秒杀系统高并发
Java电商秒杀系统深度优化
Tomcat瓶颈
不优化前,tomcat最大线程数阻碍了系统的最大并发
1. 使用spring Boot内置的Tomcat 在 application.yml中添加
* server.tomcat.accpt-count :等待队列长度,默认100
* server.tomcat.max-connections:最大可连接数,默认10000
* server.tomcat.max-threads:最大工作线程数,默认200
* server.tomcat.min-spare-threads: 最小工作线程数,默认10
- 默认配置下,连接超过10000后会出现拒绝连接情况
- 默认配置下,触发的请求超过200 + 100后会拒绝处理
2. 使用外挂Tomcat
keepAlive 是在http 1.1 中 使用长连接,可能会被黑客利用
keepAliveTimeOut:多少秒后不响应的断开keepalive
maxKeepAliveRequests:多少次请求后keepalive断开失效
使用WebServerFactoryCustomizer < ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory > 定制化内嵌tomcat配置
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatConnectorCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ConfigurableWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//当spring 容器中没有tomcatEmaeddedServletContainerFactory 这个bean时,会把此bean加载进spring
@Component
public class WebServerConfiguration implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) {
//使用对应工厂类提供给我们的接口定制化我们的Tomcat connector
( (TomcatServletWebServerFactory)factory ).addConnectorCustomizers(new TomcatConnectorCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
Http11NioProtocol protocol = (Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler();
// 定制化keepalivetimeout 这是30秒内没有请求则服务器自动断开keepalive链接
protocol.setKeepAliveTimeout(3000);
// 当客户端发送超过10000个请求 ,则自动断开keepalive
protocol.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(1000);
}
});
}
}
- 单web容器上限
线程数量 : 4核Cpu 8G内存单进程调度数800-1000以上即花费巨大的时间在cpu调度上
等待队列长度 : 队列做缓冲池用,但也不能无限长,消耗内存,出对,入队也耗cpu
- mysql 数据库
mysql数据库QPS容量问题
主键查询: 千万级别数据 = 1-10毫秒
唯一索引查询:千万级别数据 = 10-100毫秒
非唯一索引查询: 千万级别数据 = 100-1000毫秒
无索引:百万条数据 = 1000毫秒+
分布式扩展
nginx
1. 单机容量问题 ,水平扩展
表象:单机cpu使用率增高,memory占用增加,网络带宽使用增加
CPU us :用户空间的cpu使用情况(用户层代码)
cpu sy :内核空间的cpu使用情况 系统调用
load avarage :1,5,15 分钟load平均值,跟着核数系数,0代表通常 ,代表打满 1+代表等待阻塞
memory : free 空闲内存 used 使用内存
2. nginx web服务器
location 节点path : 指定url映射key
location 节点内容: root 指定location path后对应的跟路径,index 指定默认的访问页
sbin/nginx -c conf/nginx.conf启动
修改配置后直接sbin/nginx -s reload无缝重启
3. nginx 做反向代理服务器
设置upstream server
设置动态请求location为proxy pass 路径
开启tomcat access log 验证
设置 nginx 与tomcat keepAlive为长连接 :
* keepalive_timeout 60 ;
* proxy_http_version 1.1;
* proxy_set_header Connection "";
4 . nginx 高性能原因
1. epoll 多路复用
* java bio 模型,阻塞进程式
* linux select模型,变更触发轮训查找,有1024数量上限
- java server监听客户端链接,如果某个连接有变化,遍历所有的链接,找到发送变化的一个或者多个,然后执行read操作
* epoll模型,变更触发回调直接读取,理论上无上限
- java server 监听客户端链接,是否有变化,设置回调函数,若有变化则直接唤醒自己并执行回调函数
2. master worker 进程模式
3. 协程机制
* 依附于线程的内存模型,切换开销小
* 遇阻塞及归还执行权,代码同步
* 无需加锁
会话管理
基于cookie 传输sessionid :java tomcat容器session实现迁移到redis
基于token传输类似sessionid :java 代码ssession 实现迁移到redis
查询优化之多级缓存
缓存设计
多级缓存
- redis 缓存
redis sentinal redis 哨兵机制

集群cluster模式

任何一台redis服务器都知道其他redis服务器的状态,当我的 集群中有超过一半的节点存活的话,我对应的集群就任然是可以工作的,项目只需要连接集群中的任意一台服务器就可以知道其他服务器的状态。
当集群发生变化,其中一台服务器崩溃了,所有的内部分片会全部调整,都保持最新的状态,项目按照错误的列表发送给对应节点,如果发现不是调整之后的数据,会直接返回一个reask请求拉取最新的状态
jedis中已经集成了
- 商品详情动态内容实现
