Shiro简介及与spring集成
【IT168 技术】Apache Shiro是一个强大的,易用的Java安全框架。它被用作于认证,授权,加密,session管理。依赖于Shiro简单易懂的API,就可以快速的构建包括手机,大型web和商业应用。
1、权限基础
两个基本的概念
——安全实体:就是被权限系统保护的对象,比如工资数据。
——权限:就是需要被校验的行为,比如查看、修改等。
分配权限:
——把对某些安全实体的某些权限分配给某些人员。
——是向数据库里面添加数据、或是维护数据的过程
权限验证(权限匹配):
——判断某个人员或程序对某个安全实体是否拥有某个或某些权限。
——从数据库中获取相应数据进行匹配的过程。
权限的继承性:
如果多个安全实体存在包含关系,而某个安全实体没有权限限制,则它会继承包含它的安全实体的相应权限。
权限的最近匹配原则:
如果多个安全实体存在包含关系,而某个安全实体没有权限限制,那么它会向上寻找并匹配相应权限限制,直到找到一个离这个安全实体最近的拥有相应权限限制的安全实体为止。如果把整个层次结构都寻找完了都没有匹配到相应权限限制的话,那就说明所有人对这个安全实体都拥有这个相应的权限限制。
2、Shiro架构与功能介绍
Authentication: 认证。即验证是哪个用户登录。
Authorization:也被称为访问控制,即决定当前登录用户是否有权限去访问受保护的资源。
Cryptography:通过加密算法保护数据安全。
Session Management: 当用户使用你的应用是自身携带的数据。
Web Integration: 虽然Shiro是设计用来确保任何基于JVM的应用,但是很多时候是用来保护Web应用。
Integrations:可以很好的集成其他的技术和框架。
下图展示了Shiro的的四大核心功能和所支持的其它特性。
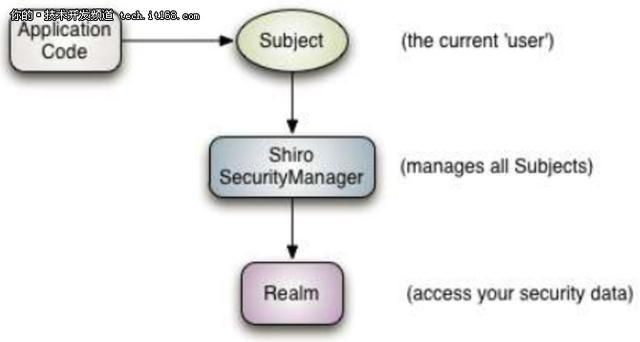
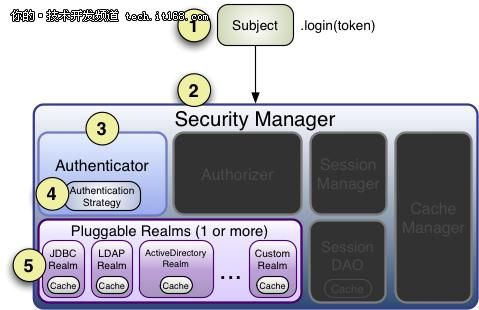
三大核心组件
Subject:正与系统进行交互的人,或某一个第三方服务。所有Subject实例都被绑定到(且这是必须的)一个SecurityManager上。
SecurityManager:Shiro架构的心脏,用来协调内部各安全组件,管理内部组件实例,并通过它来提供安全管理的各种服务。当Shiro与一个Subject进行交互时,实质上是幕后的SecurityManager处理所有繁重的Subject安全操作。
Realms:本质上是一个特定安全的DAO。当配置Shiro时,必须指定至少一个Realm用来进行身份验证和/或授权。Shiro提供了多种可用的Realms来获取安全相关的数据。如关系数据库(JDBC),INI及属性文件等。可以定义自己Realm实现来代表自定义的数据源。
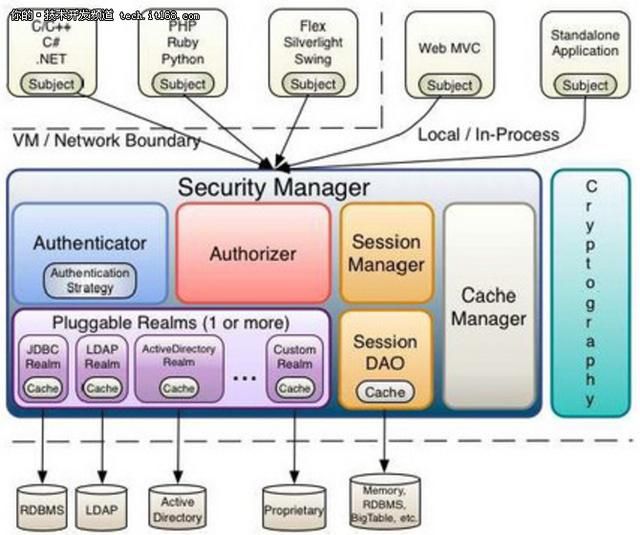
Shiro架构图
Authenticator:执行对用户的身份验证(登录)的组件。Authenticator从一个或多个Realm中获得数据以验证用户的身份。
