菜鸟教程_python3教程跟学_000
Table of Contents
- 1 Python 3 教程
- 1.1 查看 Python 版本
- 1.2 第一个Python3.x程序
- 1.3 相关内容:
- 2 跟学测试
- 2.1 查看python的版本
- 2.1.1 Jupyter 如何查看自己的python版本
- 2.1.2 Jupyter 如何查看自己基于Anconda安装的python版本
- 2.2 第一个Python程序
- 2.3 Jupyter Notebook 中查看当前 运行哪个python
- 2.4 jupyter notebook 加载py文件(test.py)
- 2.4.1 python语句不能执行Jupyter上的.py文件
- 2.4.2 执行.py文件的正确语句——>%run test.py
- 2.4.3 提取.py文件内容的语句——>%load test.py
- 2.4.4 小结:
- 2.5 jupyter notebook 加载.ipynb文件(hello.py.ipynb)
- 2.5.1 python语句不能执行Jupyter上的.ipynb文件
- 2.5.2 执行.ipynb文件的正确语句——>%run hello.py.ipynb
- 2.5.3 提取.ipynb文件内容的语句——>%load hello.py.ipynb
- 2.5.4 小结:
- 2.1 查看python的版本
Python 3 教程
Python 的 3.0 版本,常被称为 Python 3000,或简称 Py3k。相对于 Python 的早期版本,这是一个较大的升级。为了不带入过多的累赘,Python 3.0 在设计的时候没有考虑向下兼容。
Python 介绍及安装教程我们在Python 2.X 版本的教程中已有介绍,这里就不再赘述。
你也可以点击 Python2.x与3.x版本区别 来查看两者的不同。
本教程主要针对 Python 3.x 版本的学习,如果你使用的是 Python 2.x 版本请移步至 Python 2.X 版本的教程。
官方宣布,2020 年 1 月 1 日, 停止 Python 2 的更新。
查看 Python 版本
我们可以在命令窗口(Windows 使用 win+R 调出 cmd 运行框)使用以下命令查看我们使用的 Python 版本:
python -V
以上命令执行结果如下:
Python 3.3.2
你也可以进入Python的交互式编程模式,查看版本:
Python 3.3.2 (v3.3.2:d047928ae3f6, May 16 2013, 00:03:43) [MSC v.1600 32 bit (Intel)] on win32
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license()" for more information.
>>>
第一个Python3.x程序
对于大多数程序语言,第一个入门编程代码便是"Hello World!",以下代码为使用Python输出"Hello World!":
实例(Python 3.0+)
#!/usr/bin/python3
print(“Hello, World!”)
运行实例 »
你可以将以上代码保存在 hello.py 文件中并使用 python 命令执行该脚本文件。
$ python3 hello.py
以上命令输出结果为:
Hello, World!
