Docker ~ 从入门到实践
文章目录
- Docker
- 前言
- 一、虚拟机与Docker
- 1、虚拟机
- 2、Docker
- 二、Docker安装
- 三、Docker使用的三个层面
- Image
- Container
- Registry
- 四、Docker原理
- 1、Docker的基本组成
- 2、Docker依赖的Linux内核特性
- 3、Docker的隔离能力
- 五、Docker的优缺点
- 六、关于Docker禁用
- 七、Docker命令
- Dockerfile命令
- CMD 与 ENTRYPOINT
- Docker-cli命令
- docker
- docker build
- docker rmi
- docker create
- docker run
- docker ps
- docker logs
- docker exec
- docker start
- docker stop
- docker restart
- docker rm
Docker
Build once, Run anywhere
前言
现在云计算其底层的基石就是虚拟机技术,云计算厂商买回来一堆硬件搭建好数据中心后使用虚拟机技术就可以将硬件资源进行切分了,比如可以切分出100台虚拟机,这样就可以卖给很多用户
Docker 自2013年以来非常火热,无论是从 Github 上的代码活跃度,还是 Redhat 在 RHEL6.5 中集成对 Docker
的支持, 就连 Google 的 Compute Engine 也支持 Docker。京东 618,使用了 15 万个 Docker 实例,并将所有业务全部容器化。
腾讯和阿里也早在 2015 年就实现了万台 Docker 应用实践。
归根结底还是依赖于 Docker的简单部署,解放运维。
Docker 最初是在 Ubuntu 12.04 上开发实现的;Red Hat 则从 RHEL 6.5 开始对 Docker 进行支持;Google 也在其 PaaS 产品中广泛应用 Docker。
一、虚拟机与Docker
Docker支持将应用打包进一个可以移植的容器中,重新定义了应用开发,测试,部署上线的过程,核心理念就是 Build once, Run anywhere。典型应用场景是开发运维上提供持续集成和持续部署的服务
1)标准化应用发布,docker容器包含了运行环境和可执行程序,可以跨平台和主机使用;
2)节约时间,快速部署和启动,VM启动一般是分钟级,docker容器启动是秒级;
3)方便构建基于SOA架构或微服务架构的系统,通过服务编排,更好的松耦合;
4)节约成本,以前一个虚拟机至少需要几个G的磁盘空间,docker容器可以减少到MB级;
5)方便持续集成,通过与代码进行关联使持续集成非常方便;
6)可以作为集群系统的轻量主机或节点,在IaaS平台上,已经出现了CaaS,通过容器替代原来的主机。
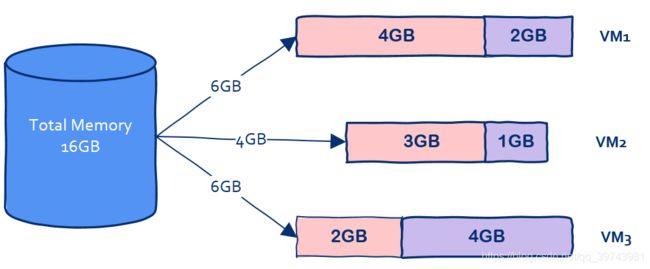
1、虚拟机
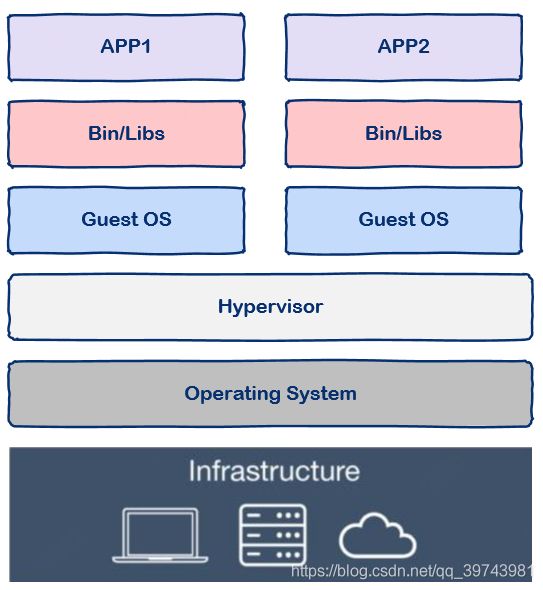
