spring-cache 雪崩
spring-cache 基本原理是利用拦截器,先尝试读取缓存,未命中缓存,先读库在写入缓存,经过查看源码如果在并发量大的时候容易造成“雪崩”。原因是在更新缓存逻辑中没有做并发更新的处理。
原始代码
private Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Process any early evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true, ExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// Check if we have a cached item matching the conditions
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
// Collect puts from any @Cacheable miss, if no cached item is found
List cachePutRequests = new LinkedList();
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class), ExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Cache.ValueWrapper result = null;
// If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit
if (cachePutRequests.isEmpty() && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
result = cacheHit;
}
// Invoke the method if don't have a cache hit
if (result == null) {
result = new SimpleValueWrapper(invokeOperation(invoker));
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), result.get(), cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(result.get());
}
// Process any late evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, result.get());
return result.get();
} 经过分析代码会发现在这里并没有任何锁来处理并发更新
// Invoke the method if don't have a cache hit
if (result == null) {
result = new SimpleValueWrapper(invokeOperation(invoker));
}测试代码
@Cacheable
public List queryAllCity() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("getAllCity");
return regionsMapper.getAllCity();
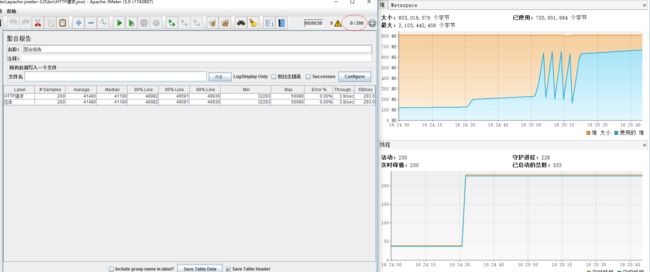
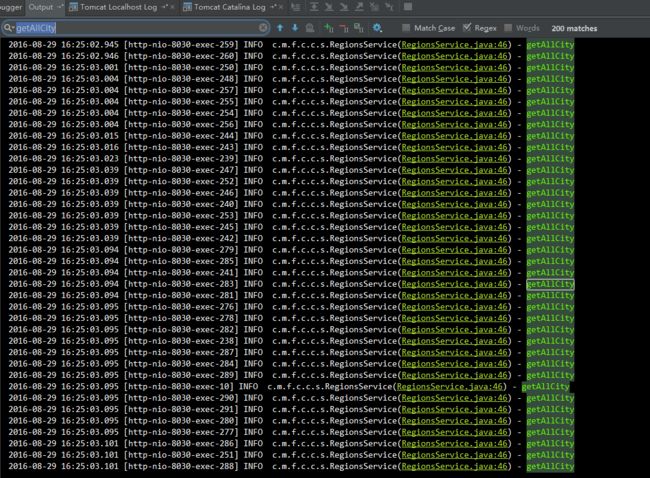
} 这里用jmeter简单的测试了一下(200个并发),效果如下
从日志中可以看到在并发更新缓存时,200次一次都没有命中,而是执行了200次读取数据方法(这里只是简单的用sleep模拟了读取数据的长时间操作)
改造
期望结果:并发更新缓存时,只会读取一次数据库,其他的请求都会命中缓存
改造后的代码样例:
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Process any early evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true, ExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// Check if we have a cached item matching the conditions
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
// Collect puts from any @Cacheable miss, if no cached item is found
List cachePutRequests = new LinkedList();
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class), ExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Cache.ValueWrapper result = null;
// If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit
if (cachePutRequests.isEmpty() && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
result = cacheHit;
}
// Invoke the method if don't have a cache hit
if (result != null) {
return result.get();
}
lock.lock();
try{
logger.info(" get lock");
result = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
if (result == null) {
result = new SimpleValueWrapper(invokeOperation(invoker));
} else {
logger.info("hit cache");
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), result.get(), cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(result.get());
}
// Process any late evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, result.get());
return result.get();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
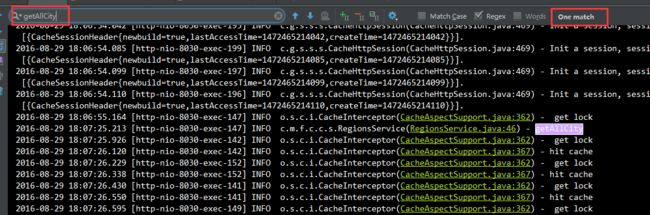
} 相同的测试200个并发
从日志可以看到获取锁(get lock)一共200次,但是实际读取数据(getAllCity)只有1次,命中(hit cache)缓存199次,这正是我们所希望的结果
这里只是使用了Lock锁,如果要处理多实例的命中缓存,就需要一个分布式锁,可以用redis实现setIfAbsent。当然也可以引入锁的超时机制。这里有个简单基于redis的分布式锁: spring-distributelock。
如果你的应用的实例只有十几个,其实只要保证每个实例只有1个线程在更新缓存就可以了(ReentrantLock),还免去了分布式的复杂和网络通信时间。