若存在多个realm,则接口AuthenticationStrategy会确定什么样算是验证成功(例如,如果一个Realm成功,而其他的均失败,是否登录成功)。
Authorizer:验证用户能否访问应用中的受保护的资源
SessionManager:可在任何应用或架构层一致地使用 Session API
SessionDAO:SessionManager执行Session持久化(CRUD)操作。
CacheManager :对Shiro组件提供缓存支持。
Cryptography:Shiro的API大幅度简化Java API中繁琐的密码加密
Realms:Shiro通过Realms来获取相应的安全数据
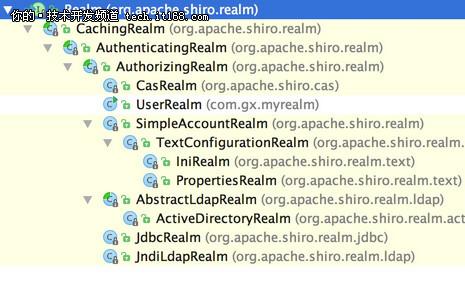
Realm 实现关系:
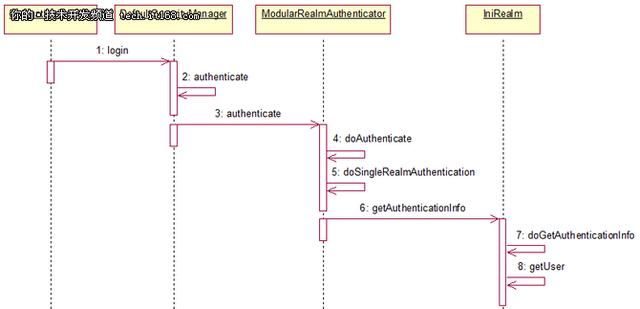
认证
Step 1:应用程序代码调用Subject.login方法,传递创建好的包含终端用户的Principals(身份)和Credentials(凭证)的AuthenticationToken实例
Step 2:Subject实例,通常为DelegatingSubject(或子类)委托应用程序的SecurityManager通过调用securityManager.login(token)开始真正的验证。
Step3:SubjectManager接收token,调用内部的Authenticator实例调用 authenticator.authenticate(token)。 Authenticator通常是一个ModularRealmAuthenticator实例,支持在身份验证中协调一个或多个Realm实例。
Step 4:如果应用程序中配置了一个以上的Realm,ModularRealmAuthenticator实例将利用配置好的AuthenticationStrategy来启动Multi-Realm认证尝试。在Realms被身份验证调用之前,期间和以后,AuthenticationStrategy被调用使其能够对每个Realm的结果作出反应。
Step 5:每个配置的 Realm 用来帮助看它是否支持提交的AuthenticationToken。如果支持,那么支持Realm的getAuthenticationInfo方法将会伴随着提交的token被调用。getAuthenticationInfo方法有效地代表一个特定Realm的单一的身份验证尝试。
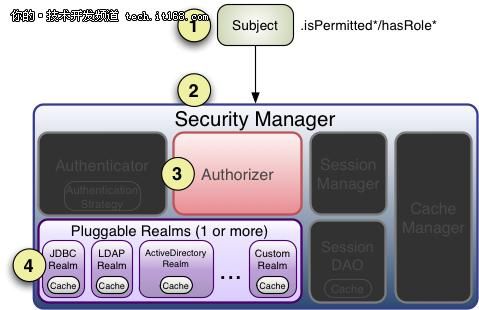
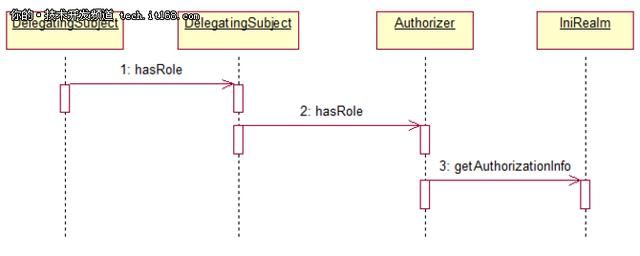
授权
Step 1:应用程序或框架代码调用任何Subject 的hasRole*, checkRole*, isPermitted*,或者checkPermission*方法的变体,传递任何所需的权限
