Java源码分析(四)--String
java.long.String
字符串操作可以说是相当美妙了,String类作为其中的典范,值得研究一番。
类定义:
以字符数组为字符串的value,设置为final,不可更改。
hash值是String常用的量了,根据后面的hashCode()方法得到,因为这是private,所以不用随value值更改,需要时再通过hashCode()计算,这是没问题的。
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
/**
* Class String is special cased within the Serialization Stream Protocol.
*
* A String instance is written into an ObjectOutputStream according to
*
* Object Serialization Specification, Section 6.2, "Stream Elements"
*/
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =
new ObjectStreamField[0];构造函数:
/**
* 默认构造器产生了一个length为1的char数组,并初始化
* hash值为0(默认)
*/
public String() {
this.value = new char[0];
}
/**
* String -> String
*/
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
/**
* char[] -> String
* hash值没有设置...
*/
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
/*
* StringBuffer -> String
* 用synchronized修饰了赋值过程
*/
public String(StringBuffer buffer) {
synchronized(buffer) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(buffer.getValue(), buffer.length());
}
}
/*
* StringBuffer -> String
* 和StringBuffer相似,但没有synchronized关键字
*/
public String(StringBuilder builder) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(builder.getValue(), builder.length());
}
/*
* 下面两个严格来说,没有单参数传入的构造方法,而是需要起始位置与长度的限制
* (byte[]单参数传递,是调用的三参数方法;而int[]没有单参数方法)
*
* byte[] -> String
* 涉及了StringCoding.decode,与解码方式相关,不常用就暂时略过了
* public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length){
* ...
* }
*
* int[] -> String
* public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count){
* ···
* }
*/
常用方法:
charAt(int) :
先进行越界判断,再读取
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}compareTo(string) :
并没有通过hash值判断,这是当然的,hash可是能多个值命中同一点。
所以遍历判断
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;//返回当前字符之差
}
k++;
}
//如果前面的字符相等,那就返回长度之差
return len1 - len2;
}contains(CharSequence) : 判断是否包含字符序列
indexOf() : 查看是否包含某个数据
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1;
}
//很多层转换:
// ·
// ·
// ·
static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
/*
*
* Code shared by String and StringBuffer to do searches. The
* source is the character array being searched, and the target
* is the string being searched for.
*
* @param source the characters being searched.
* @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
* @param sourceCount count of the source string.
* @param target the characters being searched for.
* @param targetOffset offset of the target string.
* @param targetCount count of the target string.
* @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
* 有两个数组的各项参数,就可以进行判断了
*/
//欲匹配数组长度为0 一定能匹配,return 0;
if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) {
return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1);
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
}
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
char first = target[targetOffset];
int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount);
for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) {
/* Look for first character. 第一个字符匹配*/
if (source[i] != first) {
while (++i <= max && source[i] != first);
}
/* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2
* 后续匹配
*/
if (i <= max) {
int j = i + 1;
int end = j + targetCount - 1;
for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j]
== target[k]; j++, k++);
if (j == end) {
/* Found whole string. */
return i - sourceOffset;
}
}
}
return -1;
}copyValueOf:
调用了构造函数
public static String copyValueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}equals():
equals方法很重要,但机制却十分简单,首先检查是否为同一对象,若不是再去判断对应位是否相等。
注意:”==” 只是判断是否为同一对象
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
//先判断是否为同一对象
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
//依次检查value[]的每个对应位是否相等
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}hashCode():常用的String的hash,第k位对应31的k-1次幂,很容易推导
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}isEmpty():查看value.length(),判断是否为空
replace(char oldChar, char newChar): 将String里所有的oldChar替换成newChar
replace意外的有些复杂,
先复制value产生一个char[] buf,按replace修改后再调用构造函数,传入buf,
生成新的String后返回它。
这里先判断了是否需要更改,需要再去new,而不更改的话,直接返回该句柄
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = value.length;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode
只是指针,不能修改值*/
/*
* 先找第一个不满足的点
*/
while (++i < len) {
if (val[i] == oldChar) {
break;
}
}
/**
* 如果需要更改,才新建数组,新建String
*
* 如果简单的直接用下面的代码
* 所有样例都进行new String
* 可以想象,会造成许多空间浪费
*/
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];//新建可变char[]
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
buf[j] = val[j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
i++;
}
return new String(buf, true);//调用String构造方法
}
}
return this;
}spilt(String regex, int limit) :分割字符串
看样例,很清晰
The string "boo:and:foo", for example, yields the following results with these parameters:
Regex Limit Result
: 2 { "boo", "and:foo" }
: 5 { "boo", "and", "foo" }
: -2 { "boo", "and", "foo" }
o 5 { "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" }
o -2 { "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" }
o 0 { "b", "", ":and:f" }
boolean startWith(String prefix,int toffset): 是否在第toffset位以prefix开头
String subString() : 调用构造方法生成新的String
char[] toCharArrays() : 新建字符数组,通过System.arraycopy接口赋值,并返回
toLowerCase() :
相当复杂,使用给定Locale的规则将此String中的所有字符转换为小写。
大小写映射基于Character类指定的Unicode标准版本。
由于大小写映射并不总是1:1字符映射,
因此生成的字符串可能与原始字符串的长度不同。
所以还涉及到空间增长grow()的情况,是数组的增长方式trim() : 去除首尾空格
标记首尾第一个有效值:st,len,调用substring(st, len)
valueOf() : 可以把各种数据转换为String
toString():return this;
使用要点:
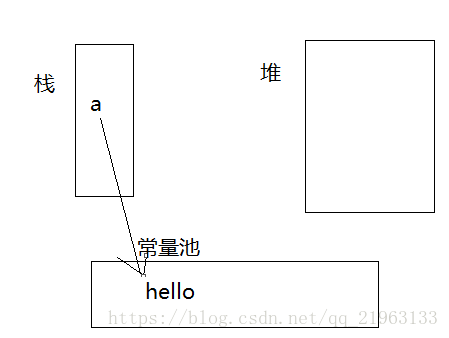
一:String在内存中的存储形式。
一般我们声明一个字符串有两种方式
1.String a = “hello”;
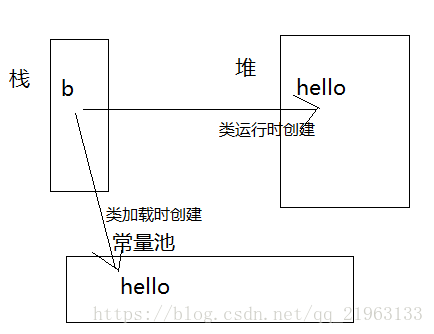
2.String b = new String(“hello”);
第一种方式创建了一个对象hello,且存在于常量池中。
第二种则会创建一个或者两个对象,如果常量池中有hello,则只会创建一个,否则会创建两个。(面试题中常会出现)
二:equals() 与 ==
== 判断是否为同一对象
equals 首先判断是否同一对象,再进行值相等的判断,见前面方法解释