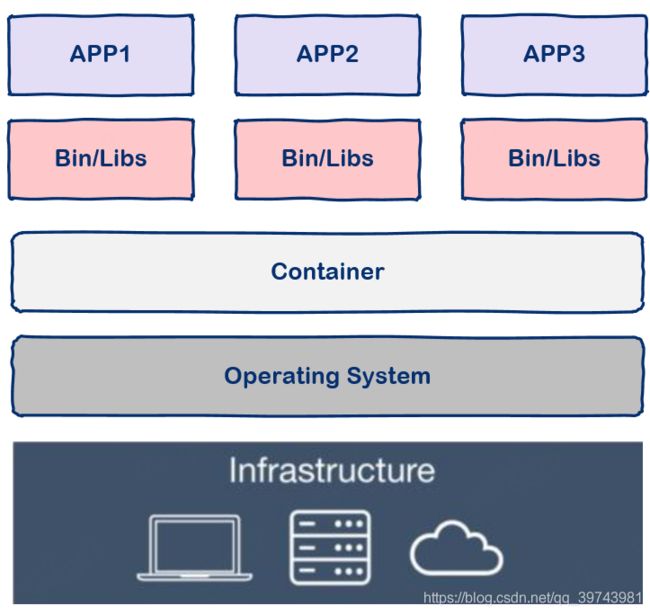
2、Docker
二、Docker安装
RedHat/CentOS
Docker 要求 CentOS 系统的内核版本高于 3.10 ,查看本页面的前提条件来验证你的 CentOS 版本是否支持。
yum -y install dockerUbuntu
apt-get -y install docker-ceWindow 10 专业版直接下载安装包安装,其他版本需要做些配置
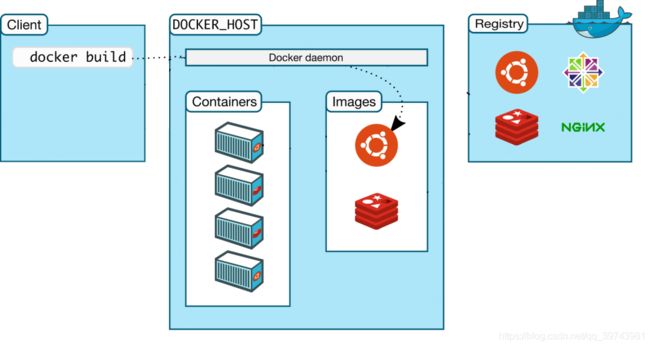
三、Docker使用的三个层面
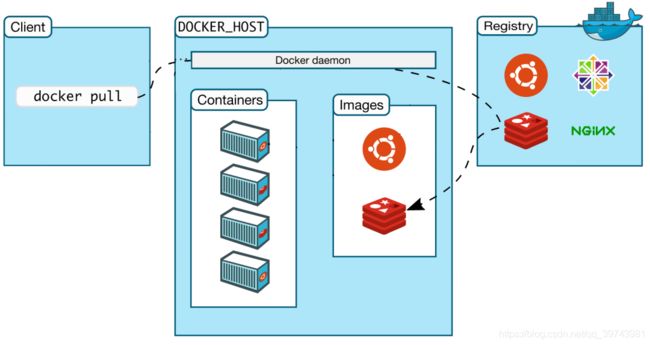
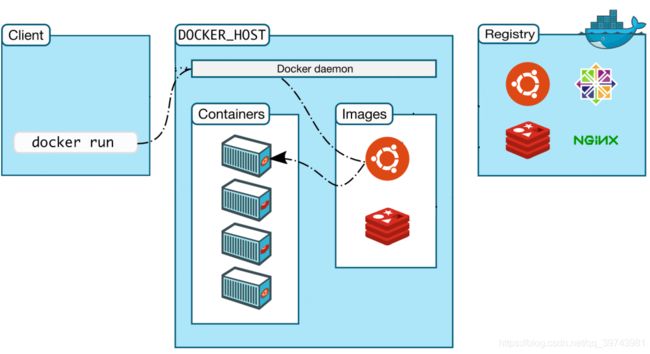
Image
Container
Registry
- 私有仓库
- 共有仓库
四、Docker原理
1、Docker的基本组成
- docker client客户端
- docker daemon守护进程
- docker image 镜像
- docker container 容器
- docker registry 仓库
2、Docker依赖的Linux内核特性
- Namespaces 命名空间
- PID(Process ID) 进程ID
- NET(Network) 管理网络接口
- IPC(InterProcess Communication) 管理跨进程通信的访问
- MNT(Mount) 管理挂载点
- UTS(Unix TimeSharing System) 隔离内核和版本标识
- Control groups (cgroups)控制组,cgroups为每种可以控制的资源定义了一个子系统。典型的子系统介绍如下:
- cpu 子系统,主要限制进程的 cpu 使用率。
- cpuacct 子系统,可以统计 cgroups 中的进程的 cpu 使用报告。
- cpuset 子系统,可以为 cgroups 中的进程分配单独的 cpu 节点或者内存节点。
- memory 子系统,可以限制进程的 memory 使用量。
- blkio 子系统,可以限制进程的块设备 io。
- devices 子系统,可以控制进程能够访问某些设备。
- net_cls 子系统,可以标记 cgroups 中进程的网络数据包,然后可以使用 tc 模块(traffic control)对数据包进行控制。
- freezer 子系统,可以挂起或者恢复 cgroups 中的进程。
- ns 子系统,可以使不同 cgroups 下面的进程使用不同的 namespace。
3、Docker的隔离能力
- 文件系统隔离(每个容器都有自己的文件系统)
- 进程隔离(每个容器都运行在自己的进程环境中)
- 网络隔离(容器间的虚拟网络接口和IP地址都是分开的)
- 资源隔离和分组(使用cgroup将CPU和内存之类的资源独立分配给每个Docker容器)
五、Docker的优缺点
1、交付物标准化
Docker是软件工程领域的“标准化”交付组件,最恰到好处的类比是“集装箱”。