Step 2:Subject的实例—通常是DelegatingSubject(或子类),调用securityManager的对应的方法。
Step 3:SecurityManager调用org.apache.shiro.authz.Authorizer接口的对应方法。默认情况下,authorizer 实例是一个ModularRealmAuthorizer实例,它支持协调任何授权操作过程中的一个或多个Realm实例。
Step 4:每个配置好的Realm被检查是否实现了相同的Authorizer接口。如果是,Realm各自的hasRole*, checkRole*,isPermitted*,或checkPermission*方法将被调用。
注销
logout(注销):currentUser.logout;
调用logout方法时,现有Session将失效,而且身份将失去关联(在Web应用程序中,RememberMe cookie将被删除)。
在Subject注销后,该Subject的实例被再次认为是匿名的。
注意:WEB应用程序记住身份往往依靠Cookie,然而Cookie只能在Response被返回后被删除,所以建议在调用subject.logout后立即向终端重定向一个新的视图或页面。这样即能保证与安全相关的Cookie都能像预期的一样被删除。
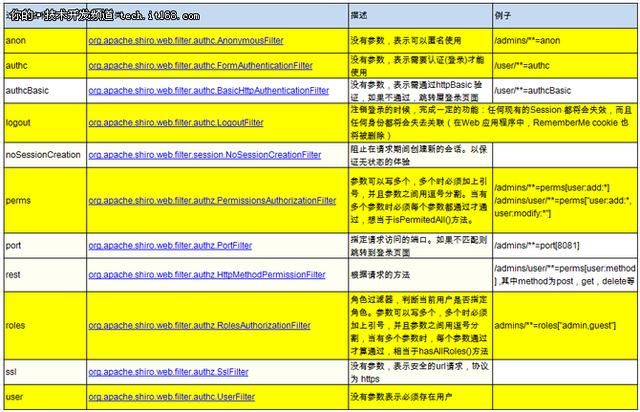
Shiro中默认的过滤器
基于注解
Shiro提供的注解
@RequiresAuthentication :要求当前Subject已经在当前的session中被验证通过才能被注解的类/实例/方法访问或调用。
@RequiresGuest :要求当前的Subject是一个“guest”,也就是他们必须是在之前的session中没有被验证或记住才能被注解的类/实例/方法访问或调用。
@RequiresPermissions:要求当前的Subject被允许一个或多个权限,以便执行注解的方法,比如:@RequiresPermissions("account:create")
@RequiresRoles:要求当前的Subject拥有所有指定的角色。如果他们没有,则该方法将不会被执行,而且AuthorizationException异常将会被抛出。比如:@RequiresRoles("administrator")
@RequiresUser:需要当前的Subject是一个应用程序用户才能被注解的类/实例/方法访问或调用。要么是通过验证被确认,或者在之前session中的‘RememberMe’服务被记住。
基于标签
需要在jsp页面中倒入shiro 标签
guest 标签
guest标签将显示它包含的内容,仅当当前的Subject 被认为是guest时。
guest是指没有身份ID的任何Subject:没有登录也没有在上一次的访问中被记住(RememberMe 服务)
guest标签与user标签逻辑相反。
Hi there! Please Loginor
Signuptoday!
