mybatis源码(二) mapper代理生成,sqlsession生成
文章目录
-
- 回顾
- SqlSession的生成
-
- 生成执行器Executor方法
- 再看看SqlSession
-
- getMapper方法
回顾
上一篇讲了DefaultSqlSessionFactory类的生成,主要讲的就是maybatis配置文件的解析,mapper的解析,然后根据Configuration生成SqlSessionFactory;
这一篇我们讲前面提到的SqlSession.和mapper的生成.
SqlSession的生成
还是前面的小例子,前面创建了SqlSessionFactory,SqlSessionFactory有个方法openSession返回SqlSession;
我们看DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSession方法:
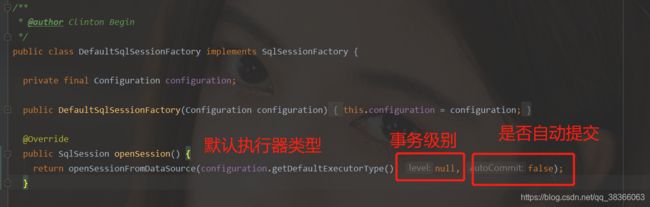
再看具体方法:
/**
* execType执行器类型,默认是ExecutorType.simple
*
* level 事务隔离级别,默认null
*
* autoCommit是否自动提交,默认false
* protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
* @Override
* public SqlSession openSession() {
* return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
* }
*
* @param execType
* @param level
* @param autoCommit
* @return
*/
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//获取环境信息
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//根据环境信息返回事务工厂,我们使用spring进行管理,返回的是SpringManagedTransactionFactory
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//根据数据源,事务隔离级别,是否自动提交生成事务管理器,返回的是Spring的事物SpringManagedTransaction
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//根据事务和执行器类别生成执行器,二级缓存默认打开,这里的SimpleExecutor会被包装成CacheExecutor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//返回默认的sqlsession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
生成执行器Executor方法
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
//如果为null,则设置为默认的tyoe,就是ExecutorType.SIMPLE
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
//如果还是为null,则手动设置为ExecutorType.SIMPLE
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
// batch开头的想必大家不陌生了,批量操作
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
//复用预处理语句
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
//simple简单的执行器