集装箱将零散、不易搬运的大量物品封装成一个整体,集装箱更重要的意义在于它提供了一种通用的封装货物的标准,卡车、火车、货轮、桥吊等运输或搬运工具采用此标准,隧道、桥梁等也采用此标准。以集装箱为中心的标准化设计大大提高了物流体系的运行效率。
传统的软件交付物包括:应用程序、依赖软件安装包、配置说明文档、安装文档、上线文档等非标准化组件。Docker的标准化交付物称为“镜像”,它包含了应用程序及其所依赖的运行环境,大大简化了应用交付的模式。
2、一次构建,多次交付
类似于集装箱的“一次装箱,多次运输”,Docker镜像可以做到“一次构建,多次交付”。当涉及到应用程序多副本部署或者应用程序迁移时,更能体现Docker的价值。
3、应用隔离
集装箱可以有效做到货物之间的隔离,使化学物品和食品可以堆砌在一起运输。Docker可以隔离不同应用程序之间的相互影响,但是比虚拟机开销更小。
六、关于Docker禁用
近日知名开源容器引擎Docker引起关注,各大技术自媒体纷纷发文表示Docker被禁止使用了。这是为什么呢?原来Docker公司最新的服务条款 8 月 13 日生效。条款申明,Docker公司提供的服务,禁止美国“实体清单”上的实体使用。看上去像是真的不能再使用Docker了,但是事实上真的不能再使用Docker了吗?
目前中国 IT 行业被美国政府列入贸易管制“实体清单”的企业包括华为、商汤科技、依图、旷视、海康威视、科大讯飞、奇虎
360、东方网力、云从科技、中科曙光与海光等。还有一些科研院校包括国防科大、北航、西工大、电子科大、哈尔滨工程大学、哈尔滨工业大学、北京计算机科学研究中心、北京高压科学研究中心等等。目前没有包括阿里巴巴、腾讯、百度这三家国内份额较大的云厂商。也就是说,依据Docker公司所谓的条款上述清单列出的企业才会被禁止使用,未列的企业目前不会被限制使用。如果你所在的企业存在被列入的风险,也是要谨慎考虑评估的。如果你是一般的不知名企业的话,这事跟你一毛钱关系也没有。
就算你所在的公司被列入了所谓的“实体清单”不能用了,也不必担心。其实Docker目前的体系是这样的,主要分为三大部分:一是商业化的DockerEE,是不开源的,而且是付费的,由Docker公司来维护;二是开源免费的DockerCE,由社区维护;三是DockerHub,这是Docker公司提供的公共镜像存储服务,可以把它看做Docker版的GitHub,是不开源的,由Docker公司说了算。关于DockerCE和DockerEE的关系有点类似Java中的Oracle JDK和Open JDK,这样就好理解了。
本次的条款针对的是DockerEE和DockerHub两款产品,DockerCE并不受影响。平常开发者在网上看到的教程基本都是DockerCE相关的,所以不必惊慌。同时作为“实体清单”的大部分企业的开发能力来说完全能够从开源的DockerCE进行fork一个自己的分支来绕开所谓的条款,一个自己享有知识产权的产品自己当然有完全的使用权。所以只要你所在的公司没有使用DockerEE和DockerHub,即使在“清单”之内又能奈我何?
