Springboot经典入门——刨根问底(起步依赖和自动配置原理分析)
随着微服务的遍地开花,SpringBoot成了框架中的一颗耀眼明星。在还没有接触SpringBoot的一段时间内,一直认为Spring已经是和轻量级的框架, 即使编程过程中需要配置的内容比较繁琐,但也是使用一段时间后才会有的感触。就像ecplise的出现扼杀了netBeans,IDEA的出现也撼动了ecplise的霸主地位。新的事物或者方式方法出现体现了行业的活力,也使从业者能不断注入新鲜的血液,更能适行业的发展。以下是学习的过程中,其实写博客更像是一种学习笔记吧。
- Springboot经典入门——踏进去的第一脚(基本概念及入门案例)
- Springboot经典入门——刨根问底(起步依赖和自动配置原理分析)
- Springboot经典入门——配置文件解读
- Springboot经典入门——综合应用(整合计数)
在学习完SpringBoot之后,一定会被两个概念产生兴趣那就是起步依赖和自动配置。这也是SpringBoot核心的两个概念。那到底 什么是起步依赖和自动配置呢?
起步依赖:
在《SpringBoot实战》对于起步依赖介绍是"起步依赖本质上是一个Maven项 目对象模型(Project Object Model,POM),定义了对其他库的传递依赖,这些东西加在一起即支持某项功能。很多起步依赖的命名都暗示了它们提供的某种或某类功能。"的确如果你
按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-parent,跳转到了spring-boot-starter-parent的pom.xml,xml配
置如下:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.0.1.RELEASE
../../spring-boot-dependencies
按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-dependencies,跳转到了spring-boot-starter-dependencies的
pom.xml,xml配置如下:
5.15.3
2.7.7
1.9.63
2.4.0
1.8.13
3.9.1
4.0.6
2.1.4
3.0.0
1.7.11
... ... ...
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot
2.0.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-test
2.0.1.RELEASE
... ... ...
org.jetbrains.kotlin
kotlin-maven-plugin
${kotlin.version}
org.jooq
jooq-codegen-maven
${jooq.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2.0.1.RELEASE
... ... ...
从上面的spring-boot-starter-dependencies的pom.xml中我们可以发现,一部分坐标的版本、依赖管理、插件管理已经定义好,所以我们的SpringBoot工程继承spring-boot-starter-parent后已经具备版本锁定等配置了。所以起步依赖的作用就是进行依赖的传递。 spring-boot-starter-web等配置依然如此。
自动配置:
点击查看注解@SpringBootApplication的源码:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes =
AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be
applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class[] exclude() default {};
... ... ...
}其中,@SpringBootConfiguration:等同与@Configuration,既标注该类是Spring的一个配置类@EnableAutoConfiguration:SpringBoot自动配置功能开启。继续更近的话查看注解@EnableAutoConfiguration:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
... ... ...
}其中,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类,继续看个究竟,查看AutoConfigurationImportSelector源码
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
... ... ...
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
}
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
return configurations;
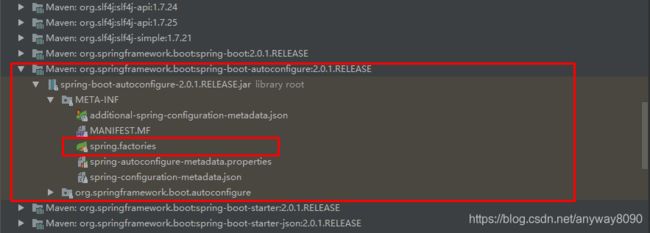
} 其中,SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 方法的作用就是从META-INF/spring.factories文件中读取指定类对应的类名称列表
spring.factories 文件中有关自动配置的配置信息如下:
... ... ...
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConf
iguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfigu
ration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
... ... ...上面配置文件存在大量的以Configuration为结尾的类名称,这些类就是存有自动配置信息的类,而SpringApplication在获取这些类名后再加载,下面以ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration为例来看下源码:
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
... ... ...
}其中,@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) 代表加载ServerProperties服务器配置属性类 ,进入ServerProperties.class源码如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
/**
* Server HTTP port.
*/
private Integer port;
/**
* Network address to which the server should bind.
*/
private InetAddress address;
... ... ...
}其中,prefix = "server" 表示SpringBoot配置文件中的前缀,SpringBoot会将配置文件中以server开始的属性映射到该类的字段中。映射关系如下:
这样自动配置的原理是不是就很清晰了。再回到起步依赖和自动配置的概念:
- 起步依赖本质上是一个Maven项目对象模型(Project Object Model,POM),定义了对其他库的传递依赖,这些东西加在一起即支持某项功能。简单的说,起步依赖就是将具备某种功能的坐标打包到一起,并提供一些默认的功能。
- Spring Boot的自动配置是一个运行时(更准确地说,是应用程序启动时)的过程,考虑了众多因素,才决定Spring配置应该用哪个,不该用哪个。该过程是Spring自动完成的。
是不是又对SpirngBoot有了一个更深刻的了解。总结来说起步依赖使我们不需要在考虑jar的版本和配置坐标的问题,自动配置使我们无法考虑配置加载的过程和选择。
文件列表:
- Springboot经典入门——踏进去的第一脚(基本概念及入门案例)
- Springboot经典入门——刨根问底(起步依赖和自动配置原理分析)
- Springboot经典入门——配置文件解读
- Springboot经典入门——综合应用(整合计数)