ESP32片外PSRAM
背景
ESP32 提供了520KB的片上SRAM,基本是可以满足大部分需求;但是在用到音频、显示方案的时候就很吃紧了,官方提供了4M的片外SPI RAM,实现内存的扩展与映射,大大提高了应用的范围
CPU0 CPU1会占用64K的SRAM用作Cache,而且系统FreeRtos启动后也会使用一部分,跳转到app_main入口后,留给用户的实际ram也就100多Kb
硬件
ESP32支持与SPI Flash芯片并联的SPI PSRAM,ESP32接口可以支持多种类型的RAM芯片,但是IDF仅支持ESP-PSRAM芯片
ESP-PSRAM32 芯片的工作电压为 1.8 V,只能与 1.8 V flash 并联使用。请确保在启动时将 MTDI 管脚设置为高电平,或者将 ESP32 中的熔丝设置为始终使用 1.8 V 的 VDD_SIO 电平,否则有可能会损坏 PSRAM 和/或 flash 芯片。
连接线序
PSRAM的CLK和CS引脚可以使用任何未被占用的GPIO,但是如果硬件系统使用的是1.8V的flash和psram,那么只能选择的指定的IO口GPIO[6,7,8,9,10,11,16,17]
| PSRAM引脚 | ESP32引脚 |
|---|---|
| CS (pin 1) | 默认GPIO16(可调整) |
| SO (pin 2) | flash DO(GPIO7) |
| SIO[2] (pin 3) | flash WP(GPIO10) |
| SI (pin 5) | flash DI(GPIO8) |
| SCLK (pin 6) | 默认GPIO17(可调整) |
| SIO[3] (pin 7) | flash HOLD(GPIO9) |
乐鑫提供 ESP32-WROVER 模组,内部搭载 ESP32 芯片,并集成 1.8 V flash 和 ESP-PSRAM32,可直接用于终端产品 PCB 中
PSRAM配置与使用
使能片外RAM内存映射
通过打开idf.py menuconfig启动配置器,勾选CONFIG_ESP32_SPIRAM_SUPPORT使能片外RAM, 选项SPI RAM config可进行高级功能配置
Component config > ESP32-specific > CONFIG_ESP32_SPIRAM_SUPPORT > SPI RAM config
- 使能片外RAM后,ESP-IDF启动过程中,片外RAM被映射到以
0x3F800000起始的数据地址空间(字节可寻址),空间大小正好为 RAM 的大小 (4 MB) - 应用程序可以通过创建指向该区域的指针手动将数据放入片外存储器,同时应用程序全权负责管理片外 RAM,包括协调 Buffer 的使用、防止发生损坏等
片外RAM内存分配
内存分配时可通过标识符MALLOC_CAP_SPIRAM指定片外存储器中分配存储空间,调用接口heap_caps_malloc(size, MALLOC_CAP_SPIRAM)分配堆空间,调用free()释放
自动分配
保证提高片内高性能RAM的利用,即优先考虑的内部没有可用的存储块,当内部RAM分配不足时,程序则会选择片外存储分配
可通过配置, 高级选项SPI RAM access method,默认选择Make RAM allocatable using malloc() as well
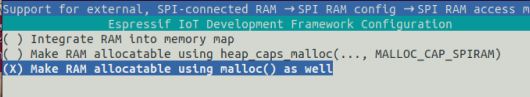
然后通过选项Maximum malloc() size配置分配空间的大小阈值,控制分配结果

- 如果分配的空间小于阈值,分配程序将首先选择内部存储器
- 如果分配的空间等于或大于阈值,分配程序将首先选择外部存储器
内部存储保留
为了防止内部内存被完全使用完的情况,导致有些仅可在内部存储器中分配Buffer申请失败,需要使用第二个配置项 CONFIG_SPIRAM_MALLOC_RESERVE_INTERNAL 定义一个内部存储池,常规 malloc() 将不会从该池中分配,仅限显式的内部存储器分配使用(例如用于 DMA 的存储器,标识符MALLOC_CAP_DMA 和 MALLOC_CAP_INTERNAL)
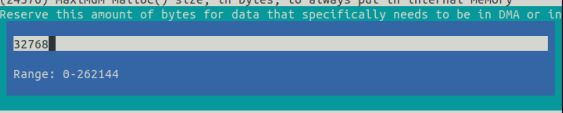
freertos堆栈会强制使用内部存储,调整该值时,需要考虑到
启动自检
CONFIG_SPIRAM_MEMTEST:SPI RAM初始化时进行内存测试,不勾选可以加快系统启动速度

wifi与lwip分配
CONFIG_SPIRAM_TRY_ALLOCATE_WIFI_LWIP:优先从PSRAM中分配wifi和lwip协议栈内存,如果分配失败,从内部RAM中进行分配
![]()
允许.bss段放入片外存储器
设置CONFIG_SPIRAM_ALLOW_BSS_SEG_EXTERNAL_MEMORY启用该选项,可以减少 BSS 段占用的内部静态存储