七、Docker命令
Dockerfile命令
-
FROM
FROM nginx -
MAINTAINER
-
LABEL
LABEL <key>=<value> <key>=<value> <key>=<value> ...设置镜像元数据
-
ENV
ENV <key> <value> ENV <key1>=<value1> <key2>=<value2>...设置环境变量,定义了环境变量,那么在后续的指令中,就可以使用这个环境变量。构建命令 docker run/create 中可以用 -e/–env <参数名>=<值> 来覆盖。
-
ARG
ARG <参数名>[=<默认值>]构建参数,与 ENV 作用一至。不过作用域不一样。ARG 设置的环境变量仅对 Dockerfile 内有效,也就是说只有 docker build 的过程中有效,构建好的镜像内不存在此环境变量。构建命令 docker build 中可以用 --build-arg <参数名>=<值> 来覆盖。
-
WORKDIR
WORKDIR <工作目录路径>指定工作目录。用 WORKDIR 指定的工作目录,会在构建镜像的每一层中都存在。(WORKDIR 指定的工作目录,必须是提前创建好的)。
docker build 构建镜像过程中的,每一个 RUN 命令都是新建的一层。只有通过 WORKDIR 创建的目录才会一直存在。
-
VOLUME
VOLUME ["<路径1>", "<路径2>"...] VOLUME <路径>定义匿名数据卷。在启动容器时忘记挂载数据卷,会自动挂载到匿名卷。
作用:避免重要的数据,因容器重启而丢失,这是非常致命的。
-
ADD
ADD [--chown=<user>:<group>] <源路径1>... <目标路径> ADD [--chown=<user>:<group>] ["<源路径1>",... "<目标路径>"]ADD 指令和 COPY 的使用格式一致(同样需求下,官方推荐使用 COPY)。功能也类似,不同之处如下:
- ADD 的优点:在执行 <源文件> 为 tar 压缩文件的话,压缩格式为 gzip, bzip2 以及 xz 的情况下,会自动复制并解压到 <目标路径>。
- ADD 的缺点:在不解压的前提下,无法复制 tar 压缩文件。会令镜像构建缓存失效,从而可能会令镜像构建变得比较缓慢。具体是否使用,可以根据是否需要自动解压来决定。
-
COPY
复制指令,从上下文目录中复制文件或者目录到容器里指定路径。
COPY [--chown=<user>:<group>] <源路径1>... <目标路径> COPY [--chown=<user>:<group>] ["<源路径1>",... "<目标路径>"]ADD命令和 COPY 命令在很大层度上功能是一样的。但是 COPY 语义更加直接,所以我们推荐尽量使用 COPY 命令。唯一例外的是 ADD 命令自带解压功能,如果需要拷贝并解压一个文件到镜像中,那么我们可以使用 ADD 命令。除此之外,我们都推荐使用 COPY 命令。
-
RUN
# shell 格式 # <命令行命令> 等同于,在终端操作的 shell 命令。 RUN <命令行命令 > # exec 格式: # RUN ["./test.php", "dev", "offline"] 等价于 RUN ./test.php dev offline # Dockerfile 的指令每执行一次都会在 docker 上新建一层。所以过多无意义的层,会造成镜像膨胀过大 # 在使用RUN命令时,多使用&&符减少镜像层 RUN ["可执行文件", "参数1", "参数2"] -
CMD
CMD <shell 命令> CMD ["<可执行文件或命令>","" ,"" ,...] CMD ["" ,"" ,...] # 该写法是为 ENTRYPOINT 指令指定的程序提供默认参数 # 推荐使用第二种格式,执行过程比较明确。第一种格式实际上在运行的过程中也会自动转换成第二种格式运行,并且默认可执行文件是 sh。作用:为启动的容器指定默认要运行的程序,程序运行结束,容器也就结束。CMD 指令指定的程序可被 docker run 命令行参数中指定要运行的程序所覆盖。
类似于 RUN 指令,用于运行程序,但二者运行的时间点不同:
- CMD 在docker run 时运行。
