React生命周期执行顺序详解
目录
一、Ract生命周期
二、React生命周期执行顺序详解
一、组件生命周期的执行次数是什么样子的???
二、组件的生命周期执行顺序是什么样子的???
三、什么时候该用componentWillReceiveProps?
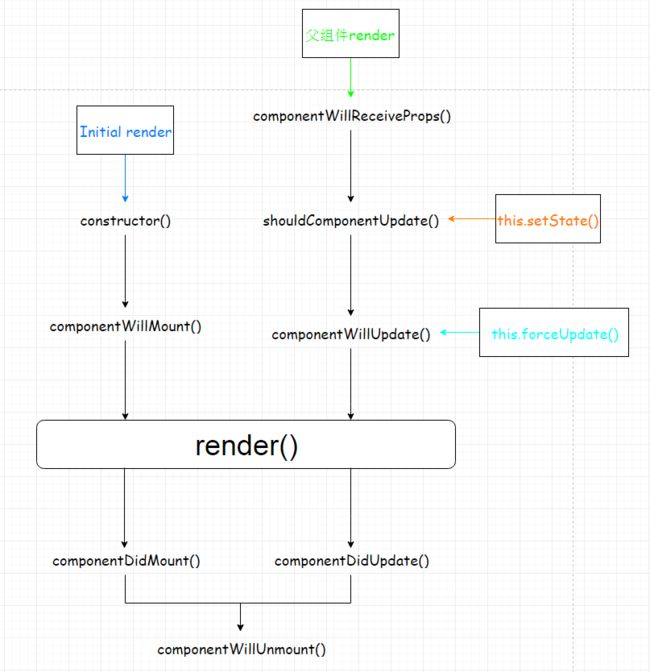
有状态组件从挂在到卸载经历一下生命周期:
constructor() {
super() // 必须在定义在内部state之前
} // super指代父类实例,调用super继承父类的this对象
UNSAFE_componentWillMount(){} //组件即将加载componentWillMount在16.3.0被弃用但目前前依然可用,以下UNSAFE_开头的均同理
render(){} //组件被渲染
componentDidMount(){} //组件已加载
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps){} // 组件将要从父组件获得props
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState){} // 是否确认重新渲染组件
render() {} // 重新渲染组件
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(){} // 组件将要更新
componentDidUpdate(){} // 组价被更新
componentWillUnmount(){} // 组件将要卸载
一、Ract生命周期
React 生命周期分为三种状态 1. 初始化 2.更新 3.销毁
![]()
- 初始化
1、getDefaultProps()
设置默认的props,也可以用dufaultProps设置组件的默认属性.
2、getInitialState()
在使用es6的class语法时是没有这个钩子函数的,可以直接在constructor中定义this.state。此时可以访问this.props
3、componentWillMount()
组件初始化时只调用,以后组件更新不调用,整个生命周期只调用一次,此时可以修改state。
4、 render()
react最重要的步骤,创建虚拟dom,进行diff算法,更新dom树都在此进行。此时就不能更改state了。
5、componentDidMount()
组件渲染之后调用,只调用一次。
- 更新
6、componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)
组件初始化时不调用,组件接受新的props时调用。
7、shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
react性能优化非常重要的一环。组件接受新的state或者props时调用,我们可以设置在此对比前后两个props和state是否相同,如果相同则返回false阻止更新,因为相同的属性状态一定会生成相同的dom树,这样就不需要创造新的dom树和旧的dom树进行diff算法对比,节省大量性能,尤其是在dom结构复杂的时候
8、componentWillUpdata(nextProps, nextState)
组件初始化时不调用,只有在组件将要更新时才调用,此时可以修改state
9、render()
组件渲染
10、componentDidUpdate()
组件初始化时不调用,组件更新完成后调用,此时可以获取dom节点。
- 卸载
11、componentWillUnmount()
组件将要卸载时调用,一些事件监听和定时器需要在此时清除。
二、React生命周期执行顺序详解
一、组件生命周期的执行次数是什么样子的???
只执行一次: constructor、componentWillMount、componentDidMount
执行多次:render 、子组件的componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate、componentDidUpdate
有条件的执行:componentWillUnmount(页面离开,组件销毁时)
不执行的:根组件(ReactDOM.render在DOM上的组件)的componentWillReceiveProps(因为压根没有父组件给传递props)二、组件的生命周期执行顺序是什么样子的???
假设组件嵌套关系是 App里有parent组件,parent组件有child组件。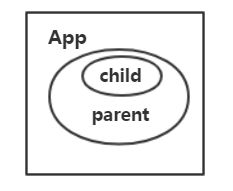
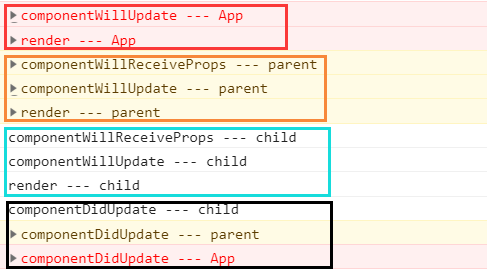
App: constructor --> componentWillMount --> render -->
parent: constructor --> componentWillMount --> render -->
child: constructor --> componentWillMount --> render -->
componentDidMount (child) --> componentDidMount (parent) --> componentDidMount (App)
这时候触发App的setState事件
App: componentWillUpdate --> render -->
parent: componentWillReceiveProps --> componentWillUpdate --> render -->
child: componentWillReceiveProps --> componentWillUpdate --> render -->
componentDidUpdate (child) --> componentDidUpdate (parent) --> componentDidUpdate (App)那如果是触发parent的setState呢?