user标签
user标签将显示它包含的内容,仅当当前的Subject 被认为是user时。
user在上下文中被定义为一个已知身份ID的Subject,或是成功通过身份验证及通过RememberMe服务的。
该标签在语义上与authenticated 标签是不同的,authenticated标签更为严格。
User标签与guest标签逻辑相反。
authenticated 标签
当当前用户在当前会话中成功地通过了身份验证authenticated标签才会显示包含的内容。比user标签更为严格。在逻辑上与notAuthenticated标签相反。
Update your contact information.
notAuthenticated标签
当前Subject还没有在其当前会话中成功地通过验证,将会显示它所包含的内容
Please loginin order to update your credit card information.
principal标签
标签将会输出Subject的主体(标识属性)或主要的属性
Hello, , how are you today?
Typed principal
User ID:
Principal property
Hello,
hasRole标签
当前Subject被分配了具体的角色时显示它所包含的内容。hasRole标签与lacksRole标签逻辑相反。
Administer the system
lacksRole标签
Sorry, you are not allowed to administer the system.
hasAnyRole标签
当前的Subject被分配了任意一个来自于逗号分隔的角色名列表中的具体角色,将会显示它所包含的内容。
You are either a developer, project manager, or administrator.
hasPermission标签
当前Subject拥有特定的权限时,会显示它所包含的内容。hasPermission标签与lacksPermission标签逻辑相反。
Create a new User
lacksPermission标签
当前Subject没有拥有(蕴含)特定的权限,将会显示它所包含的内容。也就是说,用户没有特定的能力。
Sorry, you are not allowed to delete user accounts.
3、Spring集成Shiro
配置自定义Realm:实现自定义认证和授权
配置Shiro实体类使用的缓存策略
配置SecurityManager
配置保证Shiro内部Bean声明周期都得到执行的Lifecycle Bean后置处理器
配置AOP式方法级权限检查
配置Shiro Filter
基于Maven构建项目
web.xml
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1" metadata-complete="true">
applicationContext.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
applicationContext-shiro.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
/** = anon
springDispatherServlet-servlet.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
代码实现
自定义Realm
@Component("myRealm")
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 授权方法,在配有缓存的情况下,只加载一次。
*/
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
ShiroUser shiroUser = (ShiroUser) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal;
List
Set
for (Authority authority : authorities){
roles.add(authority.getName);
}
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
info.setRoles(roles);
return info;
* 登录认证
* @param token
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
*/
@Transactional
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken uptoken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
String username = uptoken.getUsername;
User user = userService.findUserByLoginName(username);
if( user == null ) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("用户名"+username+"不存在.");
}
if (user.getEnabled != 1){
throw new LockedAccountException(user.getName+"被锁定");
}
ShiroUser principal = new ShiroUser;
String userInfo = user.getName+"("+user.getRole.getName+")";
principal.setUserInfo(userInfo);
principal.setAuthorities(user.getRole.getAuthorities);
Object hashedCredentials = user.getPassword;
ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt);
String realmName = getName;
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal,hashedCredentials, credentialsSalt,realmName);