- RUN 是在 docker build。
注意:如果 Dockerfile 中如果存在多个 CMD 指令,仅最后一个生效。
-
ENTRYPOINT
ENTRYPOINT <shell 命令> ENTRYPOINT ["" ,"" ,"" ,...]类似于 CMD 指令,但其不会被 docker run 的命令行参数指定的指令所覆盖,而且这些命令行参数会被当作参数送给 ENTRYPOINT 指令指定的程序。
但是, 如果运行 docker run 时使用了 --entrypoint 选项,此选项的参数可当作要运行的程序覆盖 ENTRYPOINT 指令指定的程序。
优点:在执行 docker run 的时候可以指定 ENTRYPOINT 运行所需的参数。
注意:如果 Dockerfile 中如果存在多个 ENTRYPOINT 指令,仅最后一个生效。
-
EXPOSE
EXPOSE <port> [<port>/<protocol>...]该
EXPOSE指令通知Docker容器在运行时监听指定的网络端口。您可以指定端口是侦听TCP还是UDP,如果未指定协议,则默认值为TCP。该
EXPOSE指令实际上并未发布端口。它充当构建映像的人与运行容器的人之间的一种文档类型,有关打算发布哪些端口的信息。要在运行容器时实际发布端口,请使用-p标记ondocker run发布和映射一个或多个端口,或者使用-P标记发布所有公开的端口并将它们映射到随机端口作用:
- 帮助镜像使用者理解这个镜像服务的守护端口,以方便配置映射。
- 在运行时使用随机端口映射时,也就是 docker run -P 时,会自动随机映射 EXPOSE 的端口。
-
HEALTHCHECK
HEALTHCHECK [选项] CMD <命令>:设置检查容器健康状况的命令 HEALTHCHECK NONE:如果基础镜像有健康检查指令,使用这行可以屏蔽掉其健康检查指令用于指定某个程序或者指令来监控 docker 容器服务的运行状态。
-
ONBUILD
ONBUILD <其它指令>用于延迟构建命令的执行。简单的说,就是 Dockerfile 里用 ONBUILD 指定的命令,在本次构建镜像的过程中不会执行(假设镜像为
test-build)。当有新的 Dockerfile 使用了之前构建的镜像 FROM test-build ,这是执行新镜像的
Dockerfile 构建时候,会执行 test-build 的 Dockerfile 里的 ONBUILD 指定的命令。 -
USER
USER <用户名>[:<用户组>]用于指定执行后续命令的用户和用户组,这边只是切换后续命令执行的用户(用户和用户组必须提前已经存在)。
-
SHELL
-
STOPSIGNAL
# user ASUS 2020.07.26 22:12
# 依赖镜像
#FROM mysql:5.7
#FROM redis:5.0
#FROM rabbitmq:management
FROM openjdk:8u252
# 创建者信息(已废弃)
MAINTAINER swyan<[email protected]>
LABEL "com.example.vendor"="ACME Incorporated"
LABEL com.example.label-with-value="foo"
LABEL maintainer="swyan<[email protected]>"
LABEL version="1.0"
LABEL description="This text illustrates \
that label-values can span multiple lines."
# 设置环境变量,定义了环境变量,那么在后续的指令中,就可以使用这个环境变量。构建命令 docker run/create 中可以用 -e <参数名>=<值> 来覆盖。
ENV APP cloud-memo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
# 构建参数,与 ENV 作用一至。不过作用域不一样。ARG 设置的环境变量仅对 Dockerfile 内有效,也就是说只有 docker build 的过程中有效,构建好的镜像内不存在此环境变量。构建命令 docker build 中可以用 --build-arg <参数名>=<值> 来覆盖。
