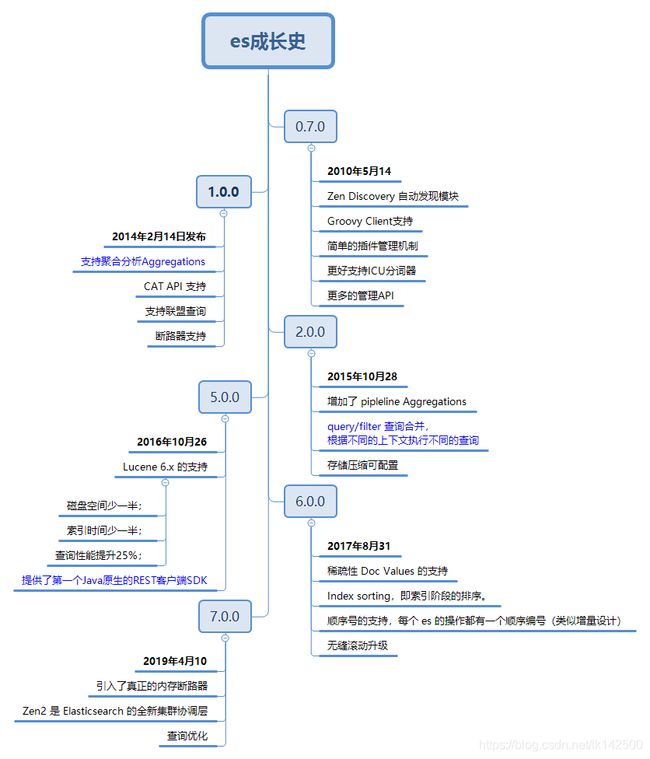
发展历史
作用
- 全文搜索
- 站内分析
Top5典型应用场景
- 记录和日志分析
- 采集和组合公共数据
- 全文搜索
- 事件数据和指标
- 数据可视化
ElasticSearch 在滴滴有着非常丰富的应用场景:
- 为线上核心搜索业务提供引擎支持;
- 作为 RDS 从库,海量数据检索需求;
- 解决公司海量日志检索问题;
- 为安全场景提供数据分析能力。
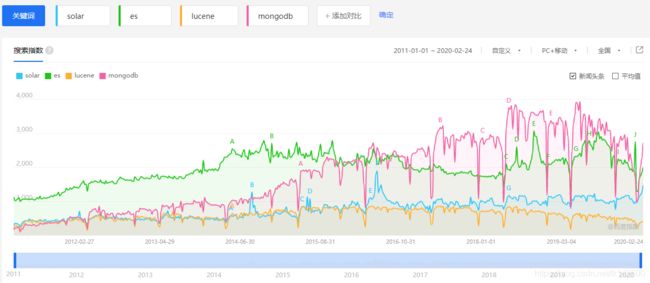
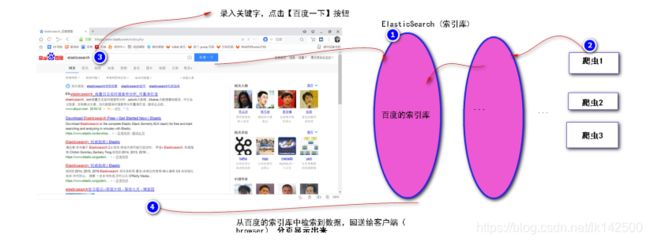
百度指数
Kibana
Kibana 是为 Elasticsearch设计的开源分析和可视化平台。你可以使用 Kibana 来搜索,查看存储在 Elasticsearch 索引中的数据并与之交互。你可以很容易实现高级的数据分析和可视化,以图标的形式展现出来。
主要用途
- 实时监控
- 问题分析
Logstash
Logstash 是开源的服务器端数据处理管道,能够同时从多个来源采集数据,转换数据,然后将数据发送到您最喜欢的“存储库”中。 集中、转换和存储数据
Logstash是一个具有实时pipeline功能的开源数据收集引擎。Logstash可以动态的统一来自不同数据源的数据,并将数据规范化到你选择的目的地。虽然Logstash最初推动了日志收集方面的创新,但它的功能现在更丰富了。任何类型的事件都可以通过丰富的input,filter,output插件进行转换,简化抽取过程
LogStash的数据源
- 日志和指标
- web
- 数据存储和流
环境搭建
下载中心
ELK技术栈全方位提供了各种安装方式,
rpm、deb、tar.gz、docker,
可以随心使用。
Elasticsearch
安装
安装并运行Elasticsearch
cd elasticsearch-
./bin/elasticsearch
如果你想把 Elasticsearch 作为一个守护进程在后台运行,那么可以在后面添加参数 -d 。 如果你是在 Windows 上面运行 Elasticseach,你应该运行 bin\elasticsearch.bat 而不是 bin\elasticsearch 。
- 如果你想把 Elasticsearch 作为一个守护进程在后台运行,那么可以在后面添加参数
-d。 - 如果你是在 Windows 上面运行 Elasticseach,你应该运行
bin\elasticsearch.bat而不是bin\elasticsearch。-
配置项
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: my-application
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
#node.name: node-1
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host: localhost
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
#discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["host1", "host2"]
#
# Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1):
#
#discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
#gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
测试ES安装是否成功,可以使用
curl 'http://localhost:9200/?pretty'
ze则表示安装成功
Kibana
安装
在Windows上安装Kibana
cd $KIBANA_HOME
.\bin\kibana
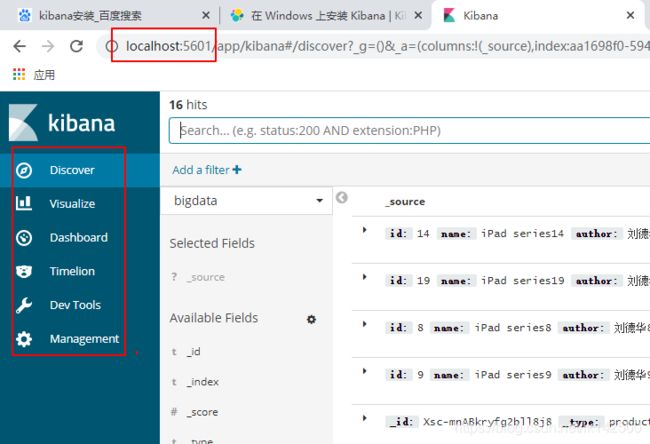
可以访问浏览器: localhost:5601测试安装是否成功。
配置
Kibana 默认情况下从 $KIBANA_HOME/config/kibana.yml 加载配置文件。
| 类型 | 描述 | 默认位置 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|---|
| home | Kibana home 目录或 $KIBANA_HOME 。 |
解压包时创建的目录 | |
| bin | 二进制脚本,包括 kibana 启动 Kibana 服务和 kibana-plugin 安装插件。 |
$KIBANA_HOME\bin |
|
| config | 配置文件包括 kibana.yml 。 |
$KIBANA_HOME\config |
|
| data | Kibana 和其插件写入磁盘的数据文件位置。 | $KIBANA_HOME\data |
|
| optimize | 编译过的源码。某些管理操作(如,插件安装)导致运行时重新编译源码。 | $KIBANA_HOME\optimize |
|
| plugins | 插件文件位置。每一个插件都一个单独的二级目录。 | $KIBANA_HOME\plugins |
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use.
#server.port: 5601
# Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values.
# The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect.
# To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address.
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
# Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. This only affects
# the URLs generated by Kibana, your proxy is expected to remove the basePath value before forwarding requests
# to Kibana. This setting cannot end in a slash.
#server.basePath: ""
# The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests.
#server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576
# The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes.
#server.name: "your-hostname"
# The URL of the Elasticsearch instance to use for all your queries.
elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"