启用该选项后,从 0x3F800000 起始的地址空间将用于存储来自 lwip、net80211、libpp 和 bluedroid ESP-IDF 库中零初始化的数据(BSS 段)
标识符EXT_RAM_ATTR 宏应用于任何静态声明(未初始化为非零值)之后,可以将附加数据从内部 BSS 段移到片外 RAM
外部RAM创建任务堆栈
当需要创建大量堆栈的任务,内部内存空间无法满足时,可以通过xTaskCreateStatic在外部RAM中创建任务堆栈
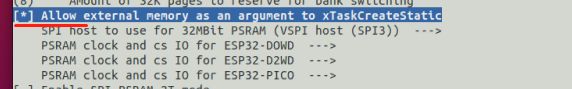
// Dimensions the buffer that the task being created will use as its stack.
// NOTE: This is the number of bytes the stack will hold, not the number of
// words as found in vanilla FreeRTOS.
#define STACK_SIZE 200
// Structure that will hold the TCB of the task being created.
StaticTask_t xTaskBuffer;
// Buffer that the task being created will use as its stack. Note this is
// an array of StackType_t variables. The size of StackType_t is dependent on
// the RTOS port.
EXT_RAM_ATTR StackType_t xStack[ STACK_SIZE ]; //静态缓存声明到外部RAM
// Function that implements the task being created.
void vTaskCode( void * pvParameters )
{
// The parameter value is expected to be 1 as 1 is passed in the
// pvParameters value in the call to xTaskCreateStatic().
configASSERT( ( uint32_t ) pvParameters == 1UL );
for( ;; )
{
// Task code goes here.
}
}
// Function that creates a task.
void vOtherFunction( void )
{
TaskHandle_t xHandle = NULL;
// Create the task without using any dynamic memory allocation.
xHandle = xTaskCreateStatic(
vTaskCode, // Function that implements the task.
"NAME", // Text name for the task.
STACK_SIZE, // Stack size in bytes, not words.
( void * ) 1, // Parameter passed into the task.
tskIDLE_PRIORITY,// Priority at which the task is created.
xStack, // Array to use as the task's stack.
&xTaskBuffer ); // Variable to hold the task's data structure.
// puxStackBuffer and pxTaskBuffer were not NULL, so the task will have
// been created, and xHandle will be the task's handle. Use the handle
// to suspend the task.
vTaskSuspend( xHandle );
}
PSRAM使用限制
- Flash cache 禁用时(比如,正在写入 flash),片外 RAM 将无法访问;同样,对片外 RAM 的读写操作也将导致 cache 访问异常。出于这个原因,ESP-IDF 不会在片外 RAM 中分配任务堆栈(详见下文)。
- 片外 RAM 不能用于储存 DMA 描述符,也不能用作 DMA 读写操作的缓冲区 (Buffer)。与 DMA 搭配使用的 Buffer 必须先使用 heap_caps_malloc(size, MALLOC_CAP_DMA) 进行分配,之后可以调用标准 free() 回调释放 Buffer。
- 片外 RAM 与片外 flash 使用相同的 cache 区域,即频繁在片外 RAM 访问的变量可以像在片上 RAM 中一样快速读取和修改。但访问大块数据时(大于 32 KB),cache 空间可能会不足,访问速度将回落到片外 RAM 访问速度。此外,访问大块数据可以“挤出” flash cache,可能会降低代码执行速度。
- 片外 RAM 不可用作任务堆栈存储器。因此 xTaskCreate() 及类似函数将始终为堆栈和任务 TCB 分配片上储存器,而 xTaskCreateStatic() 类型的函数将检查传递的 Buffer 是否属于片上存储器。
- 默认情况下,片外 RAM 初始化失败将终止 ESP-IDF 启动。如果想禁用此功能,可启用 CONFIG_SPIRAM_IGNORE_NOTFOUND 配置选项。如果启用 CONFIG_SPIRAM_ALLOW_BSS_SEG_EXTERNAL_MEMORY,CONFIG_SPIRAM_IGNORE_NOTFOUND 选项将不能使用,这是因为在链接时,链接器已经向片外 RAM 分配符号。
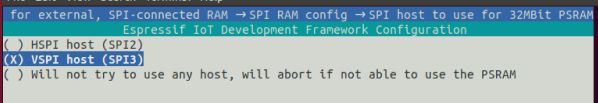
- 当PSRAM使用80Mhz的时钟频率时,PSRAM需要占用
HSPI或VSPI总线
芯片版本
ESP32在迭代过程中,不同的版本存在一些问题,会影响到外部ram的使用,详细查看勘误手册