ARG PORT 123456
# 上下文路径
WORKDIR /swyan/app
# 定义匿名数据卷。在启动容器时忘记挂载数据卷,会自动挂载到匿名卷。
# VOLUME ["<路径1>", "<路径2>"...]
# VOLUME <路径>
VOLUME /swyan/app
# 复制(解压)宿主机文件到容器
ADD start.sh /swyan/app/start.sh
ADD ["start.sh","/swyan/app/start.sh"]
# 复制指令,从上下文目录中复制文件或者目录到容器里指定路径
COPY $APP /swyan/app/cloud-memo.jar
# 镜像构建过程中运行的命令
RUN pwd && free -m
# 容器启动后运行的命令
CMD ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo \"swyan...cmd\""]
# 容器启动后运行的命令
# ENTRYPOINT java -jar /swyan/app/cloud-memo.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "cloud-memo.jar"]
# 暴露端口
# EXPOSE 80 443
EXPOSE ${PORT}/tcp
EXPOSE ${PORT}/udp
# 设置检查容器健康状况的命令,用于指定某个程序或者指令来监控 docker 容器服务的运行状态。
# HEALTHCHECK [选项] CMD <命令>:
# 关闭健康检查,如果基础镜像有健康检查指令,使用这行可以屏蔽掉其健康检查指令
HEALTHCHECK NONE
# 用于延迟构建命令的执行。简单的说,就是 Dockerfile 里用 ONBUILD 指定的命令,在本次构建镜像的过程中不会执行(假设镜像为 test-build)。当有新的 Dockerfile 使用了之前构建的镜像 FROM test-build ,这是执行新镜像的 Dockerfile 构建时候,会执行 test-build 的 Dockerfile 里的 ONBUILD 指定的命令。
ONBUILD VOLUME /swyan/app
CMD 与 ENTRYPOINT
官方解释
由官方解释可得以下结论
- 当 ENTRYPOINT不存在时,CMD为存在执行文件的 Shell命令格式 和 字符串数组格式时执行CMD
- 当 ENTRYPOINT 为Shell命令格式时,则屏蔽掉CMD命令,CMD命令则不执行
- 当 ENTRYPOINT 为字符串数组格式时:
- CMD 为存在执行文件的 Shell命令格式 和 字符串数组格式,ENTRYPOINT和CMD都会执行
- CMD 为不存在执行文件的字符串数组格式,CMD的数组全部作为ENTRYPOINT的参数,只执行ENTRYPOINT
推荐使用方式:
- ENTRYPOINT 【存在执行文件的字符串数组格式】
- ENTRYPOINT 【存在执行文件的字符串数组格式】+ CMD【全部为参数字符串数组格式】
- CMD【存在执行文件的字符串数组格式】
以上第二种配合使用的方式最佳,ENTRYPOINT 所带参数为固定参数, CMD所带参数为不变参数。
Docker-cli命令
docker
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and default
context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
builder Manage builds
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
engine Manage the docker engine
image Manage images
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
docker build
Usage: docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
Build an image from a Dockerfile
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip)
--build-arg list Set build-time variables
--cache-from strings Images to consider as cache sources
--cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the container
--compress Compress the build context using gzip
--cpu-period int Limit the CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) period
--cpu-quota int Limit the CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) quota
-c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
-f, --file string Name of the Dockerfile (Default is 'PATH/Dockerfile')
--force-rm Always remove intermediate containers
--iidfile string Write the image ID to the file
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--label list Set metadata for an image
-m, --memory bytes Memory limit
--memory-swap bytes Swap limit equal to memory plus swap: '-1' to enable unlimited swap
--network string Set the networking mode for the RUN instructions during build (default "default")
--no-cache Do not use cache when building the image
-o, --output stringArray Output destination (format: type=local,dest=path)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
--progress string Set type of progress output (auto, plain, tty). Use plain to show container output (default "auto")
--pull Always attempt to pull a newer version of the image
-q, --quiet Suppress the build output and print image ID on success
--rm Remove intermediate containers after a successful build (default true)
--secret stringArray Secret file to expose to the build (only if BuildKit enabled): id=mysecret,src=/local/secret
--security-opt strings Security options
--shm-size bytes Size of /dev/shm
--squash Squash newly built layers into a single new layer
--ssh stringArray SSH agent socket or keys to expose to the build (only if BuildKit enabled) (format:
default|<id>[=<socket>|<key>[,<key>]])
--stream Stream attaches to server to negotiate build context
-t, --tag list Name and optionally a tag in the 'name:tag' format
--target string Set the target build stage to build.