# When this setting's value is true Kibana uses the hostname specified in the server.host
# setting. When the value of this setting is false, Kibana uses the hostname of the host
# that connects to this Kibana instance.
#elasticsearch.preserveHost: true
# Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and
# dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist.
#kibana.index: ".kibana"
# The default application to load.
#kibana.defaultAppId: "discover"
# If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide
# the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana
# index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which
# is proxied through the Kibana server.
#elasticsearch.username: "user"
#elasticsearch.password: "pass"
# Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively.
# These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser.
#server.ssl.enabled: false
#server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt
#server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key
# Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files.
# These files validate that your Elasticsearch backend uses the same key files.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt
#elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key
# Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate
# authority for your Elasticsearch instance.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ]
# To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'.
#elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of
# the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting.
#elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500
# Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value
# must be a positive integer.
#elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000
# List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side
# headers, set this value to [] (an empty list).
#elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ]
# Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten
# by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration.
#elasticsearch.customHeaders: {}
# Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable.
#elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 0
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch at Kibana startup before retrying.
#elasticsearch.startupTimeout: 5000
# Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file.
#pid.file: /var/run/kibana.pid
# Enables you specify a file where Kibana stores log output.
#logging.dest: stdout
# Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output.
#logging.silent: false
# Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages.
#logging.quiet: false
# Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information
# and all requests.
#logging.verbose: false
# Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance
# metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000.
#ops.interval: 5000
# The default locale. This locale can be used in certain circumstances to substitute any missing
# translations.
#i18n.defaultLocale: "en"
通过选项elasticsearch.url来使得kibana连接elasticsearch。
脚本
可以采用批处理方式来一键启动ES和Kibana
@echo off
echo Starting Elasticsearch...
D:
cd D:\elasticsearch-6.0.0\bin
start elasticsearch.bat
echo Starting Kibana...
