ansible
一,ansible安装部署
1,yum安装
[root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release
[root@localhost ~]# yum install ansible -y
注:安装epel源前要先配置网络源
2,ansible的7个命令
(1)ansible
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -a | 后接命令 |
| -m | 执行的模块 |
| -i | 指定路径,默认为/etc/ansible/hosts |
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i /data/ansible/hosts test -a 'date'
192.168.3.40 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 03:53:29 CST 2019
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 03:53:29 CST 2019
[root@localhost ansible]# cat hosts
[test]
192.168.3.8
192.168.3.40
注:默认的模块是command;
(2)ansible-doc
该指令主要用于查看模块信息
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -l | |
| -s | 查看具体某模块的用法 |
(3)ansible-galaxy
该指令用于方便的从https://galaxy.ansible.com/站点下载第三方模块。
(4)ansible-lint
该指令是对playbook的语法进行检查的工具
(5)ansible-playbook
该指令是其通过读取playbook文件后,执行相应的动作
(6)ansible-pull
(7)ansible-valut
3,定义主机和组
hosts文件就是官方说的inventory,默认情况下这个文件是/etc/ansible/hosts,
(1)使用主机变量
[root@localhost ansible]# cat hosts
[test]
192.168.3.8 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
192.168.3.40 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
(2)组内变量
[root@localhost ansible]# cat hosts
[test]
192.168.3.8
192.168.3.40
[test:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
(3)组的包含
[root@localhost ansible]# cat hosts
[test1]
192.168.3.8
[test2]
192.168.3.40
[test:children]
test1
test2
[test:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
4,patterns介绍
patterns部分我们可以理解为正则表达式。
(1)通配符,表示所有的主机可以使用后all或*
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i /data/ansible/hosts 192.168.3.* -a 'date'
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i /data/ansible/hosts all -a 'date'
192.168.3.40 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 04:28:49 CST 2019
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 04:28:55 CST 2019
注:*也可以用在前面
(2)逻辑或
:表示两个组中的所有主机
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i /data/ansible/hosts test1:test2 -a 'date'
192.168.3.40 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 04:31:03 CST 2019
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 04:31:04 CST 2019
(3)逻辑非与逻辑and
目标主机在test1中但不在test2中
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i /data/ansible/hosts test1:\!test2 -a 'date'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 04:33:40 CST 2019
目标主机必须即在test1中又在test中
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i /data/ansible/hosts test1:\&test -a 'date'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Tue Dec 3 04:35:33 CST 2019
注:!前的\表示转义
5,解决ansile在连接时需要输入用户和密码
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:k9xqiVbdp1PGjnmLSUv2nTZEQRsh9gQi9BXSwlsoZYI [email protected]
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| o+o=o*+=.|
| E .=+=o+.o|
| ..+ o.|
| . + o . . |
| S o . * |
| o + O . |
| o + O + |
| . . + B =.|
| + +.o|
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id
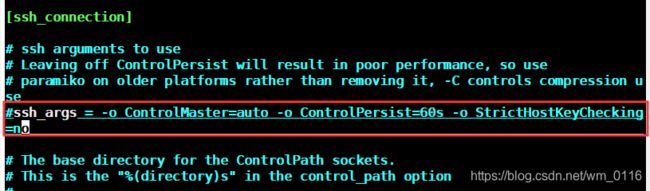
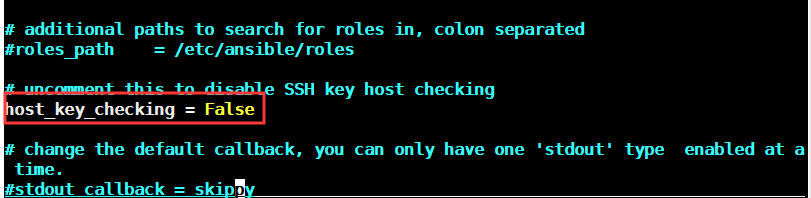
6,避免在ssh连接首次要输入yes/no
[root@localhost ansible]# vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
二,ansible常用模块
1,ping模块
测试主机是否是通的
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m ping
192.168.3.8 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
2,setup模块
获取主机信息
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_ens33'
192.168.3.8 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_ens33": {
"active": true,
"device": "ens33",
"features": {
"busy_poll": "off [fixed]",
"fcoe_mtu": "off [fixed]",
"generic_receive_offload": "on",
"generic_segmentation_offload": "on",
"highdma": "off [fixed]",
"hw_tc_offload": "off [fixed]",
"l2_fwd_offload": "off [fixed]",
"large_receive_offload": "off [fixed]",
"loopback": "off [fixed]",
"netns_local": "off [fixed]",
"ntuple_filters": "off [fixed]",
"receive_hashing": "off [fixed]",
"rx_all": "off",
"rx_checksumming": "off",
"rx_fcs": "off",
"rx_gro_hw": "off [fixed]",
"rx_udp_tunnel_port_offload": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_filter": "on [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_offload": "on",
"rx_vlan_stag_filter": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_stag_hw_parse": "off [fixed]",
"scatter_gather": "on",
"tcp_segmentation_offload": "on",
"tx_checksum_fcoe_crc": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ip_generic": "on",
"tx_checksum_ipv4": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ipv6": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_sctp": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksumming": "on",
"tx_fcoe_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gre_csum_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gre_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gso_partial": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gso_robust": "off [fixed]",
"tx_ipip_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_lockless": "off [fixed]",
"tx_nocache_copy": "off",
"tx_scatter_gather": "on",
"tx_scatter_gather_fraglist": "off [fixed]",
"tx_sctp_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_sit_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp6_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp_ecn_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp_mangleid_segmentation": "off",