--ulimit ulimit Ulimit options (default [])
docker rmi
Usage: docker rmi [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
Remove one or more images
Options:
-f, --force Force removal of the image
--no-prune Do not delete untagged parents
docker create
Usage: docker create [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Create a new container
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip)
-a, --attach list Attach to STDIN, STDOUT or STDERR
--blkio-weight uint16 Block IO (relative weight), between 10 and 1000, or 0 to disable (default 0)
--blkio-weight-device list Block IO weight (relative device weight) (default [])
--cap-add list Add Linux capabilities
--cap-drop list Drop Linux capabilities
--cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the container
--cidfile string Write the container ID to the file
--cpu-period int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) period
--cpu-quota int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) quota
--cpu-rt-period int Limit CPU real-time period in microseconds
--cpu-rt-runtime int Limit CPU real-time runtime in microseconds
-c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpus decimal Number of CPUs
--cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--device list Add a host device to the container
--device-cgroup-rule list Add a rule to the cgroup allowed devices list
--device-read-bps list Limit read rate (bytes per second) from a device (default [])
--device-read-iops list Limit read rate (IO per second) from a device (default [])
--device-write-bps list Limit write rate (bytes per second) to a device (default [])
--device-write-iops list Limit write rate (IO per second) to a device (default [])
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--dns list Set custom DNS servers
--dns-option list Set DNS options
--dns-search list Set custom DNS search domains
--domainname string Container NIS domain name
--entrypoint string Overwrite the default ENTRYPOINT of the image
-e, --env list Set environment variables
--env-file list Read in a file of environment variables
--expose list Expose a port or a range of ports
--gpus gpu-request GPU devices to add to the container ('all' to pass all GPUs)
--group-add list Add additional groups to join
--health-cmd string Command to run to check health
--health-interval duration Time between running the check (ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-retries int Consecutive failures needed to report unhealthy
--health-start-period duration Start period for the container to initialize before starting health-retries countdown
(ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-timeout duration Maximum time to allow one check to run (ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--help Print usage
-h, --hostname string Container host name
--init Run an init inside the container that forwards signals and reaps processes
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
--ip6 string IPv6 address (e.g., 2001:db8::33)
--ipc string IPC mode to use
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--kernel-memory bytes Kernel memory limit
-l, --label list Set meta data on a container
--label-file list Read in a line delimited file of labels
--link list Add link to another container
--link-local-ip list Container IPv4/IPv6 link-local addresses
--log-driver string Logging driver for the container
--log-opt list Log driver options
--mac-address string Container MAC address (e.g., 92:d0:c6:0a:29:33)
-m, --memory bytes Memory limit
--memory-reservation bytes Memory soft limit
--memory-swap bytes Swap limit equal to memory plus swap: '-1' to enable unlimited swap
--memory-swappiness int Tune container memory swappiness (0 to 100) (default -1)
--mount mount Attach a filesystem mount to the container
--name string Assign a name to the container
--network network Connect a container to a network
--network-alias list Add network-scoped alias for the container
--no-healthcheck Disable any container-specified HEALTHCHECK
--oom-kill-disable Disable OOM Killer
--oom-score-adj int Tune host's OOM preferences (-1000 to 1000)
--pid string PID namespace to use
--pids-limit int Tune container pids limit (set -1 for unlimited)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
--privileged Give extended privileges to this container
-p, --publish list Publish a container's port(s) to the host
-P, --publish-all Publish all exposed ports to random ports
--read-only Mount the container's root filesystem as read only
--restart string Restart policy to apply when a container exits (default "no")
--rm Automatically remove the container when it exits
--runtime string Runtime to use for this container
--security-opt list Security Options
--shm-size bytes Size of /dev/shm
--stop-signal string Signal to stop a container (default "SIGTERM")
--stop-timeout int Timeout (in seconds) to stop a container
--storage-opt list Storage driver options for the container
--sysctl map Sysctl options (default map[])
--tmpfs list Mount a tmpfs directory
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
--ulimit ulimit Ulimit options (default [])
-u, --user string Username or UID (format: <name|uid>[:<group|gid>])
--userns string User namespace to use
--uts string UTS namespace to use
-v, --volume list Bind mount a volume
--volume-driver string Optional volume driver for the container
--volumes-from list Mount volumes from the specified container(s)
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
docker run
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Run a command in a new container
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip)
容器内hosts绑定 --add-host memo.swyan.top:106.13.65.121
-a, --attach list Attach to STDIN, STDOUT or STDERR
--blkio-weight uint16 Block IO (relative weight), between 10 and 1000, or 0 to disable (default 0)
--blkio-weight-device list Block IO weight (relative device weight) (default [])
--cap-add list Add Linux capabilities
--cap-drop list Drop Linux capabilities
--cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the container
--cidfile string Write the container ID to the file
--cpu-period int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) period
--cpu-quota int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) quota
--cpu-rt-period int Limit CPU real-time period in microseconds
--cpu-rt-runtime int Limit CPU real-time runtime in microseconds
-c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpus decimal Number of CPUs
--cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
-d, --detach Run container in background and print container ID
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a container
--device list Add a host device to the container
--device-cgroup-rule list Add a rule to the cgroup allowed devices list