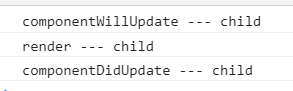
parent: componentWillUpdate --> render -->
child: componentWillReceiveProps --> componentWillUpdate --> render -->
componentDidUpdate (child) --> componentDidUpdate (parent) 那如果是只是触发了child组件自身的setState呢?
child: componentWillUpdate --> render --> componentDidUpdate (child)结论:
-
如图:完成前的顺序是从根部到子部,完成时时从子部到根部。(类似于事件机制)
-
每个组件的红线(包括初次和更新)生命周期时一股脑执行完毕以后再执行低一级别的红线生命周期。
- 第一级别的组件setState是不能触发其父组件的生命周期更新函数,只能触发更低一级别的生命周期更新函数。
总结起来就如下图:
提问:
那么这里提一个问题,如果App里面有多个parent1 parent2 ...,parent里由多个child,那么生命周期执行顺序应该时什么样的????
结论:
一套组件(父包括子,子包括孙)执行的时候一个整体,执行完毕在执行下一套,用到这里就是App里先执行parent1和parent1的子,子的子。。。,然后完毕再执行parent2这一套。
三、什么时候该用componentWillReceiveProps?
是否每个子组件都需要componentWillReceiveProps生命周期函数来更新数据吗? 你的原则是??
A、开始前首先需要知道componentWillReceiveProps函数有一个参数nextProps,它是一个 { 对象 } ,从单词就可以看出它是update时候(也就是下一次)父组件传递过来的props。
B、还要知道 "第一条中" 所讲解的有些生命周期函数只执行一次,而有的执行多次,其中componentWillReceiveProps执行多次,而constructor等执行一次。
C、还需知道在子组件中每次传递过来的this.props对象其实和componentWillReceiveProps的nextProps是一样的,都是最新的。
D、由"第一条"得知: componentWillReceiveProps生命周期是在更新子组件最先执行的,优先于compoentWillUpdate,更优先于render。
E、render函数里不能使用setState(),否则会造成死循环。
那么知道了以上呢?
由C得知, this.props 和 componentWillReceiveProps的nextProps都是一样的,通过this.props就可以取到最新的值, 那么componentWillReceiveProps还有必要吗?
所以:大部分情况下 componentWillReceiveProps 生命周期函数是没用的,即可以略去不写,因为它确实没什么用。
但是情况1:
由D得知,componentWillReceiveProps是最先执行的,所以在其内可以setState({}),在接下来的render中能拿到最新的state后值,再加上B得知,
如果是下面这种情况: 在constructor函数中初始化了某个state,必须用 componentWillReceiveProps 来更新state,以便render中为新的state值。
情况2:
如果父组件有一些请求,每次参数更新的时候才发请求,同时和子组件的关系比较密切,
可以将数据请求放在componentWillReceiveProps进行执行,需要传的参数则从(nextProps)中获取。
而不必将所有的请求都放在父组件中,于是该请求只会在该组件渲染时才会发出,从而减轻请求负担。
情况3:
watch监听props值变化,对子组件进行处理,比如:当传入的props.value发生变化,执行一些动作。
如果你接触过vue,会知道vue中有一个关于watch的选项,是根据setter获取新旧值,进行动作的执行
而react中最合适做watch的时机是在componentWillReceiveProps中
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
// this.props中的值是旧值
// nextProps中的值是新值
const { value: oldValue } = this.props;
const { value: newValue } = nextProps;
if (newValue !== oldValue) {
// TODO...
}
}结论:
-
大部分情况下 componentWillReceiveProps 生命周期函数是没用的,即可以略去不写,
-
但是在constructor函数中初始化了某个state,必须用 componentWillReceiveProps 来更新state,不可省去,否则render中的state将得不到更新。
同时如果您想在子组件监听watch值变化做处理,也可以用到componentWillReceiveProps -
使用componentWillReceiveProps的时候,不要去向上分发,调用父组件的相关setState方法,否则会成为死循环。
附:React生命周期官方解析
componentWillMount 在渲染前调用,在客户端也在服务端。
componentDidMount : 在第一次渲染后调用,只在客户端。之后组件已经生成了对应的DOM结构,可以通过this.getDOMNode()来进行访问。 如果你想和其他JavaScript框架一起使用,可以在这个方法中调用setTimeout, setInterval或者发送AJAX请求等操作(防止异步操作阻塞UI)。
componentWillReceiveProps 在组件接收到一个新的 prop (更新后)时被调用。这个方法在初始化render时不会被调用。
shouldComponentUpdate 返回一个布尔值。在组件接收到新的props或者state时被调用。在初始化时或者使用forceUpdate时不被调用。
可以在你确认不需要更新组件时使用。
componentWillUpdate在组件接收到新的props或者state但还没有render时被调用。在初始化时不会被调用。
componentDidUpdate 在组件完成更新后立即调用。在初始化时不会被调用。
componentWillUnmount在组件从 DOM 中移除的时候立刻被调用。分类: React
参考博客:
React组件生命周期小结:https://blog.csdn.net/hahahhahahahha123456/article/details/80270353
React组件生命周期流程与调用顺序及setState在生命周期中的使用注意事项:https://blog.csdn.net/Gunahao/article/details/82695555
React生命周期执行顺序详解:
https://www.cnblogs.com/soyxiaobi/p/9559117.html