Keras强化学习——FlappyBird
github地址:https://github.com/ielcome2017/FlappyBird.git
代码
数据生成
import numpy as np
import sys
import cv2
import random
from play import Game, GameOver
IMAGE_SHAPE = (80, 80)
def convert(img):
img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(img, IMAGE_SHAPE), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, img = cv2.threshold(img, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
return np.array(img)
class Memory:
def __init__(self):
self.time_step = 4
self.max_length = 50000
self.head, self.next = self.time_step, 0
self.memory = np.empty(self.max_length,
dtype=[("image", np.float, IMAGE_SHAPE), ("art", np.float, [4])])
def memory_append(self, image, art):
self.memory["image"][self.next % self.max_length] = image
self.memory["art"][self.next % self.max_length] = art
self.next = self.next + 1
self.head += 1 if self.next > self.max_length else 0
class GameMemory(Memory):
def __init__(self, func, count, flag="explore"):
self.count = count
self.func = func
self.flag = flag
self.explore = 3000000
self.observer = 10000
self.image_shape = (80, 80)
self.pre_step_epoch = 10000
super().__init__()
def show(self):
for _ in self.next_data():
yield _
def next_data(self):
# 参数设置
epsilon = 0.001 if self.flag in ["explore", "display"] else 0.1
init_epsilon, final_epsilon = 0.1, 0.001
action_dim = 2
# 初始化
num = 40 if self.flag in ["explore", "train"] else 1
game = Game(num) # game为环境
action = np.array([1, 0])
image, reward, terminal = game.frame_step(action)
image = convert(image)
for _ in range(4):
self.memory_append(image, [*action, reward, terminal])
epsilon -= (init_epsilon - final_epsilon) / self.explore * self.count * self.pre_step_epoch
epsilon = np.clip(epsilon, a_max=init_epsilon, a_min=final_epsilon)
# 获取当前状态
count = self.count * self.pre_step_epoch
try:
while True:
# 获取动作
if random.random() < epsilon:
action_ind = np.random.randint(0, action_dim)
else:
idx = (self.next - np.arange(1, self.time_step+1)) % self.max_length
state = self.memory["image"][idx]
state = np.transpose(state[np.newaxis, :, :], [0, 2, 3, 1])
action_ind = self.func(state).argmax(-1).astype("int")[0] # 智能体产生动作
epsilon -= (init_epsilon - final_epsilon) / self.explore
epsilon = np.clip(epsilon, a_max=init_epsilon, a_min=final_epsilon)
count += 1
action = game.get_event(action_ind) # 游戏中事件触发
image, reward, terminal = game.frame_step(action) # 环境的激励
image = convert(image) # 80*80
self.memory_append(image, [*action, reward, terminal])
data = self.batch_data()
if data is not None:
yield data
except GameOver:
print("\n{}> game close <{}".format("="*10, "="*10))
def batch_data(self, batch_size=32):
gamma = 0.99
num_sample = self.next - self.head
if num_sample < self.observer:
sys.stdout.write("\r num of sample is : %d/%d" % (num_sample, self.observer))
sys.stdout.flush()
return None
batch_ind = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.head, self.next), [batch_size]) % self.max_length
# 抽取数据训练
image_ind = (batch_ind[:, np.newaxis] - np.arange(self.time_step)) % self.max_length
# 当前步为预测动作产生的状态,要用上一个状态的reward与当前预测的y比较
# 如当前批次索引为[1, 3, 5, 7...] 取第一个索引,那么当前状态为[0, 1, 2, 3], next_state为[1, 2, 3, 4]
current_state = np.transpose(self.memory["image"][(image_ind - 1) % self.max_length], [0, 2, 3, 1])
next_state = np.transpose(self.memory["image"][image_ind], [0, 2, 3, 1])
art = self.memory["art"][batch_ind]
action, reward, terminal = art[:, 0:2], art[:, -2], art[:, -1]
out = self.func(next_state).max(-1)
batch_y = reward + gamma * out * (1 - terminal)
return [current_state, action], batch_y
网络
import keras
from keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, MaxPool2D, \
Input, Flatten, Dot, Activation
def NetV1():
state_shape, action_dim = [80, 80, 4], 2
actions = Input([action_dim])
state = Input(state_shape)
x = Conv2D(32, kernel_size=8, strides=4, padding="same")(state)
x = Activation("relu")(x)
x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=2)(x)