"tx_tcp_segmentation": "on",
"tx_udp_tnl_csum_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_udp_tnl_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_offload": "on [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_stag_hw_insert": "off [fixed]",
"udp_fragmentation_offload": "off [fixed]",
"vlan_challenged": "off [fixed]"
},
"hw_timestamp_filters": [],
"ipv4": {
"address": "192.168.3.8",
"broadcast": "192.168.3.255",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "192.168.3.0"
},
"ipv6": [
{
"address": "fe80::20c:29ff:fe2b:757f",
"prefix": "64",
"scope": "link"
}
],
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:2b:75:7f",
"module": "e1000",
"mtu": 1500,
"pciid": "0000:02:01.0",
"promisc": false,
"speed": 1000,
"timestamping": [
"tx_software",
"rx_software",
"software"
],
"type": "ether"
},
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
3,file模块
该模块主要用于远程主机上的文件操作。
| 选项 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| path | 定义文件/目录的路径 |
| group | 定义文件/目录的属组 |
| mode | 定义文件/目录的权限 |
| owner | 定义文件/目录的属主 |
| src | 要被链接的源文件的路径 |
| dest | 要被链接到的路径 |
| state | 如果目录不存在,创建目录 |
| file | 即使文件不存在,也不会被创建 |
| link | 创建软链接 |
| hard | 创建硬链接 |
| absent | 如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新文件,若存在,则更新其最后修改时间 |
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m file -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/fstab state=link"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/tmp/fstab",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0",
"size": 10,
"src": "/etc/fstab",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'ls -l /tmp/fstab'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 10 Dec 3 05:22 /tmp/fstab -> /etc/fstab
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m file -a "path=/tmp/fstab state=absent"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/tmp/fstab",
"state": "absent"
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m file -a "path=/tmp/fstab state=touch"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/tmp/fstab",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'ls -l /tmp/fstab' 192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Dec 3 05:25 /tmp/fstab
4,copy模块
复制文件到远程主机
[root@localhost ansible]# echo "testfile 123" >/tmp/test.txt
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m copy -a "src=/tmp/test.txt dest=/tmp/test.txt owner=foo group=foo mode=0644"
192.168.3.8 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"checksum": "e20312645ff05e44955db099538e5ac135f63de9",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"msg": "chown failed: failed to look up user foo",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/tmp/test.txt",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0",
"size": 13,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'cat /tmp/test.txt' 192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
testfile 123
5,command模块
| 选项 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| creates | 一个文件名,当该文件存在,则该命令不执行 |
| free_form | 要执行的linux指令 |
| chdir | 在执行指令前,先切换到指定的目录 |
| removes | 删除一个文件名,当该文件不存在时,则该选项不执行 |
| executable | 切换shell来执行指令,该执行路径是一个绝对路径 |
若文件存在则不执行echo test,若不存在则执行
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m command -a "creates=/tmp/test.txt echo test"
192.168.3.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
skipped, since /tmp/test.txt exists
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m command -a "creates=/tmp/test.txt echo test"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
test
6,shell模块
用法其本和command一样,不过是其通过/bin/sh执行,因此shell模块可以执行任何命令。
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m shell -a "ps -ef |grep sshd"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
root 7059 1 0 03:30 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
root 7349 7059 0 03:32 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/0
root 7353 7059 0 03:32 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@notty
root 9221 7059 14 05:47 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/1
root 9278 9277 0 05:47 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c ps -ef |grep sshd
root 9280 9278 0 05:47 pts/1 00:00:00 grep sshd
7,raw模块
和shell模块一样,可执行任意命令。
8,script模块
其原理是先将shell复制到远程主机上,再在远程主机上执行。
9,service模块
用于管理服务
| 选项 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| enabled | 是否开机启动 |
| name | 服务名称 |
| sleep | 如果执行了restarted,则在stop和start之间沉睡几秒钟 |
| state | 对当前服务执行started,stopped,restarted,reloded |
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started"
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a "systemctl status httpd"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-12-03 05:54:29 CST; 1min 40s ago
Docs: man:httpd(8)
……
10,cron模块
用于管理计划任务
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m cron -a 'name="check dirs" hour="5,2" job="ls -lha >/dev/null"'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"check dirs"
]
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a "crontab -l"
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: check dirs
* 5,2 * * * ls -lha >/dev/null