--device-read-bps list Limit read rate (bytes per second) from a device (default [])
--device-read-iops list Limit read rate (IO per second) from a device (default [])
--device-write-bps list Limit write rate (bytes per second) to a device (default [])
--device-write-iops list Limit write rate (IO per second) to a device (default [])
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--dns list Set custom DNS servers
--dns-option list Set DNS options
--dns-search list Set custom DNS search domains
--domainname string Container NIS domain name
--entrypoint string Overwrite the default ENTRYPOINT of the image
-e, --env list Set environment variables
--env-file list Read in a file of environment variables
--expose list Expose a port or a range of ports
--gpus gpu-request GPU devices to add to the container ('all' to pass all GPUs)
--group-add list Add additional groups to join
--health-cmd string Command to run to check health
--health-interval duration Time between running the check (ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-retries int Consecutive failures needed to report unhealthy
--health-start-period duration Start period for the container to initialize before starting health-retries countdown
(ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-timeout duration Maximum time to allow one check to run (ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--help Print usage
-h, --hostname string Container host name
--init Run an init inside the container that forwards signals and reaps processes
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
--ip6 string IPv6 address (e.g., 2001:db8::33)
--ipc string IPC mode to use
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--kernel-memory bytes Kernel memory limit
-l, --label list Set meta data on a container
--label-file list Read in a line delimited file of labels
--link list Add link to another container
--link-local-ip list Container IPv4/IPv6 link-local addresses
--log-driver string Logging driver for the container
--log-opt list Log driver options
--mac-address string Container MAC address (e.g., 92:d0:c6:0a:29:33)
-m, --memory bytes Memory limit
--memory-reservation bytes Memory soft limit
--memory-swap bytes Swap limit equal to memory plus swap: '-1' to enable unlimited swap
--memory-swappiness int Tune container memory swappiness (0 to 100) (default -1)
--mount mount Attach a filesystem mount to the container
--name string Assign a name to the container
--network network Connect a container to a network
--network-alias list Add network-scoped alias for the container
--no-healthcheck Disable any container-specified HEALTHCHECK
--oom-kill-disable Disable OOM Killer
--oom-score-adj int Tune host's OOM preferences (-1000 to 1000)
--pid string PID namespace to use
--pids-limit int Tune container pids limit (set -1 for unlimited)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
--privileged Give extended privileges to this container
-p, --publish list Publish a container's port(s) to the host
-P, --publish-all Publish all exposed ports to random ports
--read-only Mount the container's root filesystem as read only
--restart string Restart policy to apply when a container exits (default "no")
--rm Automatically remove the container when it exits
--runtime string Runtime to use for this container
--security-opt list Security Options
--shm-size bytes Size of /dev/shm
--sig-proxy Proxy received signals to the process (default true)
--stop-signal string Signal to stop a container (default "SIGTERM")
--stop-timeout int Timeout (in seconds) to stop a container
--storage-opt list Storage driver options for the container
--sysctl map Sysctl options (default map[])
--tmpfs list Mount a tmpfs directory
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
--ulimit ulimit Ulimit options (default [])
-u, --user string Username or UID (format: <name|uid>[:<group|gid>])
--userns string User namespace to use
--uts string UTS namespace to use
-v, --volume list Bind mount a volume
--volume-driver string Optional volume driver for the container
--volumes-from list Mount volumes from the specified container(s)
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
docker ps
Usage: docker ps [OPTIONS]
List containers
Options:
-a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print containers using a Go template
-n, --last int Show n last created containers (includes all states) (default -1)
-l, --latest Show the latest created container (includes all states)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Only display numeric IDs
-s, --size Display total file sizes
docker logs
Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Fetch the logs of a container
Options:
--details Show extra details provided to logs
-f, --follow Follow log output
--since string Show logs since timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
--tail string Number of lines to show from the end of the logs (default "all")
-t, --timestamps Show timestamps
--until string Show logs before a timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
docker exec
Usage: docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
Run a command in a running container
Options:
-d, --detach Detached mode: run command in the background
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a container
-e, --env list Set environment variables
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--privileged Give extended privileges to the command
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
-u, --user string Username or UID (format: <name|uid>[:<group|gid>])
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
docker start
Usage: docker start [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Start one or more stopped containers
Options:
-a, --attach Attach STDOUT/STDERR and forward signals
--checkpoint string Restore from this checkpoint
--checkpoint-dir string Use a custom checkpoint storage directory
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a container
-i, --interactive Attach container's STDIN
docker stop
Usage: docker stop [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Stop one or more running containers
Options:
-t, --time int Seconds to wait for stop before killing it (default 10)
docker restart
Usage: docker restart [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Restart one or more containers
Options:
-t, --time int Seconds to wait for stop before killing the container (default 10)
docker rm
Usage: docker rm [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Remove one or more containers
Options:
-f, --force Force the removal of a running container (uses SIGKILL)
-l, --link Remove the specified link
-v, --volumes Remove anonymous volumes associated with the container