public class ShiroUser{
//userName(roleName)
private String userInfo;
private List
public List
return authorities;
}
public void setAuthorities(List
this.authorities = authorities;
}
public String getUserInfo {
return userInfo;
}
public void setUserInfo(String userInfo) {
this.userInfo = userInfo;
* 初始化 使用MD5加密
*/
@PostConstruct
public void initCredentialsMatcher{
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher;
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
// 加密1024次
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
//
this.setCredentialsMatcher(hashedCredentialsMatcher);
Main方法生成salt 和password
// 利用shiro提供的随机数生成类、生成随机数,用于盐值加密
SecureRandomNumberGenerator secureRandomNumberGenerator =
new SecureRandomNumberGenerator;
String str = secureRandomNumberGenerator.nextBytes.toBase64;
System.out.println(str);//
String algorithmName = "MD5";
Object source = "123456";
//盐值 NWJtcFg3VFNtNEdEWTh6UUtoSTRkdz09
ByteSource salt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(str);
int hashIterations = 1024;
Object result = new SimpleHash(algorithmName,source,salt,hashIterations);
System.out.println(result);//数据库中密码 b9aa43cfb15649c932ac647df54101a7
LoginController.java
@RequestMapping(value = "/login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
private String login(HttpServletRequest request,Modelmodel,
@RequestParam(name = "username",required = false) String username, @RequestParam(name = "password",required = false) String password, RedirectAttributes attributes){
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
//usernamePasswordToken.setRememberMe(false);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject;
String message = null;
if(!subject.isAuthenticated){
try {
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
} catch (UnknownAccountException ex) {//用户名没有找到
//ex.printStackTrace;
message = "用户名不存在";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ex) {//用户名密码不匹配
// ex.printStackTrace;
message = "用户名和密码不匹配";
}catch (LockedAccountException lae) {// 用户被锁定
//lae.printStackTrace;
message = "用户被锁定";
}catch (AuthenticationException e) {//其他的登录错误
e.printStackTrace;
}
if(message!=null){
attributes.addFlashAttribute("message", message);
return "redirect:/shiro-login";
return "redirect:/success";
}
基于注解的权限设置
在controller list方法上加上 @RequiresRoles(value={"admin"}) 说明此方法需要有admin角色的用户才可以操作。
@RequiresRoles(value={"admin"})
@RequestMapping(value = "/list", method= RequestMethod.GET)
public String list(Model model, HttpServletRequest request){
List
model.addAttribute("list", userList);
return "user/userList";
}
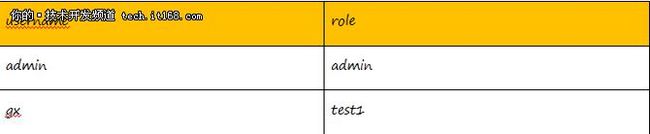
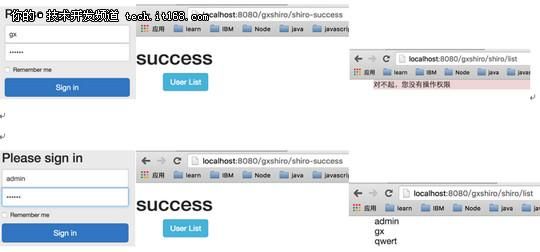
我们用两个用户来测试
可以看到admin用户可以访问list页面,而gx因为没有admin的角色,访问失败。
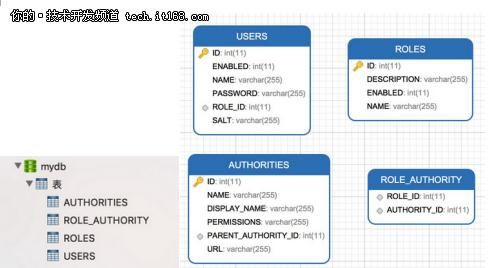
附:数据库关系图
总结:本文通过例子,简单实现了权限的控制,相比与spring secruity的复杂配置,shiro更加简单。
例子github:https://github.com/zhaoguoxin/gxshiro.git