cd D:\kibana-6.0.0-windows-x86_64\bin
start kibana.bat
echo "This is the first dos program"
exit
Elasticsearch介绍
检索工作原理
基本组成
DSL(Domain Specified Language)
DSL:以极其高效的方式描述特定领域的对象、规则和运行方式的语言。
- 需要有特定的解释器与其配合。
- 高效简洁的领域语言,与通用语言相比能极大降级理解和使用难度,同时极大提高开发效率的语言。
- 能够描述特定领域的世界观和方法论的语言。
{
"bool": {
"must": { "term": { "folder": "inbox" }},
"must_not": { "term": { "tag": "spam" }},
"should": [
{ "term": { "starred": true }},
{ "term": { "unread": true }}
]
}
}
更多的实践
Elasticsearch和MySql
区别:
- Elasticsearch是面向文档的
- MySQL关系型数据库,具有事务性,而ES没有事务性
- ES没有外键约束,MySQL支持表与表之间的外键约束
- ES采用倒排索引,关系型数据库Mysql采用的是B+树索引
- 面对大数据量简单计算的时候ES的效率远高于Mysql传统数据库
Type 可以理解成关系数据库中Table。
之前的版本中,索引和文档中间还有个类型的概念,每个索引下可以建立多个类型,文档存储时需要指定index和type。从6.0.0开始单个索引中只能有一个类型,
7.0.0以后将将不建议使用,8.0.0 以后完全不支持。
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "Rejecting mapping update to [bigdata] as the final mapping would have more than 1 type: [product, item]"
}
],
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "Rejecting mapping update to [bigdata] as the final mapping would have more than 1 type: [product, item]"
},
"status": 400
}
Elasticsearch的强大之处就是可以***模糊查询***
Elasticsearch是专门做搜索的,就是为了解决上面所讲的问题而生的,换句话说:
- Elasticsearch对模糊搜索非常擅长(搜索速度很快)
- 从Elasticsearch搜索到的数据可以根据评分过滤掉大部分的,只要返回评分高的给用户就好了(原生就支持排序)
- 没有那么准确的关键字也能搜出相关的结果(能匹配有相关性的记录)
整合
SpringBoot整合
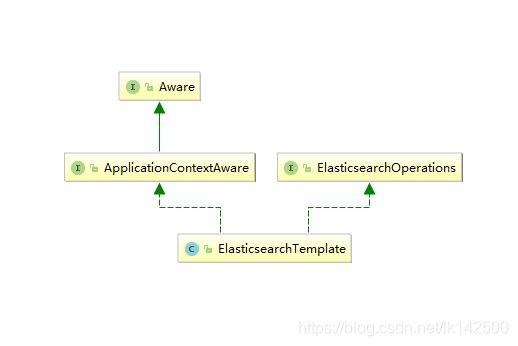
ElasticsearchTemplate类型
ElasticsearchTemplate许可的主要操作位于接口ElasticsearchOperations中,该类型源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2013-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.Client;
import org.elasticsearch.cluster.metadata.AliasMetaData;
import org.elasticsearch.common.Nullable;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.convert.ElasticsearchConverter;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.mapping.ElasticsearchPersistentEntity;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.*;
import org.springframework.data.util.CloseableIterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* ElasticsearchOperations
*
* @author Rizwan Idrees
* @author Mohsin Husen
* @author Kevin Leturc
*/
public interface ElasticsearchOperations {
/**
* @return Converter in use
*/
ElasticsearchConverter getElasticsearchConverter();
/**
* @return elasticsearch client
*/
Client getClient();
/**
* Create an index for a class
*
* @param clazz
* @param
*/
<T> boolean createIndex(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Create an index for given indexName
*
* @param indexName
*/
boolean createIndex(String indexName);
/**
* Create an index for given indexName and Settings
*
* @param indexName
* @param settings
*/
boolean createIndex(String indexName, Object settings);
/**
* Create an index for given class and Settings
*
* @param clazz
* @param settings
*/
<T> boolean createIndex(Class<T> clazz, Object settings);
/**
* Create mapping for a class
*
* @param clazz
* @param
*/
<T> boolean putMapping(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Create mapping for a given indexName and type
*
* @param indexName
* @param type
* @param mappings
*/
boolean putMapping(String indexName, String type, Object mappings);
/**
* Create mapping for a class
*
* @param clazz
* @param mappings
*/
<T> boolean putMapping(Class<T> clazz, Object mappings);
/**
* Get mapping for a class
*
* @param clazz
* @param
*/
<T> Map getMapping(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Get mapping for a given indexName and type
*
* @param indexName
* @param type
*/
Map getMapping(String indexName, String type);
/**
* Get settings for a given indexName
*
* @param indexName
*/
Map getSetting(String indexName);
/**
* Get settings for a given class
*
* @param clazz
*/
<T> Map getSetting(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return the first returned object
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return the first matching object
*/
<T> T queryForObject(GetQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return the first returned object using custom mapper
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @param mapper
* @return the first matching object
*/
<T> T queryForObject(GetQuery query, Class<T> clazz, GetResultMapper mapper);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return the first returned object
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return the first matching object
*/
<T> T queryForObject(CriteriaQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return the first returned object
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return the first matching object
*/
<T> T queryForObject(StringQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link Page}
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> Page<T> queryForPage(SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link Page} using custom mapper
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> Page<T> queryForPage(SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz, SearchResultMapper mapper);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link Page}
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> Page<T> queryForPage(CriteriaQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link Page}
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> Page<T> queryForPage(StringQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link Page} using custom mapper
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> Page<T> queryForPage(StringQuery query, Class<T> clazz, SearchResultMapper mapper);
/**
* Executes the given {@link CriteriaQuery} against elasticsearch and return result as {@link CloseableIterator}.
*
* Returns a {@link CloseableIterator} that wraps an Elasticsearch scroll context that needs to be closed in case of error.
*
* @param element return type
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
* @since 1.3
*/
<T> CloseableIterator<T> stream(CriteriaQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Executes the given {@link SearchQuery} against elasticsearch and return result as {@link CloseableIterator}.
*
* Returns a {@link CloseableIterator} that wraps an Elasticsearch scroll context that needs to be closed in case of error.
*
* @param element return type
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
* @since 1.3
*/
<T> CloseableIterator<T> stream(SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Executes the given {@link SearchQuery} against elasticsearch and return result as {@link CloseableIterator} using custom mapper.
*
* Returns a {@link CloseableIterator} that wraps an Elasticsearch scroll context that needs to be closed in case of error.