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
//是否开启二级缓存,封装为CachingExecutor
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//执行一次所有拦截方法
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
interceptorChain的实现也比较简单,就是将所有拦截器放到list里面,循环调用:
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
再看看SqlSession
前面openSession的时候,根据configuration,执行器,是否自动提交生成了默认的SqlSession:
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
// 这是sqlSession的属性
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
//mybatis配置文件,mapper信息
private final Configuration configuration;
//执行器
private final Executor executor;
//自动提交
private final boolean autoCommit;
//记录本次executor执行过程中是否有过更改操作
private boolean dirty;
//游标,,具体没研究
private List<Cursor<?>> cursorList;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
看一下sqlsession的方法,主要是增删改查,还有获取mapper方法:
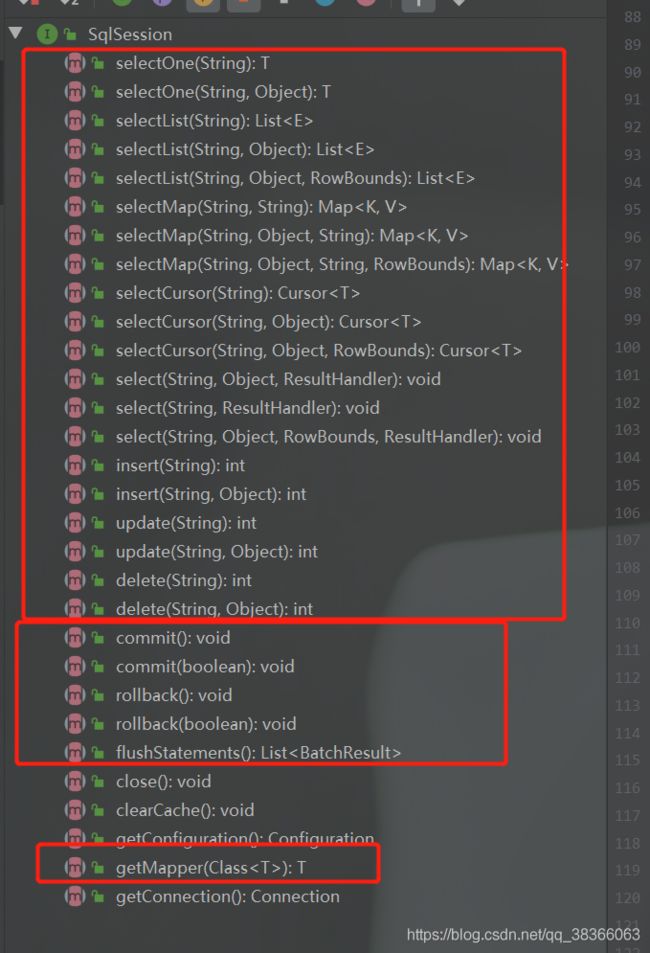
getMapper方法
上篇文章其实大部分讲过了,因为getMapper方法走的是configuration的getMapper方法,前面解析mapper文件的时候,也是解析xml的namespace类,将类加到MapperRegistry里面:
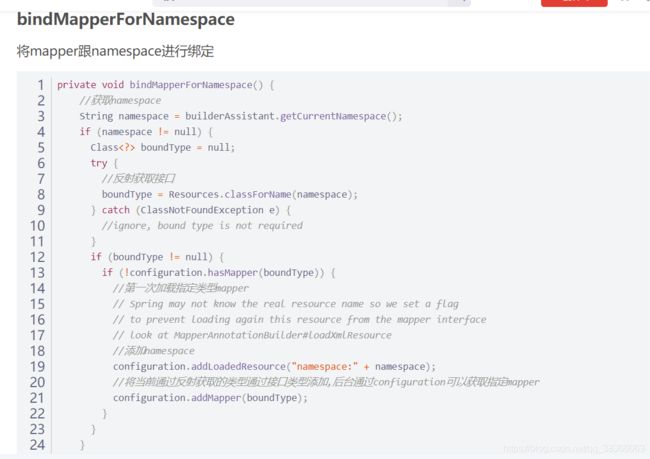
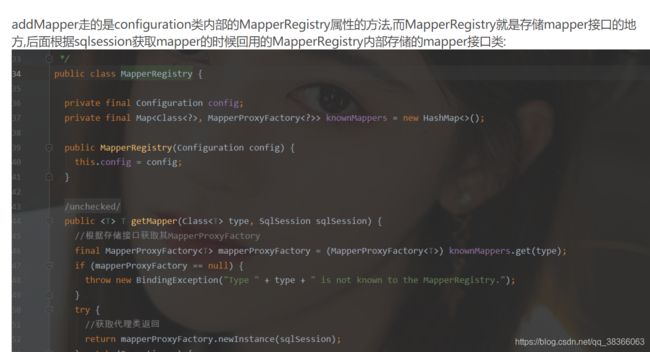
通过属性knownMappers获取到对应的maooer代理工厂类,然后通过MapperProxyFactory类生成对应的mapper代理;Proxy.newProxyInstance是通过jdk动态代理生成代理类的,详情可以了解:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38366063/article/details/105298512
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//根据mapperProxy生成代理,
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {
mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//根据传入的sqlsession生成mapperProxy类,mapperProxy类必须实现InvocationHandler接口;
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
而新建的MapperProxy类就是实现了InvocationHandler接口的具体执行方法的类;具体怎么执行,下次在讲,到这里,mapper代理就生成了;而通过spring结合mybatis的是通过往spring容器注入对应接口的方式,详见:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38366063/article/details/108120233