C++常见面试题整理
1 最大最小堆
最小堆pop最小的,最大堆pop最大的
设计一个算法,找出数组中最小的k个数。以任意顺序返回这k个数均可
//最大堆
class Solution {
public:
vector smallestK(vector& arr, int k) {
priority_queue, less> maxHeap;
vector out;
for(auto x:arr)
{
maxHeap.push(x);
if(maxHeap.size()>k)
maxHeap.pop();
}
while(!maxHeap.empty())
{
out.push_back(maxHeap.top());
maxHeap.pop();
}
return out;
}
}; 在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
//最小堆
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector& nums, int k) {
priority_queue, greater> minHeap;
for(auto x: nums)
{
minHeap.push(x);
if(minHeap.size()>k)
minHeap.pop();
}
return minHeap.top();
}
}; 2 关于DFS and 去重
给定一个整型数组, 你的任务是找到所有该数组的递增子序列,递增子序列的长度至少是2。
示例:
输入: [4, 6, 7, 7]
输出: [[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 7, 7], [6, 7], [6, 7, 7], [7,7], [4,7,7]]
那如何保证没有重复呢?我们需要给「不选择」做一个限定条件,只有当当前的元素不等于上一个选择的元素的时候,才考虑不选择当前元素,直接递归后面的元素。因为如果有两个相同的元素,我们会考虑这样四种情况:【从小(两个连续数)入手考虑重复性问题】
- 前者被选择,后者被选择
- 前者被选择,后者不被选择
- 前者不被选择,后者被选择
- 前者不被选择,后者不被选择
其中第二种情况和第三种情况其实是等价的,我们这样限制之后,舍弃了第二种,保留了第三种,于是达到了去重的目的。
这个去重我喜欢
class Solution {
public:
vector temp;
vector> ans;
void dfs(int cur, int last, vector& nums) {
if (cur == nums.size()) {
if (temp.size() >= 2) {
ans.push_back(temp);
}
return;
}
if (nums[cur] >= last) {
temp.push_back(nums[cur]);
dfs(cur + 1, nums[cur], nums);
temp.pop_back();
}
if (nums[cur] != last) {
dfs(cur + 1, last, nums);
}
}
vector> findSubsequences(vector& nums) {
dfs(0, INT_MIN, nums);
return ans;
}
}; 3 哈希表unordered_map 哈希的查找复杂度为O(1)
两个(具有不同单词的)文档的交集(intersection)中元素的个数除以并集(union)中元素的个数,就是这两个文档的相似度。例如,{1, 5, 3} 和 {1, 7, 2, 3} 的相似度是 0.4,其中,交集的元素有 2 个,并集的元素有 5 个。给定一系列的长篇文档,每个文档元素各不相同,并与一个 ID 相关联。它们的相似度非常“稀疏”,也就是说任选 2 个文档,相似度都很接近 0。请设计一个算法返回每对文档的 ID 及其相似度。只需输出相似度大于 0 的组合。请忽略空文档。为简单起见,可以假定每个文档由一个含有不同整数的数组表示。
输入为一个二维数组 docs,docs[i] 表示 id 为 i 的文档。返回一个数组,其中每个元素是一个字符串,代表每对相似度大于 0 的文档,其格式为 {id1},{id2}: {similarity},其中 id1 为两个文档中较小的 id,similarity 为相似度,精确到小数点后 4 位。以任意顺序返回数组均可。
示例:
输入:
[
[14, 15, 100, 9, 3],
[32, 1, 9, 3, 5],
[15, 29, 2, 6, 8, 7],
[7, 10]
]
输出:
[
"0,1: 0.2500",
"0,2: 0.1000",
"2,3: 0.1429"
]
这个题来学习哈希挺好的
class Solution {
public:
vector computeSimilarities(vector>& docs) {
unordered_map> mp1;
for(int i=0;i> mp2;
for(auto& item: mp1)
{
auto ids = item.second;
for(int i=0;i result;
char temp[256];
for(auto& item:mp2)
{
int id1 = item.first;
for(auto& item2: item.second)
{
int id2 = item2.first;
double similary = (double)item2.second/(docs[id1].size()+docs[id2].size()-item2.second);
//#include sprintf(buffer, format, in) buffer是一个str缓冲区Write formatted data to string
sprintf(temp, "%d,%d: %0.4f", id1,id2,similary+1e-9);