使用redis将数据进行缓存,将key和value使用自己的方式进行序列化。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.EnableRedisHttpSession;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@EnableRedisHttpSession(maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds = 3600)
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 修改redis序列化方式
// 首先解决key 的序列化方式
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
//解决value的序列化方式
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
}
- 热点内存本地缓存
热点数据
脏读非常不敏感
内存可控- Guava cache
- 可控制大小和超时时间
- 可配置的lru策略
- 线程安全
- Guava cache
import com.google.common.cache.Cache;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
import com.imooc.miaoshaproject.service.CachService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class CachServiceImpl implements CachService {
private Cache<String, Object> commonCache = null;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// 设置缓存容器的初始容量为10
commonCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(10)
.maximumSize(100)//设置缓存中最大可以存储100个key,超过100个之后会按照LRU的策略移除缓存项目
//设置写缓存后多少秒过期
.expireAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
}
@Override
public void serCommonCache(String key, Object value) {
commonCache.put(key,value);
}
@Override
public Object getFromCommonCache(String key) {
return commonCache.getIfPresent(key);
}
}
- nginx proxy cache缓存
nginx反向代理前置
依靠文件系统存索引级的文件
依靠内存缓存文件地址
申明一个cache缓存节点的内容
proxy_cache_path /usr/local/openresty/nginx/tem_cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=tmp_cache:100m inactive=7d max_size=10g;
proxy_cache tem_cache;
proxy_cache_key $uri;
proxy_cache_valid 200 206 304 7d;
数据是从本地磁盘中读取,不如内存中快,并不推荐
6. nginx lua缓存
lua协程机制
function foo(a)
print("foo 函数输出", a)
return coroutine.yield(2 * a) -- 返回2*a的值
end
co = coroutine.create(function(a, b)
print("第一次协同程序输出", a, b)
local r = foo(a + 1)
print("第二次协同程序输出", r)
local r, s = coroutine.yield(a + b, a - b) --a ,b 的值为第一次调用协同程序是传入
print("第三次协同程序输出", r, s) -- b的值为第二次调用协同程序时传入
return b, "结束协同程序"
end)
print("main",coroutine.resume(co,1,10))
print("------------------")
print("main",coroutine.resume(co,"r"))
print("------------------")
print("main",coroutine.resume(co,"x","y"))
print("------------------")
print("main",coroutine.resume(co,"x","y"))
nginx协程机制
- ngixn 的每个worker进程都只在epoll或kqueue这种时间模型之上,封装成协程。
- 每个请求都有一个协程进行处理
- 即使ngx_lua需要运行lua,相对c有一定的开销,但依旧能保证高并发能力
- nginx每个工作进程创建一个lua虚拟机
- 工作进程内的所有协程共享一个vm
- 每个外部请求由一个lua协程处理,之间数据隔离
- lua代码调用io等异步接口时,协程被挂起,上下文数据
- 自动保存,不阻塞工作进程
- io异步操作完成后还原协程上下文,代码继续执行
-
nginx 处理阶段
1) ngx_http_post_read_phase:
接收到完整的http头部后处理的阶段,它位于uri重写之前,实际上很少有模块会注册在该阶段,默认的情况下,该阶段被跳过。
2)ngx_http_server_rewrite_phase:
uri与location匹配前,修改uri的阶段,用于重定向,也就是该阶段执行处于server块内,location块外的重写指令,在读取请求头的过程中nginx会根据host及端口找到对应的虚拟主机配置。
3)ngx_http_find_config_phase:
根据uri寻找匹配的location块配置项阶段,该阶段使用重写之后的uri来查找对应的location,值得注意的是该阶段可能会被执行多次,因为也可能有location级别的重写指令。
4)ngx_http_rewrite_phase:
上一阶段找到location块后再修改uri,location级别的uri重写阶段,该阶段执行location基本的重写指令,也可能会被执行多次。
5)ngx_http_post_rewrite_phase:
防止重写url后导致的死循环,location级别重写的后一阶段,用来检查上阶段是否有uri重写,并根据结果跳转到合适的阶段。
6)ngx_http_preaccess_phase:
下一阶段之前的准备,访问权限控制的前一阶段,该阶段在权限控制阶段之前,一般也用于访问控制,比如限制访问频率,链接数等。
7)ngx_http_access_phase:
让http模块判断是否允许这个请求进入nginx服务器,访问权限控制阶段,比如基于ip黑白名单的权限控制,基于用户名密码的权限控制等。
8)ngx_http_post_access_phase:
访问权限控制的后一阶段,该阶段根据权限控制阶段的执行结果进行相应处理,向用户发送拒绝服务的错误码,用来响应上一阶段的拒绝。
9)ngx_http_try_files_phase:
为访问静态文件资源而设置,try_files指令的处理阶段,如果没有配置try_files指令,则该阶段被跳过。
10)ngx_http_content_phase:
处理http请求内容的阶段,大部分http模块介入这个阶段,内容生成阶段,该阶段产生响应,并发送到客户端。
11)ngx_http_log_phase:
处理完请求后的日志记录阶段,该阶段记录访问日志。
http无法介入的阶段有4个:
3)ngx_http_find_config_phase
5)ngx_http_post_rewrite_phase
8)ngx_http_post_access_phase
9)ngx_http_try_files_phase
剩余的7个阶段,http模块均能介入,每个阶段可介入模块的个数也是没有限制的,多个http模块可同时介入同一阶段并作用于同一请求。
nginx lua 插载点
init_by_lua: 系统启动时调用
init_worker_by_lua: worker 进程启动时调用
set_by_lua : nginx变量用复杂lua return
rewrite_by_lua: 重写url规则
access_by_lua: 权限验证阶段
content_by_lua: 内容输出节点
使用lua脚本返回数据
location /miaosha/get{
default_type “text/html”
content_by_lua_file …/lua/staticitem.lua;
}
staticitem.lua
ngx.say("hello static item lua")
openResty
- openResty由Nginx核心加很多第三方模块组成,默认集成了lua开发环境,是的nginx可以作为一个 Web Server使用。
- 借助于Nginx的时间驱动模型和非阻塞IO,可以实现高性能的Web应用程序。
- OpenResty 提供了大量组件如Mysql 、Redis、Memcached等等、使在Nginx上开发Web应用更简单方便。
OpenResty 实践
function get_from_cache(key)
local cache_ngx = ngx.shared.my_cache
local value = cache_ngx:get(key)
return value
end
function set_to_cache(key, value, exptime)
if not exptimed then
exptime = 0
end
local cache_ngx = ngx.shared.my_cache
local succ, err, forcible = cache_ngx:set(key, value, exptime)
return succ
end
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args();
local id = args["id"]
local item_model = get_from_cache("item_" .. id)
if item_model == nil then
local resp = ngx.location.capture("/item/get?id="..id)
item_model = resp.body
set_to_cache("item_"..id,item_model,1*60)
end
ngx.say(item_model)
使用openresty中的redis模块连接redis
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
local id = args["id"]
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local cache = redis:new()
local ok, err = cache:connect("11.11.11.11", 6379)
local item_model = cache:get("item" .. id)
if item_model == ngx.null or item_model == nil then
local resp = ngx.location.capture("/item/get?id=" .. id)
item_model = resp.body
end
ngx.say(item_model)
CDN
DNS 用CNAME解析到源站
回源缓存设置
强推失效
全页面静态化
定义:在服务端完成html,css,甚至js的load渲染成纯html 文件后直接以静态资源的方式部署到cdn上
phantomjs
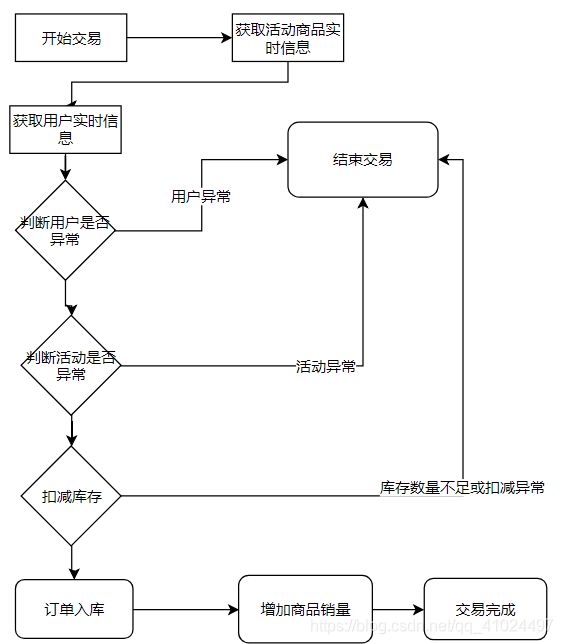
交易优化技术之缓存库存
交易验证优化
- 用户风控策略优化:策略缓存模型化
- 活动校验策略优化:映入活动发布流程,模型缓存化,紧急下线能力
扣减库存缓存化
方案:
- 活动发布同步库存进缓存
- 下单交易减缓存库缓存
- 异步消息扣减数据库内库存
- 问题
- 数据库记录不一致
流量削峰技术
- 抛缺陷
- 秒杀下单接口会被脚本不停的刷
- 秒杀验证逻辑和秒杀下单接口强关联,代码冗余度高
- 秒杀令牌原理
- 秒杀接口需要依靠令牌才能进入
- 秒杀的令牌由活动模块负责生产
- 秒杀活动模块对秒杀令牌生产全权处理,逻辑收口
- 秒杀大闸原理
- 依靠秒杀令牌的授权原理定制化发牌逻辑,做到大闸功能
- 根据秒杀商品初始库存颁发对应数量的令牌,控制大闸流量
- 用户风控策略前置到秒杀令牌发放中
- 库存售尽判断前置到秒杀令牌发放中
- 缺陷:
浪涌流量涌入后系统无法应对
多库存,多商品等令牌限制能力弱
- 队列泄洪原理
- 排队有些时候比并发更高效(列如redis单线程模型,innodb mutex key 等待)
- 依靠排队去限制并发流量
- 依靠排队和下游拥塞窗口程度调整队列释放流量大小
- 支付宝银行网关队列举例
防刷限流技术
- 掌握验证码生成与验证技术
- 包装秒杀令牌前置,需要验证码来错峰
- 数学公式验证码生成器