*
* @param element return type
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @param mapper
* @return
* @since 1.3
*/
<T> CloseableIterator<T> stream(SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz, SearchResultMapper mapper);
/**
* Execute the criteria query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link List}
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> List<T> queryForList(CriteriaQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the string query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link List}
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> List<T> queryForList(StringQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the search query against elasticsearch and return result as {@link List}
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> List<T> queryForList(SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute the query against elasticsearch and return ids
*
* @param query
* @return
*/
<T> List<String> queryForIds(SearchQuery query);
/**
* return number of elements found by given query
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> long count(CriteriaQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* return number of elements found by given query
*
* @param query
* @return
*/
<T> long count(CriteriaQuery query);
/**
* return number of elements found by given query
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> long count(SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* return number of elements found by given query
*
* @param query
* @return
*/
<T> long count(SearchQuery query);
/**
* Execute a multiGet against elasticsearch for the given ids
*
* @param searchQuery
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
<T> LinkedList<T> multiGet(SearchQuery searchQuery, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Execute a multiGet against elasticsearch for the given ids with MultiGetResultMapper
*
* @param searchQuery
* @param clazz
* @param multiGetResultMapper
* @return
*/
<T> LinkedList<T> multiGet(SearchQuery searchQuery, Class<T> clazz, MultiGetResultMapper multiGetResultMapper);
/**
* Index an object. Will do save or update
*
* @param query
* @return returns the document id
*/
String index(IndexQuery query);
/**
* Partial update of the document
*
* @param updateQuery
* @return
*/
UpdateResponse update(UpdateQuery updateQuery);
/**
* Bulk index all objects. Will do save or update
*
* @param queries
*/
void bulkIndex(List<IndexQuery> queries);
/**
* Bulk update all objects. Will do update
*
* @param queries
*/
void bulkUpdate(List<UpdateQuery> queries);
/**
* Delete the one object with provided id
*
* @param indexName
* @param type
* @param id
* @return documentId of the document deleted
*/
String delete(String indexName, String type, String id);
/**
* Delete all records matching the criteria
*
* @param clazz
* @param criteriaQuery
*/
<T> void delete(CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Delete the one object with provided id
*
* @param clazz
* @param id
* @return documentId of the document deleted
*/
<T> String delete(Class<T> clazz, String id);
/**
* Delete all records matching the query
*
* @param clazz
* @param query
*/
<T> void delete(DeleteQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Delete all records matching the query
*
* @param query
*/
void delete(DeleteQuery query);
/**
* Deletes an index for given entity
*
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> boolean deleteIndex(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Deletes an index for given indexName
*
* @param indexName
* @return
*/
boolean deleteIndex(String indexName);
/**
* check if index is exists
*
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> boolean indexExists(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* check if index is exists for given IndexName
*
* @param indexName
* @return
*/
boolean indexExists(String indexName);
/**
* check if type is exists in an index
*
* @param index
* @param type
* @return
*/
boolean typeExists(String index, String type);
/**
* refresh the index
*
* @param indexName
*
*/
void refresh(String indexName);
/**
* refresh the index
*
* @param clazz
*
*/
<T> void refresh(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Returns scrolled page for given query
*
* @param query The search query.
* @param scrollTimeInMillis The time in millisecond for scroll feature
* {@link org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequestBuilder#setScroll(org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue)}.
* @param clazz The class of entity to retrieve.
* @return The scan id for input query.
*/
<T> Page<T> startScroll(long scrollTimeInMillis, SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Returns scrolled page for given query
*
* @param query The search query.
* @param scrollTimeInMillis The time in millisecond for scroll feature
* {@link org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequestBuilder#setScroll(org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue)}.
* @param mapper Custom impl to map result to entities
* @return The scan id for input query.
*/
<T> Page<T> startScroll(long scrollTimeInMillis, SearchQuery query, Class<T> clazz, SearchResultMapper mapper);
/**
* Returns scrolled page for given query
*
* @param criteriaQuery The search query.
* @param scrollTimeInMillis The time in millisecond for scroll feature
* {@link org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequestBuilder#setScroll(org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue)}.
* @param clazz The class of entity to retrieve.
* @return The scan id for input query.
*/
<T> Page<T> startScroll(long scrollTimeInMillis, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Returns scrolled page for given query
*
* @param criteriaQuery The search query.
* @param scrollTimeInMillis The time in millisecond for scroll feature
* {@link org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequestBuilder#setScroll(org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue)}.
* @param mapper Custom impl to map result to entities
* @return The scan id for input query.
*/
<T> Page<T> startScroll(long scrollTimeInMillis, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, Class<T> clazz, SearchResultMapper mapper);
<T> Page<T> continueScroll(@Nullable String scrollId, long scrollTimeInMillis, Class<T> clazz);
<T> Page<T> continueScroll(@Nullable String scrollId, long scrollTimeInMillis, Class<T> clazz, SearchResultMapper mapper);
/**
* Clears the search contexts associated with specified scroll ids.
*
* @param scrollId
*
*/
<T> void clearScroll(String scrollId);
/**
* more like this query to search for documents that are "like" a specific document.
