python 获取某一节点下的子孙节点「适用于父子层级组织架构」
读取hive数据处理父子层级架构
准备原材料
读取hive中的数据,转化为List
conn = hive.Connection(host='test-bigdata-cdh-01', port=10000, username='XXXX', database='XXXX')
exe_sql = 'select pid,id,name from test_orginazation'
df = pd.read_sql(exe_sql,conn)
src_list = df.values.tolist()
主程序逻辑如下:
要获取某一个节点的所有子孙节点,需要将读取到的节点数据构造为树状结构
构造树状结构的步骤如下:
1. 构造节点元素类
由于树状结构的每一个节点都需要有当前节点、父节点、以及直接子节点这三个核心元素,因此节点元素类如下:
class Org:
"""
类对象初始化
"""
def __init__(self, p_id, cur_id, cur_name, children_list = []):
self.p_id = p_id
self.cur_id = cur_id
self.cur_name = cur_name
# 孩子节点构成数组[链表]
self.children_list = children_list
"""
get 和 set 方法 (类似于JavaBean)
"""
def get_p_id(self):
return self.p_id
def get_cur_id(self):
return self.cur_id
def get_cur_name(self):
return self.cur_name
def get_children_list(self):
return self.children_list
def set_p_id(self,my_p_id):
self.p_id = my_p_id
def set_cur_id(self,my_cur_id):
self.cur_id = my_cur_id
def set_cur_name(self,my_cur_name):
self.cur_name = my_cur_name
def set_children_list(self,my_children_list = []):
self.children_list= my_children_list
"""
toString方法
"""
def to_string(self):
return "cur_id is : " + str(self.cur_id) + " | and the cur_name is : " + str(self.cur_name) + " and " \
"the length of children's node is :" + str(len(self.children_list))
2. 将列表的元素全部转化为类型,构成由Org类型元素组成的列表 org_node_list
核心代码如下:
"""
将输入数据转化为节点元素列表
"""
for src in src_list:
org_node = Org(src[0],src[1],src[2])
org_node_list.append(org_node)
此列表中每个类型元素的children_list均未空
3. 遍历org_node_list列表的每一个元素ele,将ele的children_list填充,并返回新的元素列表
核心代码如下:
"""
构造节点树,更新传入数组每个元素的children_list 域 , 并返回新的元素列表
"""
def construct_tree(root_list:Org):
list_len = len(root_list)
out_start = 0
while out_start < list_len:
node = root_list[out_start]
tmp_children_list = []
inner_start = 0
while inner_start < list_len:
node1 = root_list[inner_start]
if node.get_cur_id() == node1.get_p_id() and node1.get_cur_id() != node1.get_p_id() :
tmp_children_list.append(root_list[inner_start])
inner_start += 1
root_list[out_start].set_children_list(tmp_children_list)
out_start += 1
return root_list
4. 在新的元素列表中查找传入的列表元素
核心代码如下:
"""
根据传入节点元素的id,查找节点,如果找不到则返回None
"""
def get_node_from_value(node_id, node_list : Org =[]):
if len(node_list) == 0 :
return
else:
for node in node_list:
if node.get_cur_id() == node_id:
return node
else:
continue
return None
5. 根绝传入的节点元素,从该节点开始,遍历其子孙节点「深度优先遍历」
核心代码如下:
"""
深度优先遍历,打印传入节点及其子孙节点值
"""
def display_node(ele:Org,space_num = 0 ):
print("\t" * space_num +"" + ele.get_cur_name())
if len(ele.get_children_list()) == 0 :
return
else:
space_num += 1
for ch_ele in ele.get_children_list():
display_node(ch_ele,space_num)
也可获取其子孙节点,形成列表返回,便于后续存入数据库
核心代码如下:
"""
获取当前节点的子孙节点形成列表返回
"""
def get_children_node(ele:Org, children_node_list = []):
if len(ele.get_children_list()) == 0 :
return
else:
for ch_ele in ele.get_children_list():
children_node_list.append(ch_ele)
get_children_node(ch_ele,children_node_list)
return children_node_list
"""
6. 将得到的子孙节点元素列表整合为DataFrame
7. 将DataFrame元素写入到外部介质「数据库、excel、csv、hdfs、hive等等」
主程序调用部分代码如下:
#初始化节点列表为空
org_node_list = []
"""
将输入数据转化为节点元素列表
"""
for src in src_list:
org_node = Org(src[0],src[1],src[2])
org_node_list.append(org_node)
"""
将元素列表构造为树状列表
"""
res_tree = construct_tree(org_node_list)
"""
从树状列表中寻找指定id对应的节点元素
"""
node_res = get_node_from_value(0,res_tree)
"""
打印指定节点及其下游节点
"""
# display_node(node_res)
# 得到指定节点的子孙节点的元素列表
children_node_list = get_children_node(node_res)
# 将类型的元素列表转化为2个list
child_id_list = []
child_name_list = []
for ele in children_node_list :
child_id_list.append(ele.get_cur_id())
child_name_list.append(ele.get_cur_name())
#list 转化为Dataframe
data_frame= {
"org_id":child_id_list
,"org_name":child_name_list
}
data = pd.DataFrame(data_frame)
print(data)
毕业后也是第一次写这样的代码,手稿如下:
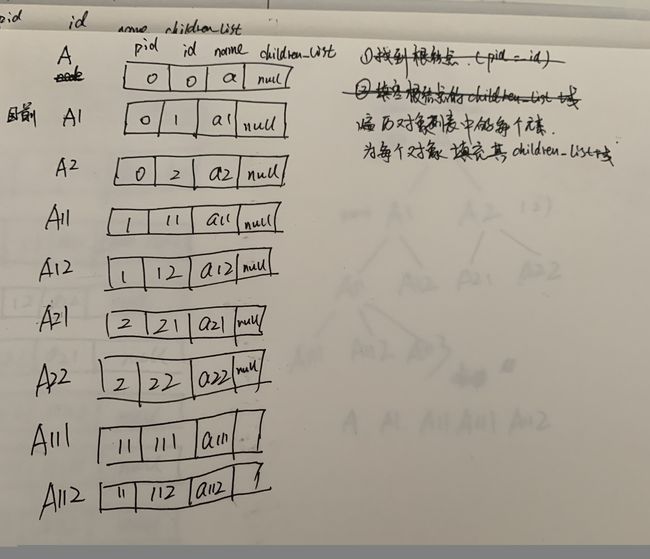
填充每个元素的children_list 成员后的结果如下:

python新手,初次手撸博客,欢迎交流。