result.push_back(temp);
}
}
return result;
}
}; 4 了解位运算中的状态机
在一个数组 nums 中除一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。请找出那个只出现一次的数字。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,4,3,3]
输出:4
示例 2:
输入:nums = [9,1,7,9,7,9,7]
输出:1
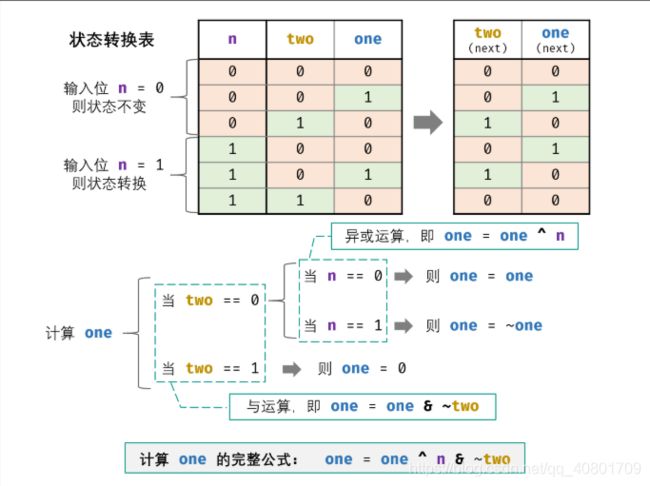
两位 two one表示各bit位出现次数,出现三次刚好恢复至0
关键设计状态机
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
ones, twos = 0, 0
for num in nums:
ones = ones ^ num & ~twos
twos = twos ^ num & ~ones
return ones
5 多指针法
丑数
有些数的素因子只有 3,5,7,请设计一个算法找出第 k 个数。注意,不是必须有这些素因子,而是必须不包含其他的素因子。例如,前几个数按顺序应该是 1,3,5,7,9,15,21。
示例 1:
输入: k = 5
输出: 9
class Solution {
public:
int getKthMagicNumber(int k) {
vector res(k);
res[0] = 1;
int a=0,b=0,c=0; //三指针
for(int i=1; i 超级丑数,多指针法:
class Solution {
public:
int nthSuperUglyNumber(int n, vector& primes) {
vector ptr(primes.size(),0); // 多指针
vector res(n);
res[0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i 至于1201. 丑数 III
用这个方法会超时,需改用二分查找,思路就是确定0-count_n之间有多少个丑数的二分,有点难,关键count_n计算,感觉[low,mid]的count不如理解为[0,mid]可以明白思路一点,到找到符合的mid时,肯定>=实际第n个,这个时候减去最小余数就可以,比如mid=100是我要找的,但0-101【mid=101】区间也满足啊,101%2==1,把1减去,就是我要的100了。顺便记录个代码做个笔记。至于count的理解,我也不是很理解。
class Solution {
public:
using LL = long long;
int nthUglyNumber(int n, int a, int b, int c) {
//看到n的范围应该马上联想到是,典型的二分思路
LL low = min(min(a,b),c); //下边界显然是a、b、c中最小者
LL high = static_cast(low) * n; //上边界是这个最小者的n倍
LL res = Binary_Search(low,high,a,b,c,n);
LL left_a = res%a;
LL left_b = res%b;
LL left_c = res%c;
return res - min(left_a,min(left_b,left_c));
}
//二分搜索
LL Binary_Search(LL low,LL high,int a,int b,int c,LL n){
if(low >= high) return low;
LL mid = (low + high)>>1;
LL MCM_a_b = MCM(a,b);
LL MCM_a_c = MCM(a,c);
LL MCM_b_c = MCM(b,c);
LL MCM_a_b_c = MCM(MCM_a_b,c);
//独立的丑数个数为,当前数分别除以a、b、c的和,减去当前数除以a、b、c两两间最小公倍数的和,再加上当前数除以 a、b、c三者的最小公倍数
LL count_n = mid/a + mid/b + mid/c - mid/MCM_a_b - mid/MCM_b_c - mid/MCM_a_c + mid/MCM_a_b_c;
if(count_n == n) return mid;
if(count_n < n) return Binary_Search(mid + 1,high,a,b,c,n);
return Binary_Search(low,mid-1,a,b,c,n);
}
//求最小公倍数:两数乘积除以最大公约数
LL MCM(LL a,LL b){
LL Multi = a * b;
//又名辗转相除法
while(b > 0){
LL tmp = a % b;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
return Multi/a;
}
}; 6 三数之和
输入:A = [1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5], target = 8
输出:20
解释:
按值枚举(A[i],A[j],A[k]):
(1, 2, 5) 出现 8 次;
(1, 3, 4) 出现 8 次;
(2, 2, 4) 出现 2 次;
(2, 3, 3) 出现 2 次。
三指针,写的比较稀碎
class Solution {
public:
int threeSumMulti(vector& A, int target) {
long long res=0;
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
int mod = 1e9+7;