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.RenderedImage;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
public class CodeUtil {
private static int width = 90;// 定义图片的width
private static int height = 20;// 定义图片的height
private static int codeCount = 4;// 定义图片上显示验证码的个数
private static int xx = 15;
private static int fontHeight = 18;
private static int codeY = 16;
private static char[] codeSequence = {
'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R',
'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9' };
/**
* 生成一个map集合
* code为生成的验证码
* codePic为生成的验证码BufferedImage对象
* @return
*/
public static Map<String,Object> generateCodeAndPic() {
// 定义图像buffer
BufferedImage buffImg = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// Graphics2D gd = buffImg.createGraphics();
// Graphics2D gd = (Graphics2D) buffImg.getGraphics();
Graphics gd = buffImg.getGraphics();
// 创建一个随机数生成器类
Random random = new Random();
// 将图像填充为白色
gd.setColor(Color.WHITE);
gd.fillRect(0, 0, width, height);
// 创建字体,字体的大小应该根据图片的高度来定。
Font font = new Font("Fixedsys", Font.BOLD, fontHeight);
// 设置字体。
gd.setFont(font);
// 画边框。
gd.setColor(Color.BLACK);
gd.drawRect(0, 0, width - 1, height - 1);
// 随机产生40条干扰线,使图象中的认证码不易被其它程序探测到。
gd.setColor(Color.BLACK);
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt(width);
int y = random.nextInt(height);
int xl = random.nextInt(12);
int yl = random.nextInt(12);
gd.drawLine(x, y, x + xl, y + yl);
}
// randomCode用于保存随机产生的验证码,以便用户登录后进行验证。
StringBuffer randomCode = new StringBuffer();
int red = 0, green = 0, blue = 0;
// 随机产生codeCount数字的验证码。
for (int i = 0; i < codeCount; i++) {
// 得到随机产生的验证码数字。
String code = String.valueOf(codeSequence[random.nextInt(36)]);
// 产生随机的颜色分量来构造颜色值,这样输出的每位数字的颜色值都将不同。
red = random.nextInt(255);
green = random.nextInt(255);
blue = random.nextInt(255);
// 用随机产生的颜色将验证码绘制到图像中。
gd.setColor(new Color(red, green, blue));
gd.drawString(code, (i + 1) * xx, codeY);
// 将产生的四个随机数组合在一起。
randomCode.append(code);
}
Map<String,Object> map =new HashMap<String,Object>();
//存放验证码
map.put("code", randomCode);
//存放生成的验证码BufferedImage对象
map.put("codePic", buffImg);
return map;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件输出流对象
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("/Users/hzllb/Desktop/javaworkspace/miaoshaStable/"+System.currentTimeMillis()+".jpg");
Map<String,Object> map = CodeUtil.generateCodeAndPic();
ImageIO.write((RenderedImage) map.get("codePic"), "jpeg", out);
System.out.println("验证码的值为:"+map.get("code"));
}
}
- 限流原理与实现
- 流量远比你想要的多
- 系统活着比挂了要好
- 宁愿只让少数人能用,也不要让所有人不用
- 限流方案
- 限并发
- 令牌桶算法
private ExecutorService executorService; private RateLimiter orderCreateRateLimiter; @PostConstruct public void init(){ executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20); orderCreateRateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(300); } if(orderCreateRateLimiter.acquire() <= 0){ throw new BusinessException(EmBusinessError.RATELIMIT); }- 漏桶算法
- 集群限流:依赖redis或其他中间件技术锁统一计数器,往往会产生性能瓶颈
- 单机限流:负载均衡的前提下单机平均限流效果更好
- 防黄牛技术