*
* @param query
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> Page<T> moreLikeThis(MoreLikeThisQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* adding new alias
*
* @param query
* @return
*/
Boolean addAlias(AliasQuery query);
/**
* removing previously created alias
*
* @param query
* @return
*/
Boolean removeAlias(AliasQuery query);
/**
* get all the alias pointing to specified index
*
* @param indexName
* @return
*/
List<AliasMetaData> queryForAlias(String indexName);
<T> T query(SearchQuery query, ResultsExtractor<T> resultsExtractor);
ElasticsearchPersistentEntity getPersistentEntityFor(Class clazz);
}
POM
在POM文件中,需要引入spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearchartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>releasesid>
<name>Releasesname>
<url>http://localhost:8081//repository/maven-central/url>
<releases>
<enabled>trueenabled>
releases>
repository>
repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>releasesid>
<name>Releasesname>
<url>http://localhost:8081//repository/maven-central/url>
<releases>
<enabled>trueenabled>
releases>
pluginRepository>
pluginRepositories>
配置项application.yml
spring:
data:
elasticsearch:
cluster-name: my-application
cluster-nodes: 127.0.0.1:9300
9300为Java客户端使用的端口,9200为elasticsearch使用的端口
在Spring Boot中的自动装配工作时,这两个配置项映射的类型为
/**
* Configuration properties for Elasticsearch.
*
* @author Artur Konczak
* @author Mohsin Husen
* @since 1.1.0
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.data.elasticsearch")
public class ElasticsearchProperties {
/**
* Elasticsearch cluster name.
*/
private String clusterName = "elasticsearch";
/**
* Comma-separated list of cluster node addresses.
*/
private String clusterNodes;
在此简要论述Spring Boot的自动装配原理:
而ElasticsearchTemplate自动装配到ioc容器中使用了如下的类型
- ElasticSearchProperties
- ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration
- ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration
- ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration
ElasticsearchTemplate组件生成位于ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration
ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration类型声明如下:
/**
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
* Auto-configuration} for Elasticsearch.
*
* @author Artur Konczak
* @author Mohsin Husen
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @since 1.1.0
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Client.class, TransportClientFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.data.elasticsearch", name = "cluster-nodes", matchIfMissing = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ElasticsearchProperties.class)
public class ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration {
private final ElasticsearchProperties properties;
public ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration(ElasticsearchProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
实体类Document
在使用ElasticsearchTemplate时,必须存在由**@Document**标注的实体类,来映射索引库中某类型的映射结构
package com.example.entity;
import lombok.*;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
/**
* @author songquanheng
* @Time: 2020/2/27-16:58
*/
@Accessors(chain = true)
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
@ToString
@Document(indexName = "bigdata", type = "product")
@Data
public class Product {
@Id
private String id;
private String name;
private String author;
private String version;
private int age;
}
实体类要注意**@Document**标注的作用为文档,在该实体类上,可以指定字段的类型、分析器、该实体类所属的索引库、类型等重要信息。
@Document(indexName = "item",type = "docs",shards = 1,replicas = 0)
public class Item {
@Id
private Long id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text,analyzer = "ik_max_word")
private String title;
@Field(type=FieldType.Keyword)
private String category;
@Field(type=FieldType.Keyword)
private String brand;
@Field(type=FieldType.Double)
private Double price;
@Field(index = false,type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String images;
}
另外,要注意FieldType枚举中keyword和text的区别
- text类型:会分词,先把对象进行分词处理,然后再再存入到es中。
当使用多个单词进行查询的时候,当然查不到已经分词过的内容!
- keyword:不分词,没有把es中的对象进行分词处理,而是存入了整个对象!
这时候当然可以进行完整地查询!默认是256个字符!
Spring Data通过注解来声明字段的映射属性,有下面的三个注解:
@Document 作用在类,标记实体类为文档对象,一般有两个属性
indexName:对应索引库名称
type:对应在索引库中的类型
shards:分片数量,默认5
replicas:副本数量,默认1
@Id 作用在成员变量,标记一个字段作为id主键
@Field 作用在成员变量,标记为文档的字段,并指定字段映射属性:
type:字段类型,是枚举:FieldType,可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等
text:存储数据时候,会自动分词,并生成索引
keyword:存储数据时候,不会分词建立索引
Numerical:数值类型,分两类
基本数据类型:long、interger、short、byte、double、float、half_float
浮点数的高精度类型:scaled_float
需要指定一个精度因子,比如10或100。elasticsearch会把真实值乘以这个因子后存储,取出时再还原。
Date:日期类型
elasticsearch可以对日期格式化为字符串存储,但是建议我们存储为毫秒值,存储为long,节省空间。
index:是否索引,布尔类型,默认是true
store:是否存储,布尔类型,默认是false
analyzer:分词器名称,这里的ik_max_word即使用ik分词器
JUnit测试
package com.example;
import com.example.entity.Item;
import com.example.entity.Product;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.IdsQueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.NativeSearchQuery;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.SearchQuery;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
/**
* @author songquanheng
* @Time: 2020/2/27-12:12
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ElasticsearchTest {
@Autowired
ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate;
@Test
public void indexExists() {
assertTrue(elasticsearchTemplate.indexExists("bigdata"));
}
/**
* 在elasticsearch添加索引
*/
@Test
public void createIndex() {
boolean res = elasticsearchTemplate.createIndex(Item.class);
assertTrue(elasticsearchTemplate.indexExists("bigdata"));
}
@Test
public void deleteIndex() {
boolean smalldata = elasticsearchTemplate.deleteIndex(Item.class);
}
/**
* 检索
*/
@Test
public void query() {
QueryBuilder queryBuilder = new IdsQueryBuilder().addIds("1", "2");
SearchQuery query = new NativeSearchQuery(queryBuilder);
List<Product> products = elasticsearchTemplate.queryForList(query, Product.class);
products.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
实战
创建索引
elasticsearchTemplate
/**
* Create an index for a class
*
* @param clazz
* @param
*/
<T> boolean createIndex(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Create an index for given indexName
*
* @param indexName
*/
boolean createIndex(String indexName);
/**
* Create an index for given indexName and Settings
*
* @param indexName
* @param settings
*/
boolean createIndex(String indexName, Object settings);
/**
* Create an index for given class and Settings
*
* @param clazz
* @param settings
*/
<T> boolean createIndex(Class<T> clazz, Object settings);
实例
/**
* 在elasticsearch添加索引
*/
@Test
public void createIndex() {
elasticsearchTemplate.createIndex(Product.class);
assertTrue(elasticsearchTemplate.indexExists("bigdata"));
}
curl
使用curl创建索引的请求如下:
curl -XPUT "http://localhost:9200/product"
在es中,索引库必须唯一存在,这意味着,如果用户想要创建两个相同的索引库,es会报错:
删除索引
Elasticsearch可以删除索引,但是不能像数据库一样直接删除type,如果想要删除type有两种方式
a.删除index,这样会把所有该index的所有的type都会删除
b.重新创建一个新的type,使用新的type,这种方式安全一点
如果一个index下面只有一个type,那么就可以直接删除index
如果一个index下面有多个type ,那么删除一个type的时候就要考虑到其他的type
elasticsearchTemplate
/**
* Deletes an index for given entity
*
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> boolean deleteIndex(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Deletes an index for given indexName
*
* @param indexName
* @return
*/
boolean deleteIndex(String indexName);
/**
* check if index is exists
*
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> boolean indexExists(Class<T> clazz);
实例
/**
* Deletes an index for given entity
*
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
<T> boolean deleteIndex(Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Deletes an index for given indexName
*
* @param indexName
* @return
*/
boolean deleteIndex(String indexName);
curl
删除索引的curl命令表达为
curl -XDELETE "http://localhost:9200/bigdata"
插入文档
elasticsearchTemplate
在向索引库插入文档时,主要是调用elasticsearchTemplate方法的index操作
/**
* Index an object. Will do save or update
*
* @param query
* @return returns the document id
*/
String index(IndexQuery query);
实际操练:
/**
* 添加文档到索引中
*/
@Test
public void addDocuments() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Product product = Product.of()
.setAge(i + 5)
.setAuthor(String.format("刘德华%s", i))
.setId(String.valueOf(i))
.setName("iPad series" + i);
IndexQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new IndexQueryBuilder()
.withId(product.getId())
.withObject(product);
String index = elasticsearchTemplate.index(queryBuilder.build());
System.out.println(index);
}
}
另外,可以使用es提供的bulk操作批量添加文档。
/**
* Bulk index all objects. Will do save or update
*
* @param queries
*/
void bulkIndex(List<IndexQuery> queries);
curl请求
保存时不带id,id会自动生成
curl -XPOST "http://localhost:9200/bigdata/product" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"name": "pencial",
"author": "sqh",
"version": "2.3.5",
"age":1
}'
可以携带id保存,格式如下:
curl -XPOST "http://localhost:9200/bigdata/product/5" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"name": "Lenovo",
"author": "sqh",
"version": "4.5",
"age":7
}'
响应结果如下:
{
"_index": "bigdata",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "5",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 9
}
如果上述同样的请求再连续发两次,则可以得到如下的响应:
{
"_index": "bigdata",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "5",
"_version": 3,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 3,
"_primary_term": 9
}
上述要关注的字段包括**“result”: “updated”、"_version": 3**、"_id": “5”,这表示对于同一个_id文档的操作,elasticsearch会记录对于该文档的操作,并且记录版本信息,是一种内部管理措施。
更新文档
在es中,文档是不可变的,它们不能被更改,只能被替换。
es中更新文档有两种策略
- 脚本更新
- 局部更新文档
elasticsearchTemplate
在ElasticsearchTemplate类中,用来更新文档的操作为
/**
* Partial update of the document
* 文档的局部更新
* @param updateQuery
* @return
*/
UpdateResponse update(UpdateQuery updateQuery);
/**
* Bulk update all objects. Will do update
*
* @param queries
*/
void bulkUpdate(List<UpdateQuery> queries);
更新之前,0号文档内容如下:
@Test
public void updateDoc() {
// 以doc的方式更新0号id
Product product = Product.of()
.setId("0")
.setName("易小川")
.setAge(53)
.setVersion("2.5");
// The number of object passed must be even but was [1]
// 如果采用doc(product)会报出如上的错误,必须把product的属性
// 平铺成key, value的形式
Map<String, String> update = new HashMap<>();
update.put("name", "易小川");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 0);
map.put("name", "易小川");
map.put("age", 53);
map.put("version", "2.5");
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest(BIGDATA, PRODUCT, "0")
.doc(map);
UpdateQuery updateQuery = new UpdateQueryBuilder().
