mybatis的一级和二级缓存原理及源码解析
一、作用:
一级缓存:默认开启,对于同一个SqlSession会话下,参数和SQL语句完全一样时,第一次查询的结果会放入缓存,之后的查询将从缓存中获取,只要当前会话有写操作,缓存会被清空。
二级缓存:默认关闭,对于同一个namespace下,参数和SQL语句完全一样时,第一次查询的结果会放入缓存,之后的查询将从缓存中获取,但只要当前namespace有写操作,当前的namespace会被清空缓存会被清空。
二、原理
流程图(图片来源于https://www.cnblogs.com/happyflyingpig/p/7739749.html)
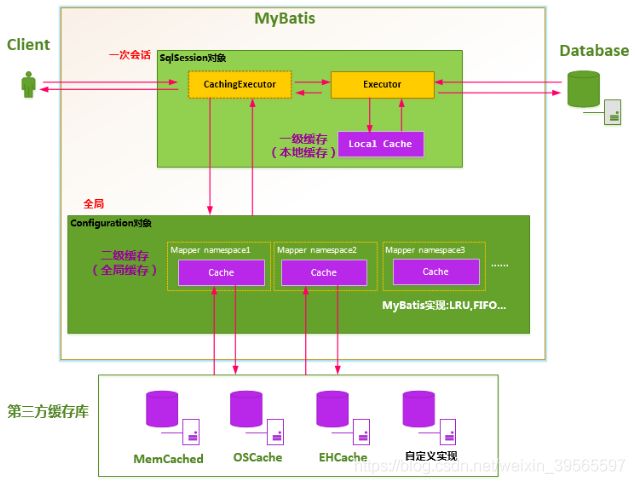
执行流程:
1、Mapper接口执行方法时,对于一级缓存会忽略CachingExecutor对象,由具体的Executor调用queryFromDatabase查询数据库,并将查询结果保存到本地缓存(一级缓存)
2、在相同的SqlSession会话下,再次执行相同参数、方法时,Executor调用handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters获取本地缓存(一级缓存)而不查询数据库。
3、对于二级缓存,在执行方法时,由CachingExecutor对象先根据namespace获取Cache对象,如果Cache存在,则直接返回。由于CachingExecutor内部对Executor的封装(delegate),如果不存在则由Executor(delegate)调用queryFromDatabase查询数据库,查询的
具体实现:
1、Mapper接口执行方法时,由MapperProxy代理对象执行
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
...
// 获取(缓存)方法,再调用MapperMethodInvoker执行方法
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
// methodCache为方法缓存,此处是如果方法缓存没有,则添加该方法的MapperMethodInvoker实现处理
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
...
// 此处放出几个关键对象,均为MapperMethodInvoker实现类
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
});
}
}
2、执行MapperMethod方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
...
case SELECT: {
// 关键代码,MapperMethod方法实际由SqlSession调用实现
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
case FLUSH:
default:
}
return result;
}
3、由CachingExecutor对象执行查询
// 先获取MappedStatement(sql的具体信息),再由执行器执行查询,此处的执行器为CachingExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
}
// 此处的Executor为什么是CachingExecutor呢,其它的为什么是BaseExecutor?
// 原因是启动时会去加载配置信息,查看对应的xml有无配置Cache元素,是否开启了二级缓存,具体代码如下
// 3.1:由SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法中用XMLConfigBuilder加载配置文件
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
...
// 关键代码,parser.parse()则解析配置文件
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
}
}
// parser.parse()具体的解析
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
// ...
settingsElement(settings);
// ...
}
// 设置开启缓存
private void settingsElement(Properties props) {
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
}
// 3.2:由SqlSessionFactory调用openSession()获取SqlSession时,获取执行器时,指定为CachingExecutor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
// 3.2.1:
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 3.2.2:由于上述初始化时开启了缓存,所以此处是true,则将3.2.1处初始化的executor作为参数封装在CachingExecutor中,在内部为一个delegate变量中,该变量类型为Executor
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
具体查询:
// 该方法由CachingExecutor调用的查询,先去获取Cache缓存,如果开启了二级缓存,有数据则之间返回,无数据则调用内部的Executor delegate去查询
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
4、Executor执行机查询数据
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// ...
// 关键代码,由执行机查询之前,先去查看是否由本地缓存,本地缓存Cache实现类为PerpetualCache对象
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// ...
} else {
// 无本地缓存则查询数据库
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// ...
}
5、查询数据库
// 查询数据库
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) {
List<E> list;
// 本地缓存放入一个查询的占位符
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 具体查询结果返回
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 将占位符的本地缓存移除
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 将结果放入本地缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
三、区别:
一级缓存:是SqlSession级别,对于commit、close、写操作后,缓存都会清空
二级缓存:是namespace级别,如果有多个namespace,对同一个表进行操作,可能出现数据不一致的情况。如果读多写少、单表操作可以选择开启二级缓存
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35688140/article/details/89848539
https://www.cnblogs.com/happyflyingpig/p/7739749.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u012489412/article/details/86712331