x = Conv2D(64, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding="same")(x)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same")(x)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(512)(x)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
out1 = Dense(action_dim)(x)
out2 = Dot(-1)([actions, out1])
model = keras.Model([state, actions], out2)
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-6)
# optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1e-5, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
loss = keras.losses.mse
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss)
model.summary()
return model
训练
from agent import GameMemory
import keras
from net import NetV1, NetV2
import os
EPOCHS = 400
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 10000
FLAG = "train"
def get_net(net_version):
train_net, path = (NetV1(), "NETV1/") if net_version == 0 else (NetV2(), "NETV2/")
call_function = [
keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=path + "weight.{epoch:02d}.h5")]
if len(os.listdir(path)) == 0:
return train_net, call_function, 0
counts = [int(file.split(".")[1]) for file in os.listdir(path)]
count = max(counts)
filename = path + "weight.%02d.h5" % count
train_net.load_weights(filename)
return train_net, call_function, count
def train():
net, call_function, count = get_net(net_version=0)
agent = keras.backend.function(net.input[0], net.layers[-2].output)
data = GameMemory(agent, count, flag=FLAG) # flag in ["train", "explore", "display"] 训练过程随机动作较多
net.fit(data.next_data(), epochs=EPOCHS, initial_epoch=data.count,
steps_per_epoch=STEPS_PER_EPOCH, callbacks=call_function)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
模型下载
下载完成后,将里面的内容解压到当前项目的根目录FlappyBird下面FlappyBird
|–model
|–|-- bird-dqn-2920000
|–|-- weight.292.h5
|–NETV1
|–|-- weight.200.h5
运行过程
main.py中train()函数定义好网络和回调函数。
| 变量 | 参数 |
|---|---|
| 网络 | net |
| 预测函数 | func = Model(net.input[0], net.out1) |
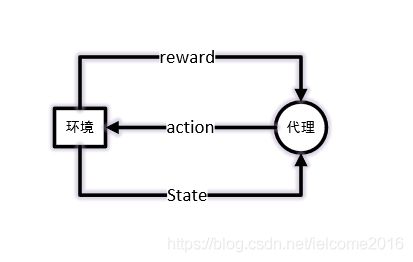
强化学习有5个元素:环境,代理,状态,激励函数(reward),动作。
代理产生动作,环境根据动作反馈该动作之后的环境状态以及reward。需要注意该State知识环境反馈的一个画面,数据根据游戏的画面而生成,4帧为一个游戏状态,为current_state, next_state。
环境会根据游戏状态,用激励函数给出激励,但是环境的激励通常只有结束(-1)、胜利(1)和正在进行(0.1)三种
强化网络的目标是训练代理,这个代理也叫智能体,训练过程的数据格式如下:
-
当前游戏状态current_state,
-
当前游戏动作(action),
-
(Q_value)下个游戏状态(next_sate)理想中的
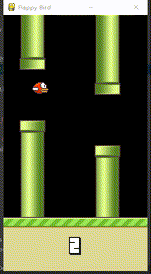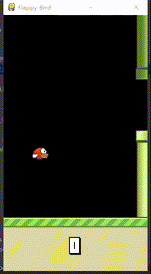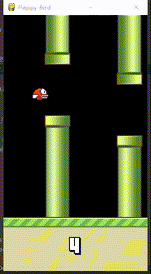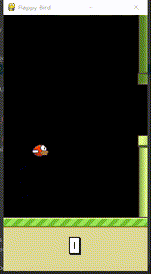
代理的训练过程实质为代理激励函数的拟合过程。FlappyBird中,飞过中心线才获得为1的激励,但是靠近中心线以及在管道外面飞的激励均为0.1,这对于环境是正常的,如下图。
但是对于人的大脑两者的价值绝不等同,靠近中心线的状态(下图中的2)人们会在下意识觉得鸟更棒,需要更高的激励值。但是初始化的网络不能够正常反馈这种激励函数,因此训练代理就是拟合这种激励函数,使之接近于人的想法。
Q_value为net的out1
那么代理觉得Bird在游戏状态中真正的激励为:
terminal表示Bird是否翻车 为1就是翻车了
代理根据游戏的current_sate和action根据自己拟合出来的激励函数,给出的激励值为current_reward为net的out2.
最终优化current_reward与agent_reward的差,两者越小越好。
为了加快数据产生速度,开始将游戏的帧率提高,正常的fps为30,训练时调整为1000,因为游戏每一帧过去,就会训练一次,如果帧数过慢,网络训练就会陷入等待。调整后训练每一批次一万条记录,训练事件为2分50秒左右,200轮训练将近9.5到10个小时之间。
292轮后的效果移步
文件结构
net.py 网络结构包含两个网络V1和V2, 目前只训练V1 。
| 文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| main.py | 训练文件 |
| agent.py | 产生数据 |
| play.py | 游戏运行包 |
| game\control.py | 游戏调度文件 |
| game\element.py | 游戏配置文件 |
| game\engine.py | 游戏后端,两种选择PyQt5和pygame |
| game\display.py | PyQt5写的游戏引擎 |
网络结构 net.py
| Layer (type) | Input Shape | Kernel | stride | Output Shape | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | input_state | (None, 80, 80, 4) | |||
| 1 | input_action | (None, 2) | |||
| 2 | 卷积(conv) | (None, 80, 80, 4) | (8, 8, 4, 32) | 4 | (None, 20, 20, 32) |
| 3 | 池化(pool) | (None, 20, 20, 32) | 2 | (None, 10, 10, 32) | |
| 4 | 卷积(conv) | (None, 20, 20, 32) | (4, 4, 32, 64) | 2 | (None, 5, 5, 64) |
| 5 | 卷积(conv) | (None, 5, 5, 64) | (3, 3, 64, 64) | 1 | (None, 5, 5, 64) |
| 6 | flatten | (None, 1600) | |||
| 7 | 全连接(fully_connect) | 1600 | (1600, 512) | (None, 512) | |
| 8 | out1_全连接(fully_connect) | 512 | (512, 2) | (None, 2) | |
| 9 | out2_点乘(dot) | (None, 2)[action, out1] | (None, 1) |