withId("0")
.withIndexName(BIGDATA)
.withType(PRODUCT)
.withUpdateRequest(updateRequest)
.build();
UpdateResponse updateResponse = elasticsearchTemplate.update(updateQuery);
System.out.println(updateResponse);
}
curl
注意更新文档为POST请求。更新API还支持传递部分文档,该文档将合并到现有文档中(简单的递归合并,对象的内部合并,替换核心"键/值"和数组)。
curl -XPOST "http://localhost:9200/bigdata/product/0/_update" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"doc":{
"name": "狄仁杰"
}
}'
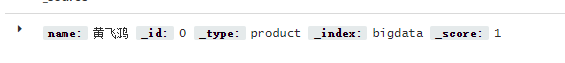
执行更新操作之后,通过kibana可以看到更新之后的结果为:
注意,更新操作不要使用如下的实践方式,通过PUT请求,会导致之前其他的字段删掉,而仅剩下此次操作的字段
curl -XPUT "http://localhost:9200/bigdata/product/0" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"name": "黄飞鸿"
}'
显然,这不是我们的本意。
删除文档
elasticsearchTemplate
删除文档有关的操作如下所示:
/**
* Delete the one object with provided id
*
* @param indexName
* @param type
* @param id
* @return documentId of the document deleted
*/
String delete(String indexName, String type, String id);
/**
* Delete all records matching the criteria
*
* @param clazz
* @param criteriaQuery
*/
<T> void delete(CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Delete the one object with provided id
*
* @param clazz
* @param id
* @return documentId of the document deleted
*/
<T> String delete(Class<T> clazz, String id);
/**
* Delete all records matching the query
*
* @param clazz
* @param query
*/
<T> void delete(DeleteQuery query, Class<T> clazz);
/**
* Delete all records matching the query
*
* @param query
*/
void delete(DeleteQuery query);
从上述的API可以看出,删除操作可以通过id来进行,亦或者通过DeleteQuery来删除符合条件的文档。
实操:
// 删除年纪从8到10的文档
@Test
public void delete() {
QueryBuilder queryBuilder = new RangeQueryBuilder("age")
.from(8)
.to(10);
DeleteQuery deleteQuery = new DeleteQuery();
deleteQuery.setIndex(BIGDATA);
deleteQuery.setType(PRODUCT);
deleteQuery.setQuery(queryBuilder);
elasticsearchTemplate.delete(deleteQuery);
}
操作执行之后,age属于[8, 10]的记录都被删除了。
curl请求
删除文档对应REST请求中的DELETE请求
curl -XDELETE "http://localhost:9200/bigdata/product/2"
如果能找到待删除的文档,则删除的响应类似如下所示:
{
"_index": "bigdata",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 4,
"_primary_term": 1
}
否则,意味着删除不存在的文档,则得到如下的响应:
{
"_index": "bigdata",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 1,
"result": "not_found",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 5,
"_primary_term": 1
}
"result":"not_found"
查询文档
Query DSL 是 elasticsearch 的核心,搜索方面的项目大部分时间都耗费在对查询结果的调优上。因此对 Query DSL 的理解越深入,越能节省项目时间,并给用户好的体验。
Elasticsearch提供基于JSON的完整查询DSL来定义查询。将Query DSL视为查询的AST(抽象语法树),由两种类型的子句组成:
-
叶子查询子句
- 叶查询子句中寻找一个特定的值在某一特定领域,如
match,term或range查询。这些查询可以自己使用。
- 叶查询子句中寻找一个特定的值在某一特定领域,如
-
复合查询子句
- 复合查询子句包装其他叶查询或复合查询,并用于以逻辑方式组合多个查询(例如
bool或dis_max查询),或更改其行为(例如constant_score查询)。
- 复合查询子句包装其他叶查询或复合查询,并用于以逻辑方式组合多个查询(例如
查询字句的行为取决于它在查询上下文还是过滤器上下文中使用。
- 查询上下文是有效每当查询子句被传递给一个
query参数,如query该参数search的API。 - 每当将查询子句传递到
filter参数(例如查询中的filter或must_not参数,bool查询中的filter参数constant_score或filter聚合)时, 过滤器上下文即有效。
Query DSL实例
- 该
title字段包含单词search。 - 该
content字段包含单词elasticsearch。 - 该
status字段包含确切的单词published。 - 该
publish_date字段包含从2015年1月1日开始的日期。
GET / _search { " query" :{
"布尔" :{
"必须" :[ { "匹配" :{ "标题" :"搜索" }},
{ " match" :{ " content" :" Elasticsearch" }}
]," filter" :[
{ " term" :{ " status" :" published" }},
{ " range" :{ " publish_date" :{ " gte" :" 2015-01-01" }}}