for(int i=0;i 大佬的动态规划,解决所有多指针问题,佩服
class Solution {
public:
int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int threeSumMulti(vector& A, int target) {
//dp[i][j][k]表示考虑前i个数时,从中选出j个数,组成k大小的方案数
int n = A.size();
int dp[n + 1][4][target + 1];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) dp[i][0][0] = 1;
//这里要从1开始,因为前0个数是初始的条件
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j ++ )
for (int k = 0; k <= target; k ++ )
{
//这里用A[i - 1]是因为从1开始枚举下标,对于A数组来说,要从0开始,因此错后一个
if (k >= A[i - 1]) dp[i][j][k] =(dp[i][j][k] + dp[i - 1][j - 1][k - A[i - 1]]) % mod;
dp[i][j][k] = (dp[i][j][k] + dp[i - 1][j][k]) % mod;
}
//最终答案就是考虑前n个数时,选择其中3个数,组成target大小的方案数
return dp[n][3][target];
}
}; 7. 统计封闭岛屿的数目
有一个二维矩阵 grid ,每个位置要么是陆地(记号为 0 )要么是水域(记号为 1 )。
我们从一块陆地出发,每次可以往上下左右 4 个方向相邻区域走,能走到的所有陆地区域,我们将其称为一座「岛屿」。
如果一座岛屿 完全 由水域包围,即陆地边缘上下左右所有相邻区域都是水域,那么我们将其称为 「封闭岛屿」。
请返回封闭岛屿的数目。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0],[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0],[1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0],[1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]]
输出:2
解释:
灰色区域的岛屿是封闭岛屿,因为这座岛屿完全被水域包围(即被 1 区域包围)。
BFS,广度优先搜索,把遍历过的点置1.
class Solution {
public:
int closedIsland(vector>& grid) {
int row = grid.size();
if(!row) return 0;
int col = grid[0].size();
int islands = 0;
queue> que;
for(int i=0;i-1 && grid[curPos.first-1][curPos.second]==0)
{
if(curPos.first-1==0) cut=1;
grid[curPos.first-1][curPos.second]=1;
que.emplace(curPos.first-1,curPos.second);
}
if(curPos.first+1-1 && grid[curPos.first][curPos.second-1]==0)
{
if(curPos.second-1==0) cut=1;
grid[curPos.first][curPos.second-1]=1;
que.emplace(curPos.first,curPos.second-1);
}
if(curPos.second+1
8 BFS【考察递归迭代】
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例 :
给定二叉树
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int MAX; //key
public:
int deepth(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)
return 0;
int L = deepth(root->left);
int R = deepth(root->right);
if(MAX9 二分
二分法注意左右相加越界问题,改进为int mid = left + ((right-left)>>1);//位运算符等级最低。
实现 int sqrt(int x) 函数。
计算并返回 x 的平方根,其中 x 是非负整数。
由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留整数的部分,小数部分将被舍去。
class Solution {
public:
void erfen(int left,int right, int target)
{
if(left>right)
return;
//这样操作防止越int的界
int mid = left + ((right-left)>>1);//位运算符等级最低。
cout<target/(mid+1)) || left==right)
{
res=mid;
return;
}
if(mid>target/mid)
erfen(left,mid-1,target);
else
erfen(mid+1,right,target);
}
int mySqrt(int x) {
if(0==x || 1==x)
return x;
res = 0;
erfen(1, x, x);
return res;
}
private:
int res;
};