Mybatis 源码学习(七) 缓存的刷新
之前学习了mybatis的一级缓存和二级缓存。
那么当数据库数据有跟新的时候,缓存是如何被刷新的呢?
找到update的实现源码:
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}看来是在executor中清理的。
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms); //这里清空了二级缓存
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
dirty = true; // issue #524. Disable using cached data for this session
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
}public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
clearLocalCache();//这里清空一级缓存
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
} public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}一级缓存比较简单清晰,同一个sqlSession执行查询的时候缓存,再执行相同查的时候使用缓存,当执行修改操作的时候,直接刷新整个sqlSession的缓存(在Executer上的localCache)。
二级缓存的更新一直让我有点困惑,缓存是在MappedStatement上的,怎么能在修改的时候把其他的查询缓存清除呢,他们是在不同的MappedStatement上的啊?
先看查询的时候是怎么放到缓存的
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List list = (List) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate. query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate. query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) {
TransactionalCache txCache = transactionalCaches.get(cache);
if (txCache == null) {
txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache);
transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache);
}
return txCache;
}
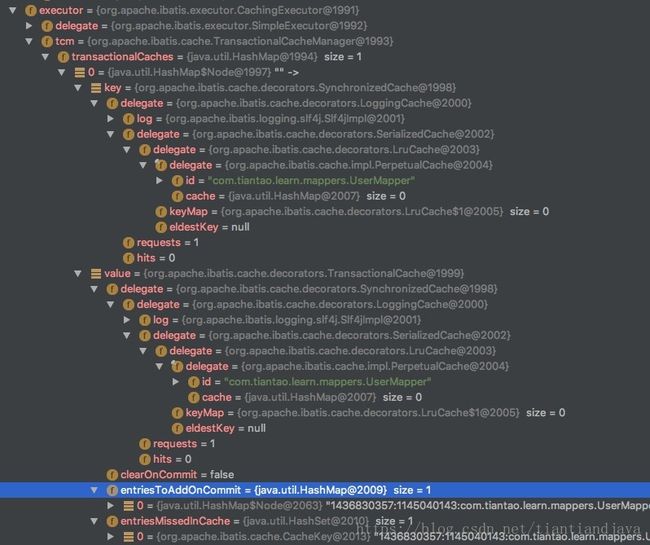
从以上的三个方法可以看到,是通过TransactionalCacheManager来放入缓存的。在放入mappedStatement的缓存同时,还被存入了executror下的tcm属性的transactionalCaches对象内容。这是有点绕。如下图所看到的,通过层层代理,最终看到id是mapper的名字。这样其他的SqlSession在查询的时候先查缓存中是否已经存在。刷新的时候也是按照mapper来刷新的。大功告成!