相关内容:
Python 3.6.3 中文手册
Python 2.X 版本的教程
原文链接
https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-tutorial.html
跟学测试
查看python的版本
Jupyter 如何查看自己的python版本
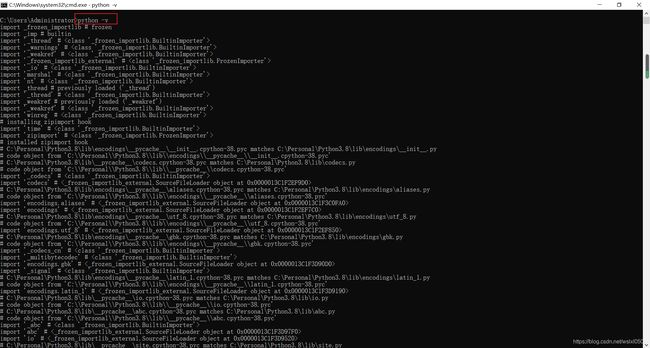
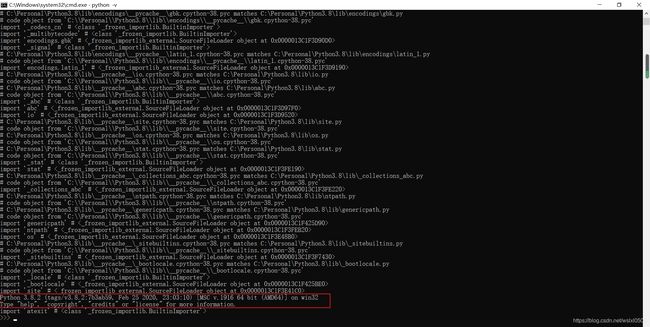
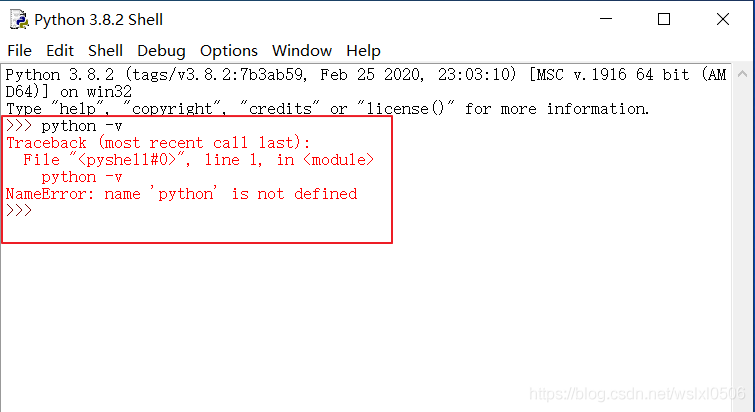
print(python -v)
#cmd环境或者Anaconda Prompt终端下输入
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
----> 1 print(python -v)
NameError: name 'python' is not defined
在Jupyter、python Idle下,输入python -v不能正确执行

Jupyter 如何查看自己基于Anconda安装的python版本
import sys
print('\n',sys.version)
sys.version
#sys.version对应的是交互模式输出
3.7.6 (default, Jan 8 2020, 20:23:39) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]
'3.7.6 (default, Jan 8 2020, 20:23:39) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)]'
第一个Python程序
print("Hello, World!")
Hello, World!
Jupyter Notebook 中查看当前 运行哪个python
import sys
print(sys.executable)
#python2的语句print sys.executable
D:\Program_Code\Anaconda3\python.exe
jupyter notebook 加载py文件(test.py)
python语句不能执行Jupyter上的.py文件
python hello.py
#不存在的文件,不能成功加载
File "", line 1
python hello.py
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
python test.py
#存在的文件,不能成功加载
File "", line 1
python test.py
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
执行.py文件的正确语句——>%run test.py
%run hello.py
#不存在的文件,不能成功加载
ERROR:root:File `'hello.py'` not found.
%run test.py
#存在的文件,成功加载
Hello World!
提取.py文件内容的语句——>%load test.py
# %load test.py
print('Hello World!')
#文件中的内容,直接被读取出来
Hello World!
小结:
使用%run和%load,都能实现运行.py文件的代码语句;
使用%run和%load的区别:%run是直接运行.py文件的内容,%load是将load语句注释掉,并提取出.py文件的内容
jupyter notebook 加载.ipynb文件(hello.py.ipynb)
python语句不能执行Jupyter上的.ipynb文件
python hello.py.ipynb
#存在的文件,不能成功加载
File "", line 1
python hello.py.ipynb
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
执行.ipynb文件的正确语句——>%run hello.py.ipynb
%run hello.py.ipynb
#存在的文件,成功加载
Hello, World!
提取.ipynb文件内容的语句——>%load hello.py.ipynb
# %load hello.py.ipynb
{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 1,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"Hello, World!\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"print(\"Hello, World!\")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": []
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.7.6"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}
小结:
使用%run和%load,都能实现运行.ipynb文件的代码语句;
使用%run和%load的区别:%run是直接运行.ipynb文件的内容,%load是将load语句注释掉,并提取出.ipynb文件的内容