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m cron -a 'name="check dirs" state=absent'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
11,filesystem模块
在块设备上创建文件系统
| 选项 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| dev | 目标块设备 |
| force | 在一个已有文件系统的设备上强制创建 |
| fstype | 文件系统的类型 |
| opts | 传递给mkfs命令的选项 |
在机器上添加一块新磁盘
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'fdisk -l'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000c8e4a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 41943039 19921920 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/sdb: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes, 10485760 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m filesystem -a 'fstype=ext4 dev=/dev/sdb'格式化磁盘
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'mkdir /tmp/app'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'ls -l /tmp/app'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
total 0
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m mount -a 'name=/tmp/app src=/dev/sdb fstype=ext4 state=mounted opts=rw' 挂载
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dump": "0",
"fstab": "/etc/fstab",
"fstype": "ext4",
"name": "/tmp/app",
"opts": "rw",
"passno": "0",
"src": "/dev/sdb"
}
12,yum模块
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=latest'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"changes": {
"installed": [
"httpd"
……
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'rpm -qa httpd'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
httpd-2.4.6-88.el7.centos.x86_64
13,user模块和group模块
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m user -a 'name=user password=123456 state=present'
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m shell -a 'cat /etc/passwd |grep user'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
user:x:1000:1000::/home/user:/bin/bash
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m user -a 'name=user remove=yes state=absent' 删除用户
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "user",
"remove": true,
"state": "absent"
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m group -a 'name=user'
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m shell -a 'cat /etc/group |grep user'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
user:x:1000:
14,synchronize模块
使用rsync同步文件
[root@localhost ansible]# echo "hello" >/tmp/hello
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m file -a 'path=/var/www state=directory'
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m synchronize -a 'src=/tmp/hello dest=/var/www'
192.168.3.8 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"cmd": "/usr/bin/rsync --delay-updates -F --compress --archive --rsh=/usr/bin/ssh -S none -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null --out-format=<>%i %n%L /tmp/hello 192.168.3.8:/var/www" ,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"stdout_lines": []
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'cat /var/www/hello'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
hello
注:使用该模块时要先下载rsync,在hosts文件中不能有ansible_ssh_…
15,mount模块
创建设备
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'dd if=/dev/zero of=/disk.img bs=4k count=1024'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
1024+0 records in
1024+0 records out
4194304 bytes (4.2 MB) copied, 0.00442478 s, 948 MB/s
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'losetup /dev/loop1 /disk.img'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
格式化
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m filesystem -a 'fstype=ext3 force=yes opts=-F dev=/dev/loop1'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true
}
挂载
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m mount -a 'name=/mnt src=/dev/loop1 fstype=ext3 state=mounted opts=rw'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dump": "0",
"fstab": "/etc/fstab",
"fstype": "ext3",
"name": "/mnt",
"opts": "rw",
"passno": "0",
"src": "/dev/loop1"
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'df -h'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 1.4G 16G 9% /
devtmpfs 475M 0 475M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 7.7M 479M 2% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sr0 11G 11G 0 100% /media
/dev/sda1 1014M 133M 882M 14% /boot
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/sdb 4.8G 20M 4.6G 1% /tmp/app
/dev/loop1 2.9M 34K 2.7M 2% /mnt
创建文件
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m file -a 'path=/mnt/test.txt state=touch'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/mnt/test.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:unlabeled_t:s0",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -a 'ls /mnt'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
lost+found
test.txt
卸载
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m file -a 'path=/mnt/test.txt state=absent'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/mnt/test.txt",
"state": "absent"
}
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible -i hosts test1 -m mount -a 'name=/mnt src=/dev/loop1 fstype=ext3 state=unmounted'
192.168.3.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dump": "0",
"fstab": "/etc/fstab",
"fstype": "ext3",
"name": "/mnt",
"opts": "defaults",
"passno": "0",
"src": "/dev/loop1"
}