] } } }
elasticsearchTemplate
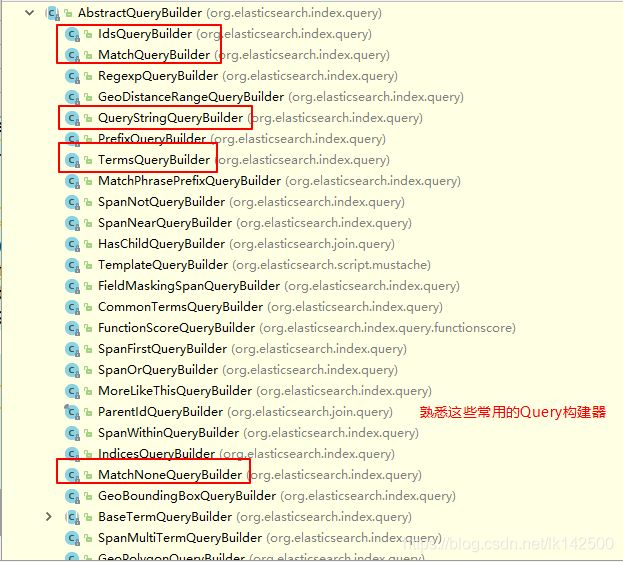
通过JavaAPI来操作ES与Query DSL一摸一样,只要能尽可能熟悉即可,可以说熟悉了DSL语言之后,es的操作和使用就算入门了。
常用的QueryBuilder如下图所示:
在构造Query语法树主要使用了NativeSearchQuery类,该类用来聚拢Query、Filter、Sort、以及用于高亮的HightLightBuilder。
public NativeSearchQuery(QueryBuilder query) {
this.query = query;
}
public NativeSearchQuery(QueryBuilder query, QueryBuilder filter) {
this.query = query;
this.filter = filter;
}
public NativeSearchQuery(QueryBuilder query, QueryBuilder filter, List<SortBuilder> sorts) {
this.query = query;
this.filter = filter;
this.sorts = sorts;
}
public NativeSearchQuery(QueryBuilder query, QueryBuilder filter, List<SortBuilder> sorts, HighlightBuilder.Field[] highlightFields) {
this.query = query;
this.filter = filter;
this.sorts = sorts;
this.highlightFields = highlightFields;
}
在查询过程中主要使用的类型继承体系如下图所示:
获取bigdata索引库下product类型的所有文档的Java代码如下:
// 用于获取所有的文档
@Test
public void queryAll() {
SearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQuery(new MatchAllQueryBuilder());
List<Product> products = elasticsearchTemplate.queryForList(searchQuery, Product.class);
products.forEach(System.out::println);
}
获取name中包含iPad,并且按照age降序排列
@Test
public void queryBySort() {
List<SortBuilder> sortBuilders = new ArrayList<>();
sortBuilders.add(SortBuilders.fieldSort("age").order(SortOrder.DESC));
SearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQuery(new MatchQueryBuilder("name", "iPad"), new MatchAllQueryBuilder(), sortBuilders);
List<Product> products = elasticsearchTemplate.queryForList(searchQuery, Product.class);
products.forEach(System.out::println);
}
以通配符的方式获取name中包含series1?的文档
@Test
public void queryBySort() {
List<SortBuilder> sortBuilders = new ArrayList<>();
sortBuilders.add(SortBuilders.fieldSort("age").order(SortOrder.DESC));
SearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQuery(new WildcardQueryBuilder("name", "series1?"), new MatchAllQueryBuilder(), sortBuilders);
List<Product> products = elasticsearchTemplate.queryForList(searchQuery, Product.class);
System.out.println(products.size());
products.forEach(System.out::println);
}
curl-DSL
查询年龄从11到13岁的记录
curl -XGET "http://localhost:9200/bigdata/product/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 13
}
}
}
}'
Elasticsearch提供了一种JSON样式的特定于域的语言,可用于执行查询。这称为查询DSL
查询类型字段包含经济的记录、记录排序以VideoSize字段降序排列,同时进行分页处理。
match_class_order_page = {
"query": {
"match": {
"class1": "经济"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"VideoSize": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"from": 1, # 从第几个数据开始
"size": 5 # 每页数据个数
}
多条件
must :: 多个查询条件的完全匹配,相当于 and。
must_not :: 多个查询条件的相反匹配,相当于 not。
should :: 至少有一个查询条件匹配, 相当于 or。
这些参数可以分别继承一个过滤条件或者一个过滤条件的数组
must_should = {
"query": {
"bool":{
"must":[
{
"match": {
"class1": "经济"
}
},
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"VideoSize": {
"gte": 3000,
"lte": 5000
}
}
}
},
}
}
返回指定字段的数据
all = {
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": ['id', "class1", "VioceSize"]
}
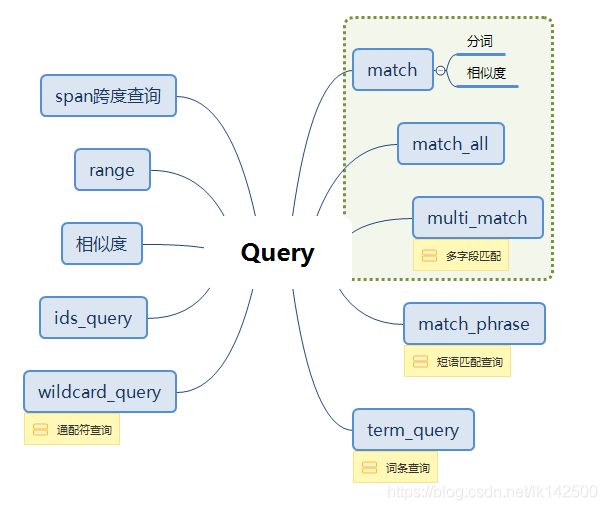
其他对于查询的笔记如下图所示:
查询的具体种类如下图所示:
分词
中文分词
- ik
- 庖丁解牛中文分词
总结
本文主要内容是梳理了ELK技术栈中ES的入门,核心的内容有:
- ES的应用场景、发展历史
- ES、Kibana的安装和配置
- ES Query DSL的阐述
- Spring Boot与ES集成。
- 通过curl来操作ES
希望为之后使用ES打下基础。